Mendel's Contributions | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Heredity |

|
| Gregor Johann Mendel(1822 - 1884) |

|
| Rules for the Inheritance of Traits: Mendel's Contributions |

|
| Some Important Definitions |

|
| Laws of Mendel |

|
Heredity
This branch of biology unravels the mechanisms through which traits are passed from one generation to the next. From the study of DNA to Mendel's principles, we will explore the fascinating world of genetic inheritance and discover how traits shape the diversity of life. Get ready for an exciting journey into the code of life!
Gregor Johann Mendel(1822 - 1884)
- Mendel was born on 22 July 1822 at Heinzendorf in Austria at Silesia village. Mendel worked in Augustinian Monastery as a monk at Brun city, Austria.
- Mendel was unable to get any popularity as no one could understand his work. He died in 1884 (due to kidney disease (Bright disease)) without getting any credit for his work. After 16 years of Mendel's death in 1900, Mendel's postulates was rediscovered. Mendel's experiment remained hidden for 34 years.
Rules for the Inheritance of Traits: Mendel's Contributions
Character: A recognizable feature of human beings or any other organisms are called characters.
Examples: Height, Complexion, Shape of hair, Colour of eyes, Shape of the nose.
Traits: Various forms of a character are called traits. 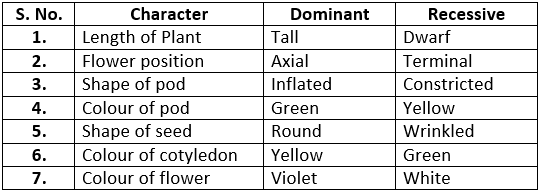
Mendel's Monohybrid Cross
- A breeding experiment dealing with a single character is called a monohybrid cross.
- Mendel first selected 'pure line' plants (i.e., the plants that produced similar traits generation after generation). He, then, cross-pollinated such plants having contrasting traits, considering one trait at a time.
Example: In one such cross-breeding experiment, he cross-bred garden pea plant having round seeds with the plant having wrinkled seeds. - In this monohybrid cross, the pollen grains from the flower of the desired plant, raised from round seeds were transferred over the previously emasculated flower of a plant raised from wrinkled seeds or vice-versa.
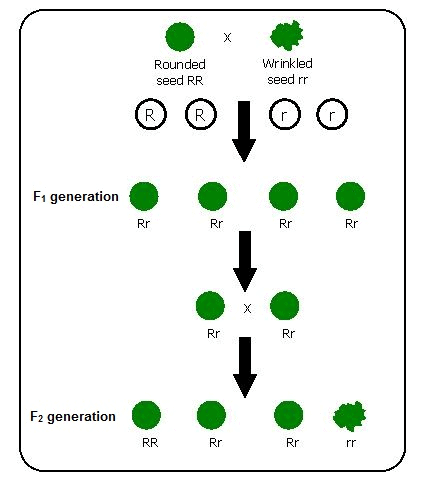 Mendel's Monohybrid Cross
Mendel's Monohybrid Cross - After the transfer of pollen grains, the cross-pollinated flower was properly covered and seeds produced were allowed to mature. All the seeds of the F1 generation were carefully observed.
- Mendel observed that all the seeds of the F1 generation were of a round type and there were no intermediate characteristics.
- He raised plants from F1 seeds and allowed the flowers to self-pollinate to produce the seeds of the F2 generation. The flowers were kept covered from the beginning to avoid unwanted pollen grains to reach these flowers.
- In the F2 generation, Mendel observed the appearance of both round and wrinkled seeds in approximately 3:1 proportion.
Mendel's Dihybrid Cross
- A cross involving two pairs of contrasting characters i.e. two pair of contrasting characters are studied at a time.
- In one such cross, Mendel considered the shape as well as the colour of the seeds simultaneously.
- He selected pure line plants and then cross-pollinated flowers raised from seeds of round shape and yellow colour with those from wrinkled seeds and green colour.
- Mendel observed that in F1 generation all seeds had the features of only one parent type, i.e., round shape and yellow colour.
