Mendel's Laws of Inheritance | Agriculture Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Why was Pea Plant Selected for Mendel’s Experiments? |

|
| Mendel’s Experiments |

|
| Mendel’s laws |

|
Introduction
Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel performed hybridization experiments using garden peas. During this time, he selected specific pea traits with distinct characteristics and carried out controlled cross-pollination or artificial pollination on these pea lines. He focused on those lines where the traits consistently passed on to subsequent generations, and he allowed them to self-pollinate continuously. These specific pea lines are referred to as true-breeding pea lines.
Why was Pea Plant Selected for Mendel’s Experiments?

He chose the pea plant as his subject for the following reasons:
- Pea plants are easy to cultivate and maintain.
- They naturally self-pollinate but can also be cross-pollinated.
- They are annual plants, allowing for the study of many generations in a short time.
- Pea plants exhibit multiple distinct characteristics.
Mendel conducted two primary experiments to establish the principles of inheritance:
- Monohybrid Cross
- Dihybrid Cross
While conducting these experiments, Mendel observed that certain factors consistently passed on to the offspring in a predictable manner. These factors are now referred to as genes, serving as the fundamental units of inheritance.
Mendel’s Experiments
Mendel conducted experiments on pea plants, where he focused on seven major traits with distinct contrasts. He conducted two experiments to elucidate the laws of inheritance.
A concise description of these two experiments is provided below:
Monohybrid Cross
Mendel's experiment involved taking two pea plants with opposing traits, such as one being short and the other tall, and crossbreeding them. The first-generation offspring were tall and referred to as the F1 progeny. Subsequently, he crossed the F1 progeny and observed a ratio of three tall plants to one short plant.
Mendel repeated this experiment with various other contrasting traits, like green peas versus yellow peas and round peas versus wrinkled peas. Remarkably, the outcomes were consistent across all cases. This consistency led him to formulate the laws of Segregation and Dominance.
Dihybrid Cross
In a dihybrid cross experiment, Mendel examined two traits, each with two alleles. He conducted a cross between wrinkled-green seeds and round-yellow seeds, and all the offspring in the first generation (F1 progeny) turned out to be round-yellow. This indicated that the dominant traits were round shape and yellow color.
Following this, Mendel performed self-pollination on the F1 progeny and observed the emergence of four different traits: round-yellow, round-green, wrinkled-yellow, and wrinkled-green seeds, in a specific ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
After conducting research for other traits, the results were found to be similar. From this experiment, Mendel formulated his second law of inheritance i.e. law of Independent Assortment.
Conclusions from Mendel’s Experiments
- The genetic constitution of a plant is referred to as its genotype, while its observable physical characteristics are called the phenotype.
- Genes are passed on from parents to their offspring in pairs, which are termed alleles.
- During gamete formation, when chromosomes are divided, there is a 50% probability for one of the two alleles to combine with the allele from the other parent.
- When the alleles are identical, they are called homozygous alleles, and when they are different, they are referred to as heterozygous alleles.
Mendel’s laws
The two experiments lead to the formulation of Mendel’s laws known as laws of inheritance which are:
- Law of Dominance
- Law of Segregation
- Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Dominance
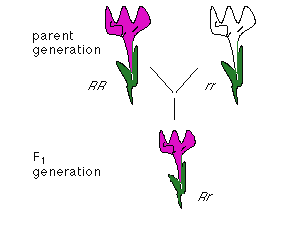 This is often referred to as Mendel's first law of inheritance. As per the law of dominance, when it comes to hybrid offspring, they will only exhibit the dominant trait in their observable characteristics (phenotype). The alleles responsible for the suppressed traits are termed recessive, while the alleles dictating the expressed traits are known as dominant.
This is often referred to as Mendel's first law of inheritance. As per the law of dominance, when it comes to hybrid offspring, they will only exhibit the dominant trait in their observable characteristics (phenotype). The alleles responsible for the suppressed traits are termed recessive, while the alleles dictating the expressed traits are known as dominant.
Law of Segregation

The law of segregation, also known as Mendel's third law of inheritance, explains that when gametes are formed, two copies of each hereditary factor (allele) separate from each other. As a result, offspring inherit one factor from each parent. To put it simply, allele pairs segregate during gamete formation and then randomly come back together during fertilization.
Law of Independent Assortment
The law of independent assortment, also referred to as Mendel's second law of inheritance, describes how one pair of traits segregates independently of another pair during the formation of gametes. Because individual hereditary factors assort independently, different traits have an equal chance of occurring together.
Key Points on Mendel’s Laws
- Gregor Mendel formulated the laws of inheritance following seven years of experimentation with pea plants.
- Mendel's laws of inheritance encompass the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment.
- According to the law of segregation, each individual carries two alleles, but only one allele is transmitted to the offspring.
- The law of independent assortment dictates that the inheritance of one pair of genes is not influenced by the inheritance of another pair.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















