UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Meaning and Reasons
Meaning and Reasons | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Meaning of International Trade
- International trade is referred to as the exchange or trade of goods and services between different nations.
- This kind of trade contributes and increases the world economy. The most commonly traded commodities are television sets, clothes, machinery, capital goods, food, and raw material, etc.,
- International trade has increased exceptionally, including foreign transportation, travel and tourism, banking, warehousing, communication, advertising, and distribution and advertising.
- Other equally important developments are the increase in foreign investments and foreign goods and services in an international country.
- This foreign investments and production will help companies come closer to their international customers and serve them with goods and services at a very low rate.
- All the activities mentioned are a part of international business. It can be concluded by saying that international trade and production are two aspects of international business, growing day by day across the globe. Question for Meaning and ReasonsTry yourself:International trade is defined asView Solution
Reasons for International Trade
- Production
- A single country can't produce equally at a cheap cost.
- That is why international trade is taken into account.
- Factors of Production
- Factors of production like labour, capital raw material,
- For producing goods & services which are available at different rates in different countries.
- Cost of Production
- Each country finds it advantageous to produce only those goods & services.
- That it can produce efficiently.
- Rest of the activities is rest to other countries at a lower cost.
- Resources Distribution
- Many of the times, companies face problems in the availability of natural resources.
- There is an unequal distribution of the resources in the country.
- Examples
- Different countries are specialized in different sectors like
- In India, Maharashtra is involved in textiles, West Bengal in jute products, Haryana and Punjab in food products, Kerala in spices, etc.
- Same is categorized for other countries.
Importance of International Trade
International trade between various nations is an essential factor responsible for the increase in the standard of living, creating employment and empowering consumers to enjoy different kinds of goods. Few other important factors that are influenced by the International Trade are:
- Utilization of raw materials - Some countries are naturally blessed with an abundance of raw materials, for example, Qatar for oil, Iceland for metals and fish (Iceland), etc. Without international trade, these countries would never benefit from their natural resources or raw materials.
- Greater choice for consumers - More international trade results in more choices of products.
- Specialization and economies of scale – greater efficiency- This means that it doesn’t matter what a country is specialized in. The essential thing is to pursue a specialization that allows companies to profit outweighs most of the other factors.
- Global growth and economic development - International trade influentials economic growth of a country. This increase also leads to the reduction of poverty levels.
Scope of International Business:
- Exports and Imports
- It includes merchandise (tangible or having physical existence) of Goods.
- Export merchandise means sending goods to other nations.
- Import merchandise means receiving goods from other nations.
- It does include the trade of services.
- Service Trade
- It is also known as invisible trade.
- It includes the trade of services (intangible or no physical existence).
- There is both export and import of services.
- Services like tourism, hotel, transportation, training, research etc.,
- Licensing & Franchising
- Under this permission is given to the organization of other countries.
- To sell the product of a particular company.
- Under its trademark, patents in return of some fees. Example– Pepsi and Coca Cola are produced and sold through different sellers abroad.
- Franchising is similar to licensing but associated with services. Example-Dominos, burger king, etc.,
- Foreign Investment
- It includes the investment of available funds in foreign companies to get returns.
- It can be of 2 types:
(I). Direct investment means investing funds in plant and machinery for marketing and production, also known as a foreign direct investment (FDI). Sometimes these investments are done jointly known as joint ventures.
(ii) Portfolio investment means one company invests in another company by investing in its securities and earning income in the form of interest and dividends.
Advantages of International Business:
- Income
- It helps in earning foreign exchange to the organizations.
- Forex helps in paying off the cost of imports of capital goods, technologies, fertilizers etc. From abroad.
- Efficient Resources
- It is said that under international trade,
- Countries produce what they can produce efficiently.
- And rest the other activities too other nation.
- In which they can work efficiently.
- This helps the different nations to distribute the activities and work efficiently in their areas.
- Growth and Employment Potentials
- International trade helps in faster growth of organizations as well as countries.
- Sometimes organizations are not able to create employment in the market,
- As they produce on a small scale.
- Initially, countries like China, Japan, South Korea.
- Taken the whole world as a single market for trade.
- This helped them in employment generation across the world.
- Standard of Living
- Due to these people in one country can enjoy the goods and services of other nations.
- This helped them in improving the standard of living.
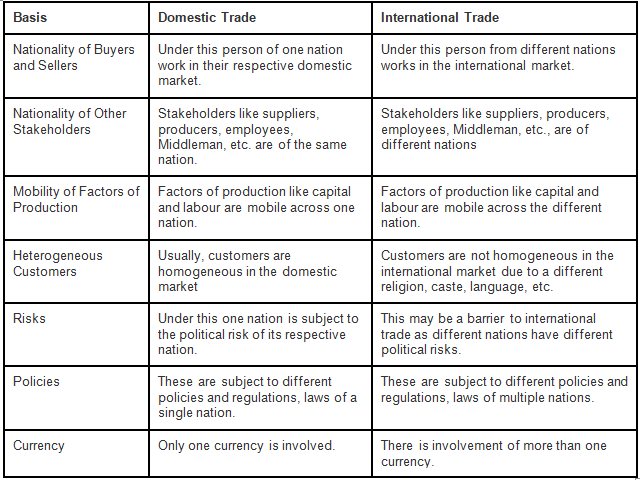
Difference Between Domestic and International Trade
Advantages and Disadvantages of Licensing and Franchising
➤ Advantages of Licensing and Franchising
- Nature
- Under this system licensor/franchisor invests
- Their own money in setting up their busies,
- There is no cost of investing the funds abroad.