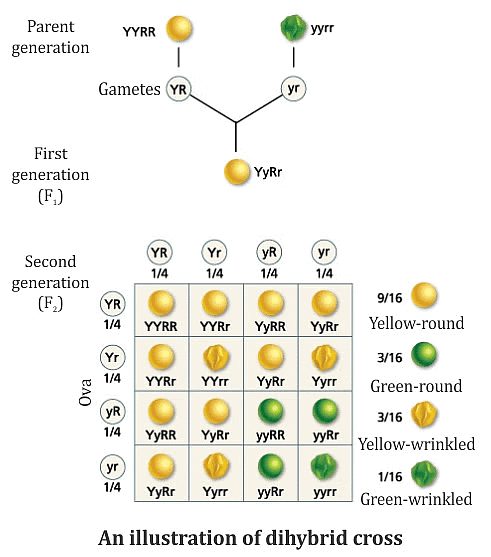
- He raised plants from F1 generation seeds and allowed the flowers to self pollinate to produce the seeds of F2 generation. These flowers were kept covered from the beginning.
- In F2 generation, Mendel observed the appearance of four types of combinations. These included two-parent types (round-shaped and yellow coloured seeds, and wrinkled shaped and green coloured seeds) and two new combinations (round-shaped and green coloured seeds, and wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds) in the approximately same proportion. (giving the ratio of 9:3:3:1)
Some Important Definitions
Dominant gene: The gene which decides the appearance of an organism even in the presence of an alternative gene.
Recessive Gene: The gene which can decide the appearance of an organism only in the presence of another identical gene.
Chromosomes: A thread-like structure in the nucleus of a cell formed of DNA that carries the genes.
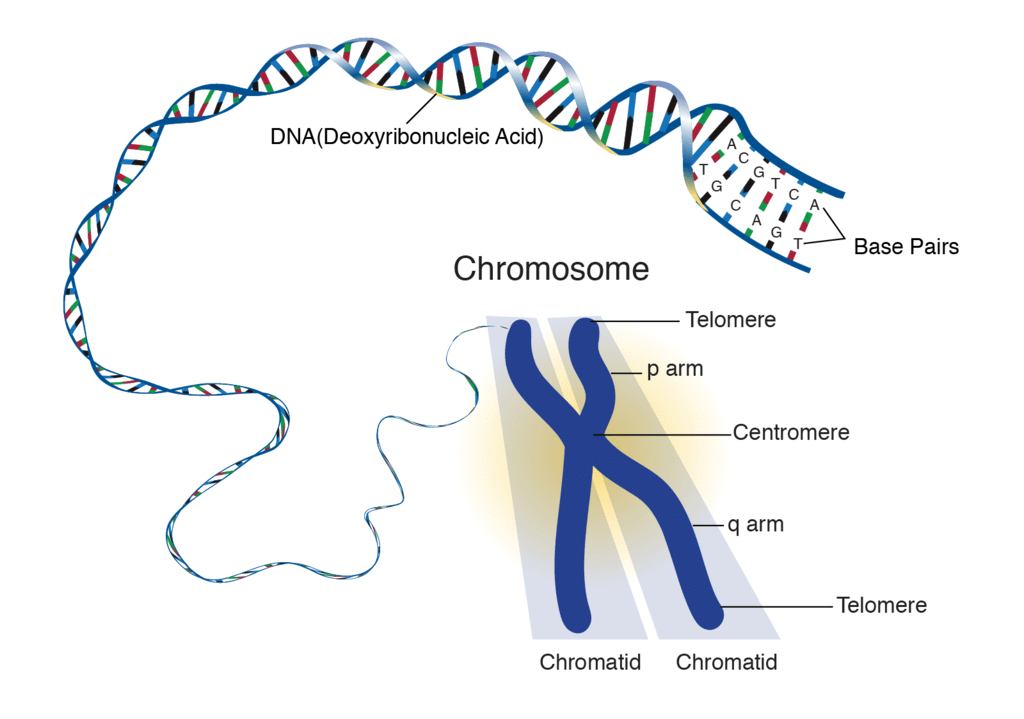
Chromosome
Genotype: The genetic constitution of an organism i.e. description of genes present in an organism.
Example: TT, tt, Tt.
Phenotype: External and morphological appearance of an organism for a particular character.
Allele: Alternative forms of a gene that are located in the same position [loci] on the homologous chromosome.
F1 Generation: When two parents cross or breed to produce progeny [or offspring], then their progeny is called F1 generation or first filial generation.
The offspring produced by the parental generation.
