Methods of problem Solving | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Typologies of Problems |

|
| Stages of Problem Solving |

|
| Factors Affecting Problem Solving |

|
Introduction
Problem-solving is the cognitive process in which individuals attempt to overcome obstacles to reach a desired goal. It plays a crucial role in critical thinking and decision-making, whether it involves significant life choices or routine problems. Psychological research has revealed various aspects of problem-solving behavior, which will be explored in the following sections.
Key Terms Related to Problem Solving
Initial State: Problem-solving starts with a specific original state referred to as the initial state of a problem.
- Goal State: The desired outcome that will be achieved upon solving the problem. The person involved in the initial state aims to reach this goal state and makes efforts to overcome obstacles along the way. The goal state is defined by the individual and may have specific properties.
- Person/Operator: Refers to the individual who is in the initial state and strives to achieve the goal state through the application of skills and techniques. The operator internally manipulates the elements of the problem using global or personal symbols or visual images.
- Problem Space: The combination of the initial state, goal state, and operator forms the problem space. It consists of various elements that need to be organized in a particular manner. Understanding the problem space successfully requires coherence, correspondence, and a connection to background knowledge. Coherent understanding involves meaningfully connecting the elements, and there should be a close correspondence between the internal representation and the elements of the problem space. All elements should be properly matched and connected.
- Rules: These are the guidelines or principles that facilitate the transformation of the problem state into the goal state. They provide a systematic approach for problem solving.
Example of Problem Solving: A classic illustration of problem-solving behavior is demonstrated through Kohler's experiments with a chimpanzee. In one experiment, a hungry chimpanzee (operator) was placed in a closed cage with bananas hanging from the roof (goal state) and three boxes on the floor. The chimpanzee could only reach the bananas by stacking the three boxes vertically (rule). After engaging in various irrelevant behaviors, the chimpanzee suddenly solved the problem and reached the bananas. This solution emerged from the internal representation and understanding of the problem, which was occurring unconsciously in the chimpanzee's mind and is referred to as insight by Kohler and other Gestalt psychologists.
Typologies of Problems
- Well-defined and Ill-defined Problems: A problem is considered well-defined when it has a clearly identifiable initial state, goal state, a specific number of operators, and explicit rules and sub-goals to convert the initial state into the goal state. The problem faced by the chimpanzee in Kohler's experiment serves as an example of a well-defined problem. On the other hand, an ill-defined problem lacks clear definitions for one or more elements in the problem space, such as the initial state, goal state, operators, and rules. Creating a painting is an example of an ill-defined problem.
- Problems of Inducing Structure: Problems of inducing structure involve determining the relationships among various elements within the problem. An analogy problem is an example of this type, where the operator needs to identify a structure with well-defined rules among the elements. For instance, "bird to sky as fish is to water" presents a structured analogy problem. Solving such problems requires three cognitive skills: attribute discovery, encoding, and comparing encoded attributes to evaluate the structure among the elements.
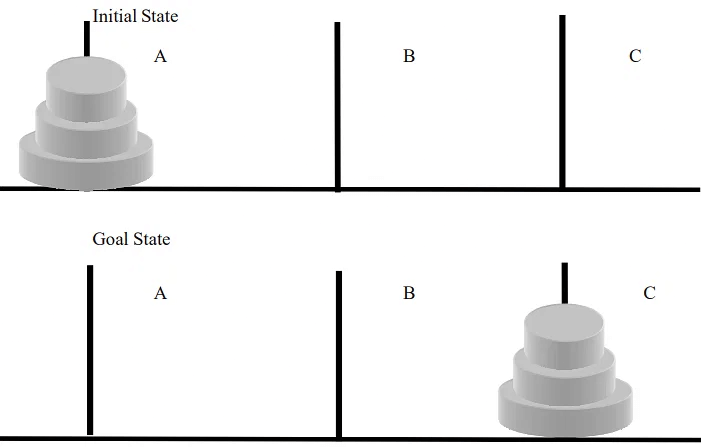
- Problems of Transformation: Problems of transformation require finding a sequence of operations to transform the initial state into the goal state. The Tower of Hanoi is a classic example of this type of problem. The figure below illustrates a modified version of the Tower of Hanoi problem. At the initial state, there are three discs placed in peg A. Operator is required to move all the three discs on to the peg C. Rules of the game are that only one and the top disc can be moved at a time and the bigger disc cannot be placed over the smaller one.

