Metering Flumes and its Types | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
A Metering flume or flow measuring flume is an artificial channel section which is used to measure the discharge of a channel. Flumes are of different types and can be made up of materials such as aluminum, fiberglass, steel, wood etc. Different types of metering flumes and their working is explained in this article.
Types of Metering Flumes
Metering flumes are classified into following types :- Submerged Venturi Flume
- Free flow Venturi Flume
- Parshall Flume
- Cut-throat Flume
1. Submerged Venturi Flume
Submerged Venturi flume consists of gradual contraction on its upstream throat section in the middle and the gradual expanding section from the throat. Here, the downstream level of flume is kept equal to the level of throat section hence, there may be backward flow into the throat section. So, it is said to be submerged Venturi flume.
To measure discharge in submerged Venturi flume, two head measurements are required, one at the entrance and one at the throat. These measurements are taken by providing stilling wells at the entrance and throat. The discharge through submerged Venturi flume can be calculated by the following formula :

Where, a1 = Area at the entrance
a2 = Area at throat
g = acceleration due to gravity
h = head difference between two stilling wells
Cd = Coefficient of discharge of Venturi flume (generally varies from 0.92 to 1.0)
 Submerged Venturi Flume
Submerged Venturi Flume2. Free flow Venturi Flume
Free flow Venturi flume is also known as standing wave flume since it is designed in such a way as to form a hydraulic jump or standing wave on the downstream portion of the flume. In this case, the level of the downstream portion of flume is kept lower than throat level to form hydraulic jump. Hence, the discharge through the throat section depends only on the upstream head.
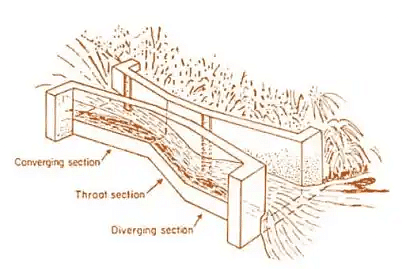 Standing wave Flume or Free Flow FlumeIn this case, single head measurement at the throat section is enough to calculate the discharge of channel. Stilling well is provided at the throat to measure the head. Discharge through free flow Venturi flame is calculated by using the following expression :
Standing wave Flume or Free Flow FlumeIn this case, single head measurement at the throat section is enough to calculate the discharge of channel. Stilling well is provided at the throat to measure the head. Discharge through free flow Venturi flame is calculated by using the following expression :
Where, Cd = Coefficient of discharge of Venturi flume (generally varies from 0.92 to 1.0)
B = width of throat section
H = Head measured in stilling well.
 Free Flow Flume
Free Flow FlumeParshall flume is a modified version of venturi flume. Some modifications are made in venturi flume to change the flow conditions from sub critical to supercritical and those modifications are as follows :
- Increase in throat length
- Reduction in angle of convergence of inlet walls
- Reduction in angle of divergence of outlet walls
- Drop in elevation through the throat of the flume
Design of Parshall flume can be done as either free flow parshall flume or submerged parshall flume like in venturi flume.
 Parshall Flume
Parshall FlumeA cut-throat flume consists of a gradually contracting channel section followed by a gradually expanding channel section. Throat section is eliminated in case of cut-throat flumes. The bottom surface of a cut-throat flume is flat and horizontal.
The construction of cut-throat flume is easier compared to other types of flume since it requires horizontal floor and flat metal sheets and, also, there is no need of throat section.
 Cut-throat Flume
Cut-throat Flume|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Metering Flumes and its Types - Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are metering flumes used for? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of metering flumes available? |  |
| 3. How do metering flumes work to measure flow rate? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using metering flumes for flow measurement? |  |
| 5. How can I determine the best type of metering flume for my application? |  |
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