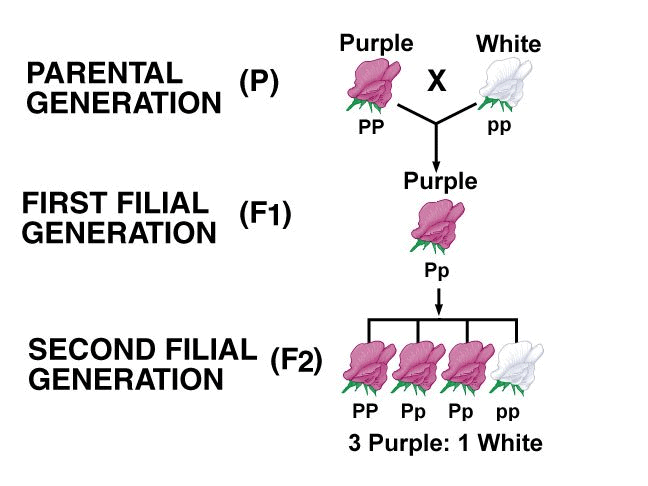 F1 and F2 generationF2 generation: When the first generation progeny crossbreed among themselves to produce second progeny, then this progeny is called second filial generation or F2 generation.
F1 and F2 generationF2 generation: When the first generation progeny crossbreed among themselves to produce second progeny, then this progeny is called second filial generation or F2 generation.
The offspring produced by the F1 generation.
- Hybrid: A new form of the plant resulting from cross-breeding of different varieties of a plant is known as a hybrid.
- Pure-breeding: Characteristics that appear unchanged generation after generation.
- Dominant characters: Any character that appears in the F1 generation offspring from a cross between parents possessing contrasting characters such as tallness & dwarfness in pea plants.
- Recessive characters: Any character present in the parental generation that does not appear in the F1 generation but reappears in the F2 generation.
- Homozygous: A condition in which the 2 members of an allelic pair are similar.
Example: TT, tt.
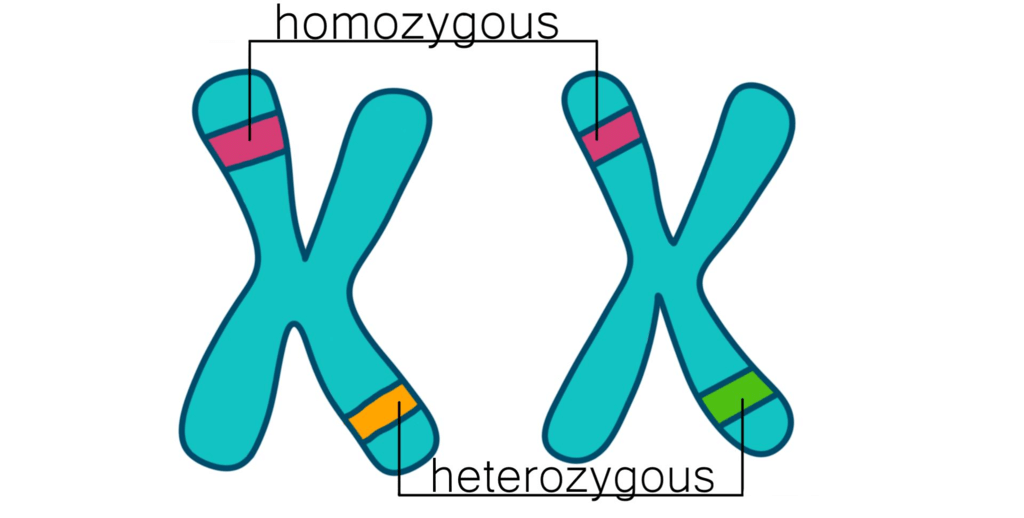 Homozygous and Heterozygous
Homozygous and Heterozygous
- Heterozygous: A condition in which the 2 members of an allelic pair are dissimilar.
Example: Tt. - Offspring: Organisms produced as a result of sexual reproduction.
- Homologous chromosomes: All chromosomes found in a pair & chromosomes of a pair are called homologous chromosomes.
- Non-homologous chromosomes: Chromosomes of different pair are called non-homologous chromosomes.
- Genes: Unit of heredity which transfers characters from parents to their offspring during reproduction.