- So, it is less expensive than in other modes.
- Interventions
- The whole business is owned and managed by the local person.
- Then government interventions or takeovers do not take place.
- Existing Contracts
- Since the local people manage the business under licensing or franchising.
- His existing contacts become helpful in marketing operations.
➤ Disadvantages of Licensing and Franchising
- Competition
- When the brand become popular after licensing or franchising,
- There is the threat of substitute products having difference slightly.
- So, it increases competition.
- Secrecy
- If the business is not transacted properly,
- Then confidential information can be leaked to competitors in the foreign market.
- Due to which the licensor can suffer stiff competition or losses.
- Litigations
- It is of no doubt that,
- Conflicts will arise among the licensor and licensee.
- On the factors like maintenance of accounts, payment of royalty, etc.
- This can lead to costly long litigations.
The document Meaning and Reasons | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|472 docs|197 tests
|
FAQs on Meaning and Reasons - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the meaning of international trade? |  |
Ans. International trade refers to the exchange of goods, services, and capital between countries. It involves buying and selling products across national borders, allowing countries to benefit from the specialization and comparative advantage they possess.
| 2. What are the main reasons for engaging in international trade? |  |
Ans. There are several key reasons why countries engage in international trade. These include:
1. Comparative advantage: Countries can produce certain goods or services more efficiently than others due to factors like natural resources, technology, or skilled labor. Engaging in trade allows countries to focus on producing what they are best at and acquire other goods through trade.
2. Market expansion: International trade provides access to larger markets beyond domestic borders. By trading internationally, countries can increase their customer base, leading to greater sales and profits.
3. Access to resources: Not all countries have abundant resources necessary for production. International trade enables countries to access raw materials, energy sources, or components that may not be available domestically.
4. Economies of scale: International trade allows for increased production, which leads to economies of scale. By producing on a larger scale, businesses can reduce costs and offer competitive prices in the global market.
5. Risk diversification: Engaging in international trade reduces dependence on a single market. If the domestic market experiences a downturn, businesses can rely on international markets to maintain sales and revenue.
| 3. How does international trade benefit countries? |  |
Ans. International trade provides various benefits to countries, including:
1. Economic growth: By participating in international trade, countries can experience increased economic growth and development. Trade allows for the expansion of industries, job creation, and improved living standards.
2. Increased productivity: International trade promotes competition, which drives businesses to become more efficient and innovative. This leads to increased productivity and the development of new technologies.
3. Consumer access to a wider variety of goods: Trade allows consumers to access a broader range of products from different countries, often at competitive prices. This increases consumer choice and enhances their standard of living.
4. Foreign investment: International trade attracts foreign direct investment (FDI) as businesses seek to establish a presence in new markets. FDI brings capital, technology, and expertise to the host country, contributing to its economic development.
5. Cultural exchange and understanding: International trade fosters cultural exchange and understanding between countries. Through trade, countries learn about each other's customs, traditions, and values, leading to increased global cooperation and harmony.
| 4. What are the potential challenges of international trade? |  |
Ans. International trade also presents some challenges, including:
1. Trade barriers: Countries may impose tariffs, quotas, or other trade barriers to protect domestic industries from foreign competition. These barriers can hinder trade flows and limit market access.
2. Political instability: Political instability or conflicts in certain regions can disrupt international trade. Unpredictable policies, sanctions, or trade disputes between countries can create uncertainties and negatively impact trade relationships.
3. Economic inequality: International trade can exacerbate economic inequality within countries. If certain industries or regions are unable to compete internationally, it can lead to job losses and income disparities.
4. Environmental impact: Trade can contribute to environmental degradation through increased carbon emissions, deforestation, or pollution. The transportation of goods over long distances can have a significant ecological footprint.
5. Dependency on imports: Relying heavily on imports can make countries vulnerable to supply disruptions or price fluctuations. It is important for countries to maintain a balance between imports and domestic production to ensure stability and self-sufficiency.
| 5. How does international trade affect developing countries? |  |
Ans. International trade can have both positive and negative impacts on developing countries:
1. Economic growth and poverty reduction: International trade can stimulate economic growth in developing countries by creating employment opportunities, attracting investment, and increasing export revenues. This, in turn, can contribute to poverty reduction and improved living standards.
2. Income inequality and vulnerability: Developing countries may face challenges in competing with more advanced economies, leading to income inequality and vulnerability. Unequal distribution of trade benefits can result in marginalized communities or regions being left behind.
3. Dependence on primary commodities: Many developing countries heavily rely on the export of primary commodities like agricultural products or raw materials. This dependency can expose them to price fluctuations, market volatility, and limited diversification of their economies.
4. Technology transfer and capacity building: International trade can facilitate technology transfer and knowledge sharing from more developed countries to developing ones. This can enhance their production capabilities, improve infrastructure, and foster industrialization.
5. Sustainable development: Developing countries face the challenge of balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. International trade should be pursued in a manner that promotes sustainable development, taking into account social, economic, and environmental factors.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