- Problems of Arrangement: Problems of arrangement require the operator to rearrange the elements of the problem based on a specific criterion. In some cases, the criterion for arrangement is predefined, while in others, the operator needs to discover it. An example of such a problem is an anagram, where the order of letters in a word is changed, and the operator is tasked with rearranging them to form a meaningful word. The cognitive skill needed to solve an anagram is constructive search, where the operator systematically explores different combinations of letters until a meaningful sequence is found.
Stages of Problem Solving
According to Gestalt psychologists, problem-solving behavior follows stages that are similar to those in creative thinking: preparation, incubation, illumination or insight, and verification. These stages have been discussed earlier. Additionally, Polya suggests four stages involved in problem solving:
- Stage 1: Define, understand, and think about the problem. This stage involves identifying the actual problem, its attributes, the relevant area of knowledge, and collecting necessary information.
- Stage 2: Devise a plan for the solution. This stage includes brainstorming alternate ways to solve the problem and creating a flowchart or outline of the solution.
- Stage 3: Execute the plan. In this stage, the problem-solving process involves carrying out the steps outlined in the plan to reach a solution.
- Stage 4: Reflect and verify. This final stage involves checking if the problem solved matches the original definition, assessing the reasonableness of the solution, considering any criteria and constraints, and communicating the results.
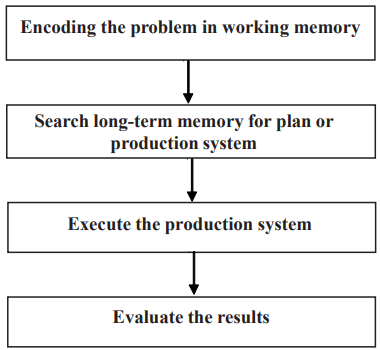
A model based on information processing has also been described as a translation of Polya's stages, which is presented in the figure below.
Problem-Solving Strategies:
- Even with a solid foundation of knowledge and skills, there is no guarantee of successful problem-solving. To increase the chances of finding a solution, it is important to employ a general strategy. A strategy is a set of sequential steps or procedures used by a problem solver to reach a solution. The strategy should assist the operator in efficiently extracting relevant information from the problem space and provide a systematic approach to problem-solving. Cognitive psychologists have identified two major types of strategies commonly used by operators: algorithms and heuristics.
Algorithms:
- An algorithm is a strategy that guarantees the correct solution to a problem if the defined rules are followed accurately. For example, in an anagram problem, an algorithm would involve attempting all possible letter sequences until the correct and meaningful word is formed. There are four essential properties of an algorithm: exactness (each step must be precisely described), termination (the algorithm must have a finite number of steps), effectiveness (it must provide the correct answer), and generality (it should solve every instance of the problem). However, due to the significant effort and time required, human operators rarely rely on algorithms as a problem-solving strategy.
Heuristics:
- Heuristics are general suggestions or "rules of thumb" that are useful in solving various problems. Unlike algorithms, heuristics do not guarantee a correct solution. There are numerous heuristics available, and if one does not work, another can be tried. General heuristics are often context-free and can be applied across different situations, while specific heuristics are used in specialized areas. One widely used and general heuristic is means-end analysis, which suggests taking actions to get closer to the goal by breaking down the problem into smaller pieces. Another strategy is working backward, starting from the goal state and moving toward the initial state. Analogies are another heuristic that involves using past problem-solving experiences to find similarities and common attributes between previous problems and the current problem.
- Meta-cognition, or self-monitoring, is crucial in problem-solving as it allows the problem solver to be aware of the current activity, the overall goal, the strategies being used, and their effectiveness. Employing strategies such as working backward, using analogies, and employing meta-cognition can enhance problem-solving abilities and increase the chances of finding successful solutions.
Factors Affecting Problem Solving
The effectiveness of problem-solving behavior can be evaluated based on two criteria: the time taken to solve the problem and the probability of finding a solution. The efficacy of a solution depends on various factors, some inherent to the problem itself and others related to the personal characteristics of the problem solver. These factors include:
- Nature of the problem: This involves considering the magnitude and difficulty level of the problem. If the initial state of the problem differs significantly from the desired goal state, it increases the difficulty level and makes problem-solving more challenging. As the size of a problem increases, with a greater number of elements in the problem space, finding a solution becomes even more difficult and time-consuming. For instance, anagrams with more letters present a higher level of difficulty.
- Degree of difference between the initial and goal states: The greater the disparity between the initial and goal states, the lower the likelihood of finding a solution. In such cases, the problem space is disorganized, requiring the problem solver to take more steps to reach a solution. An example of this is a jumbled collection of letters in an anagram, which represents a situation where the initial and goal states differ significantly. If the problem is a common one that is frequently encountered, the problem solver becomes familiar with the steps required to reach a solution, making the problem less difficult.
The concept of the perceiver's set involves perceiving and responding to a specific stimulus in a stereotypical manner. A set is formed when a person consistently and systematically perceives and responds to a stimulus in a similar way. This set can either facilitate or hinder problem solving. If past experiences have shaped a particular mental set, finding a solution becomes easier. However, when there is a greater disparity among experiences, the mental set can impede problem-solving. An example illustrating the effect of set can be observed when pronouncing the words: MACDONALD, MACMOHAN, MACGREGOR, MACHINERY. - If you pronounced the last word as "MacHinery," the influence of set affected you. Nonetheless, the impact of set can be minimized by increasing the time interval between practice and the actual task, explicitly instructing not to follow previously learned rules, and introducing exceptions during practice.
- Functional fixedness is the tendency to perceive objects based on their customary and stereotypical use, categorizing them according to their functional features in our daily lives.
|
165 videos|205 docs
|