Gene → Protein synthesis → Enzymes [Controls phenotype of a character]
Laws of Mendel
On the basis of Mendel's work, 3 basic laws of inheritance were proposed:
(i) Law of Dominance
(ii) Law of Segregation
(iii) Law of Independent Assortment
1. Law of Dominance
- In crossing between organisms having contrasting characters, only one character of the pair appears in the F1 generation. This character is termed dominant while the one which does not express itself in F1 generation is termed recessive.
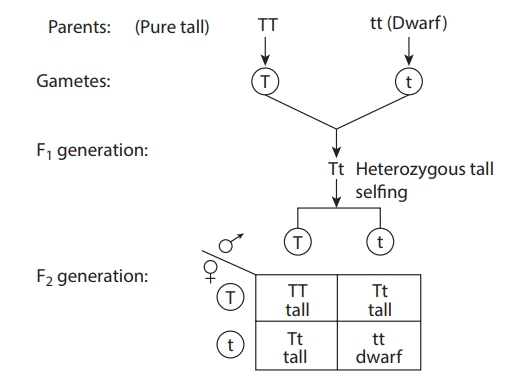 Law of Dominance
Law of Dominance
2. Law of Segregation
- Allele or genes remain together and segregate at the time of gamete formation. This means that the alleles do not mix in the hybrids [Non-mixing of alleles]. This is also known as the Law of Purity of Gametes.
3. Law of Independent Assortment
- This law states that - when individuals differing in 2 or more than 2 pairs of contrasting characters are crossed, the inheritance of anyone pair is not affected by the presence of the other.
Example: The inheritance of a tall character is in no way related to the smooth character of the seed. Rather, the 2 characters are inherited independently of each other.
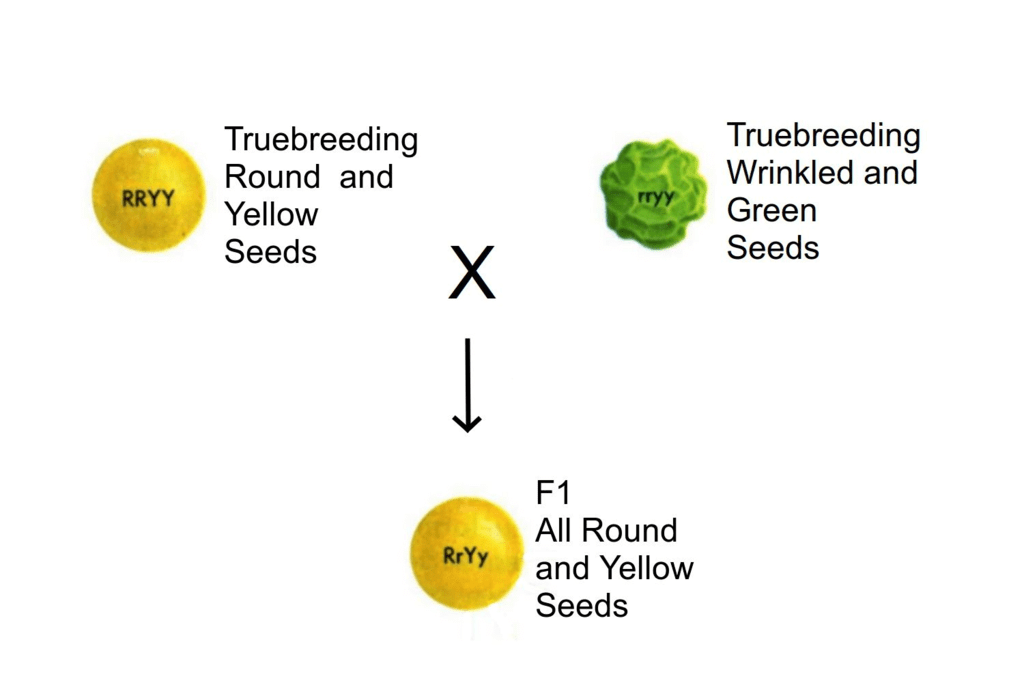 Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Independent Assortment
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Mendel's Contributions - Science Class 10
| 1. What is heredity? |  |
| 2. Who is Gregor Johann Mendel? |  |
| 3. What were Mendel's contributions to the study of heredity? |  |
| 4. What are some important definitions related to heredity? |  |
| 5. What are the laws of Mendel? |  |
















