UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC > Masonry and its Types
Masonry and its Types | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Masonry involves constructing buildings using individual units bound together with mortar, with bricks, stones, and concrete blocks being common materials. While masonry offers several advantages, it also has limitations. There are various types of masonry construction:
1. Brick masonry is a widely used construction method with several advantages and drawbacks:
Pros:
- Doesn't require highly skilled labor: Bricklaying is relatively straightforward, and workers can quickly learn the necessary techniques.
- Lightweight and easy to handle: Bricks are lighter than stones and concrete blocks, making them easier to transport and maneuver on construction sites.
- Cost-effective: Bricks are generally cheaper than stones and concrete blocks, making brick masonry a more economical option for many projects.
- Versatile mortar types: Different types of mortar can be used with bricks, offering flexibility in construction methods and applications.
- Thinner walls and joints: Bricks allow for thinner walls and joints compared to other masonry materials, resulting in cost savings and a more streamlined appearance.
Cons:
- Low resistance to tension and torsion: Bricks have limited strength when subjected to tension and torsion forces, making them less suitable for structural elements exposed to such loads.
- Less strong and durable: While bricks are durable, they are not as strong or long-lasting as stones and concrete blocks, particularly in harsh environmental conditions.
- Limited sizes and colors: Bricks come in a relatively limited range of sizes and colors compared to stones and concrete blocks, limiting design options.
- Requires plasterwork finishing: Brick surfaces typically require plasterwork finishing to achieve a smooth and aesthetically pleasing appearance, adding to construction costs.
- Increased construction costs: While brick masonry is generally cost-effective, the need for plasterwork finishing and other considerations may increase overall construction costs compared to other materials.

Brick Masonry
2. Stone masonry is a renowned construction method known for its durability and aesthetic appeal, but it also comes with certain challenges:
Pros:
- Highly durable and strong: Stone is a naturally durable material that can withstand harsh weather conditions, making it ideal for long-lasting structures.
- Weather-resistant: Stone masonry is highly resistant to weathering, erosion, and decay, ensuring the longevity of the construction even in extreme climates.
- Suitable for high-traffic areas: Due to its durability and strength, stone masonry is well-suited for structures subjected to heavy use or frequent foot traffic.
- Aesthetically pleasing: Stone comes in various colors, textures, and sizes, offering endless design possibilities and adding a timeless charm to buildings.
- Low maintenance: Once properly constructed, stone masonry requires minimal maintenance over time, reducing long-term upkeep costs.
Cons:
- Thick and heavy walls: Stone walls tend to be thicker and heavier compared to other masonry materials, which can reduce usable floor space and increase construction costs.
- High self-weight: The weight of stone masonry structures can exert significant downward pressure on the foundation and surrounding soil, requiring careful structural design and reinforcement.
- Low flexural and tensile strength: While stone is strong in compression, it has relatively low flexural and tensile strength, limiting its suitability for certain structural elements and applications.
- Time-consuming construction: Stone masonry requires skilled labor and meticulous craftsmanship, resulting in longer construction times and potentially higher labor costs.
- Difficult to alter or repair: Once built, stone masonry structures are challenging to modify or repair due to the labor-intensive nature of working with stone and the need for specialized skills and tools.
Stone Masonry
3. Concrete block masonry is a popular construction method with several advantages and drawbacks:
Pros:
- Resistant to weather, pests, mold, and fire: Concrete blocks offer excellent protection against external elements, making them suitable for various climates and environments.
- Locally available: Concrete blocks are typically produced locally, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact associated with long-distance shipping.
- Versatile in sizes, finishes, and colors: Concrete blocks come in a variety of sizes, finishes, and colors, allowing for customizable designs to meet project requirements.
- Good insulating properties: Concrete blocks provide effective insulation against heat, sound, and moisture, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in buildings.
Cons:
- Heavy blocks requiring more manpower: Concrete blocks are heavier than other masonry materials, requiring more manpower and equipment for handling and installation.
- Increased steel requirement: Due to the weight of concrete blocks, reinforced concrete structures may require additional steel reinforcement to support the load, increasing construction costs.
- Price variability: The cost of concrete blocks can vary depending on factors such as region, demand, and availability of materials, leading to price fluctuations and budget uncertainty.
- Plumbing issues and internal flooding: Poorly installed or maintained plumbing systems in concrete block structures can lead to internal flooding, requiring costly repairs and remediation efforts.
- Effective drainage is crucial: Proper drainage design is essential to prevent water infiltration and accumulation within concrete block walls, which can lead to moisture-related issues and structural damage over time.
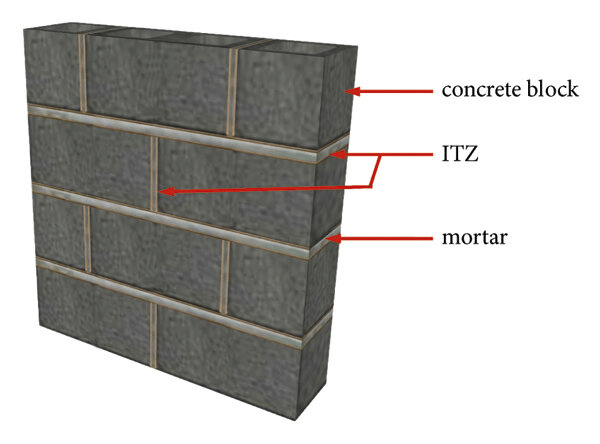
Schematic Diagram of Concrete Block Masonry
The document Masonry and its Types | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches