Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Heredity and Evolution
Short Question Answer
Q1: What is heredity?
Ans: The continuity of features from one generation to another is known as heredity. It is also defined as the transmission of traits from parents to offsprings. The transmission of characters or traits from parents to their offspring (children) is termed as heredity.
 (i) Free and (ii) attached earlobes
(i) Free and (ii) attached earlobes
Q2: All the variations in a species do not have equal chances of survival. Why?
Ans: All the variations do not have equal chances of survival in the environment in which they live. Depending on the nature of variations, different individuals would have different kinds of advantages. The organisms which are most adapted to the environment will survive.
Q3: What is a sex chromosome?
Ans: Chromosomes that are responsible for the determination of sex in an individual are known as sex chromosomes. There are two types sex chromosomes – the X chromosome and the Y chromosome. Males possess one X and one Y chromosome and females possess two X chromosomes.
Q4: Name the plant on which Mendel performed his experiments.
Ans: Mendel performed his experiments on the plant, Pisum sativum – the garden pea plant. Through the selective cross-breeding of common pea plants (Pisum sativum) over many generations, Mendel discovered that certain traits show up in offspring without any blending of parent characteristics. For instance, the pea flowers are either purple or white, intermediate colours do not appear in the offspring of cross-pollinated pea plants.
Q5: Define variation.
Ans: Variation can be defined as any difference between the individuals in a species or groups of organisms of any species. The differences can be caused by environmental factors (phenotypic variation), called environmental variation. The variation passed on from parents to offspring, via genes, during reproduction is called inherited variation.
Q6: Define a gene.
Ans: A gene is a small portion of the DNA, with codes for a particular polypeptide or a protein. In other words, it is the functional unit of the DNA. It is also responsible for the transmission of hereditary characteristics from the parents to the offspring.
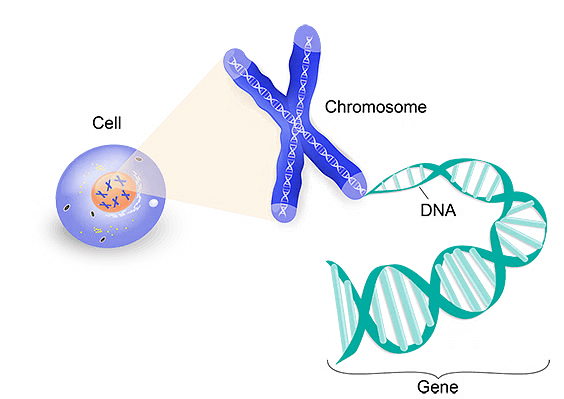 Q7: How is sex determined in human beings?
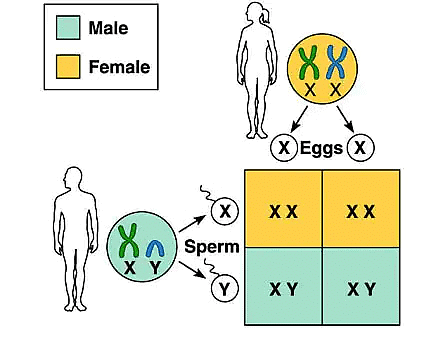
Q7: How is sex determined in human beings?
Ans: The male sex gametes have X and Y chromosomes, whereas the female sex gametes have two X chromosomes. When a sperm containing a Y chromosome fuses with the ovum containing X chromosome, the zygote develops into a male. When a sperm containing the X chromosome fuses with an ovum containing X chromosome, the zygote develops into a female. Thus the sex of an individual is determined by the sex chromosomes X and Y, which is present in the male chromosomes.
Q8: Write a difference between inherited traits and acquired traits giving one example of each.
Ans: A trait (or characteristic) of an organism which is ‘not inherited’ but develops in response to the environment is called an acquired trait. For example, if a man gets a cut during his lifetime and develops a scar , that scar will not pass to offspring. This is so because scar is an acquired character.
A trait (or characteristic) of an organism which is caused by a change in its genes (or DNA) is called an inherited trait. Inherited traits can be passed on to the progeny of the organism because they have produced changes in the genes (or DNA) of the organism. For example, skin colour in human beings.
Long Question Answer
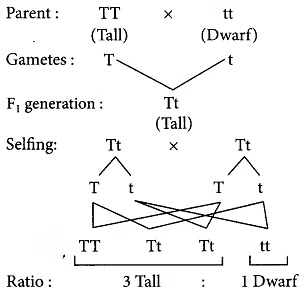
1: With the help of an example justify the following statement: “A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed.”Ans: A trait may be inherited but may not be expressed, this could be explained by the given example. When a tall pea plant was crossed with a dwarf pea plant, then F1 generation plants were all tall. When F1 plants were selfed, then F2 generation plants were both tall and dwarf. This shows that the F1 plants had inherited both the parental traits but did not express dwarfness or recessive trait in the presence of the trait for tallness or dominant trait. This could be explained by the given cross :
Q2: The cross was made between pure breeding pea plants, one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds.
(a) Write the phenotype of F1 progeny. Give reason for your answer.
(b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ratio when F1 progeny was selfed. (Delhi 2014, Delhi 2013C)
Ans: (a) The given cross was made between pure breeding pea plants, one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds.
Yellow seed colour and round seed shape is dominant over green seed colour and wrinkled seed shape. In F1 generation, dominant traits express itself, whereas recessive traits get suppressed.
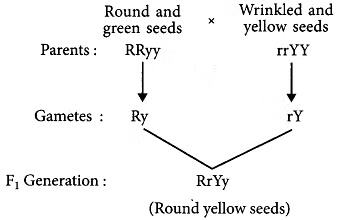 Therefore, the phenotype of F1 progeny is round and yellow.
Therefore, the phenotype of F1 progeny is round and yellow.
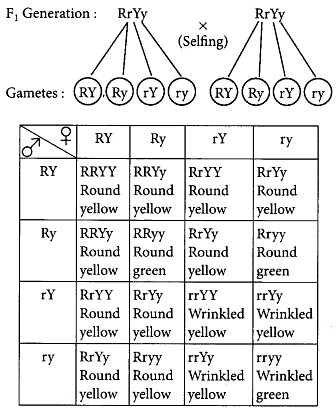
Round yellow seeds – 9 ; Round green seeds – 3; Wrinkled yellow seeds – 3; Wrinkled green seeds – 1
Q3: Define Genetics. What is the contribution of Mendel in the field of genetics?
Ans: The branch of biology that deals with the study of heredity and variations is known as Genetics. Gregor Johann Mendel is considered the Father of Genetics. He was the first person to carry out experiments regarding the heredity of certain characters from one generation to another in a scientific manner.
- Mendel conducted breeding experiments in a plant called garden pea (Pisum sativum) with contrasting pair of characters, found that only one character of the pairs appeared in the first generation but both the characters appeared in the subsequent generation.
- On the basis of these results of his experiments, he put forth the various principles of inheritance. He also suggested that each character is controlled by a pair of factors which are now called as genes.
Q4: It is a matter of chance whether a couple will have a male or a female child.” Justify this statement by drawing a flow chart.
Ans: Sex is determined at the time of fertilisation when male and female gametes fuse. Male produces two types of gametes, i.e., having X or Y chromosome and female produces same type of gametes containing X chromosomes. The sex of the child is determined at the time of fertilisation when male and female gametes fuse to form zygote.
If a sperm (male gamete) carrying X chromosome fertilises an egg or ovum (female gamete) carrying X chromosome, then the offspring will be a girl (female). This is because the offspring will have XX combination of sex chromosomes.
If a sperm (male gamete) carrying Y chromosome fertilises an egg or ovum (female gamete) which has X chromosome, then the offspring will be a boy (male). This is because the offspring will have XY combination of sex chromosomes.
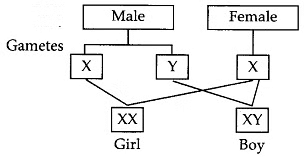
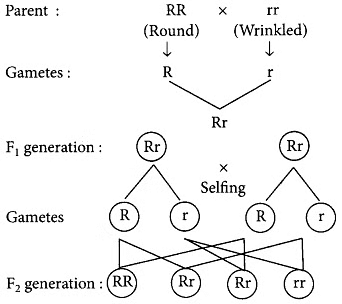
Q5: List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel’s cross between round and wrinkled pea plants? (Foreign 2016)
Ans: Differences between dominant traits and recessive trait are given below: Dominant traitRecessive trait
(i) It is the trait controlled by dominant allele. It is the trait controlled by recessive allele.
(ii) It is the trait which is expressed in F1 generation. It is the trait which remains suppressed in F1 generation and appears in F2 generation. Out of total 4 genotypes possible in F2 generation 31 genotypes result in phenotypic expression of round seeds. So, the percentage of plants with round seeds will be 75%. This can be illustrated as follows:
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Heredity and Evolution
| 1. What is heredity and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of inheritance patterns? |  |
| 3. How do environmental factors influence heredity? |  |
| 4. What role do mutations play in heredity? |  |
| 5. How can heredity affect the likelihood of genetic disorders? |  |






















