Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 > Mind Map: Introduction to Trigonometry
Mind Map: Introduction to Trigonometry | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Download
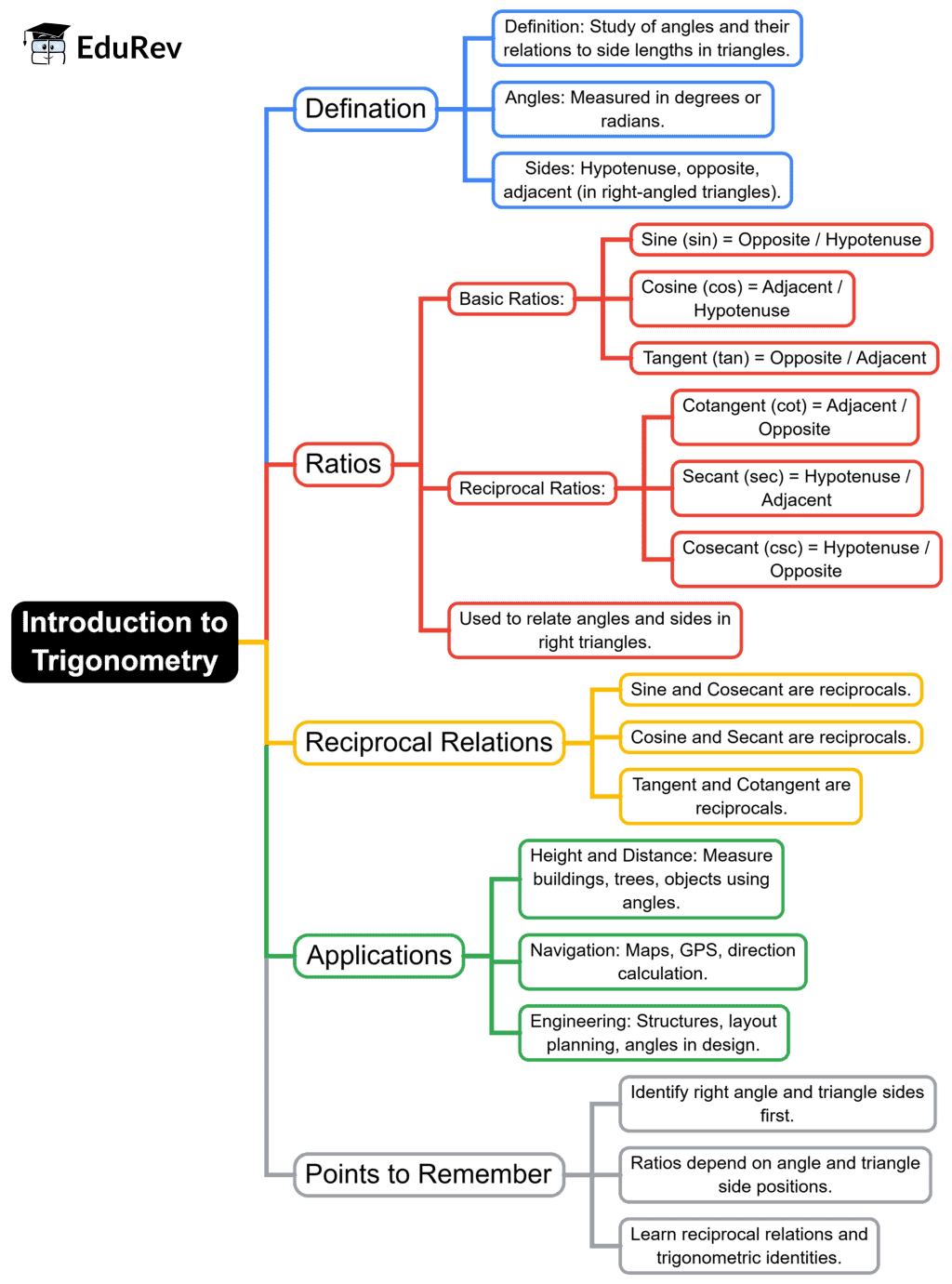
The document Mind Map: Introduction to Trigonometry | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics (Maths) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Introduction to Trigonometry - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10
| 1. What is trigonometry and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
Ans. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles, particularly right triangles. It is important because it provides tools for solving problems involving angles and distances, which are essential in fields such as physics, engineering, computer graphics, and architecture.
| 2. What are the basic trigonometric ratios? |  |
Ans. The three basic trigonometric ratios are sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan). These ratios are defined for a right triangle as follows:
- Sine of an angle = Opposite side / Hypotenuse
- Cosine of an angle = Adjacent side / Hypotenuse
- Tangent of an angle = Opposite side / Adjacent side.
| 3. How do you use the unit circle in trigonometry? |  |
Ans. The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It is used in trigonometry to define the sine and cosine of angles. The x-coordinate of a point on the unit circle represents the cosine of the angle, while the y-coordinate represents the sine. This allows for the evaluation of trigonometric functions for any angle, including those greater than 90 degrees.
| 4. What are the Pythagorean identities in trigonometry? |  |
Ans. The Pythagorean identities are fundamental relationships between the trigonometric functions that arise from the Pythagorean theorem. The most common identities are:
1. sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1
2. 1 + tan²(θ) = sec²(θ)
3. 1 + cot²(θ) = csc²(θ)
These identities are useful for simplifying expressions and solving trigonometric equations.
| 5. How can I solve basic trigonometric equations? |  |
Ans. To solve basic trigonometric equations, follow these steps:
1. Isolate the trigonometric function on one side of the equation.
2. Use known trigonometric values and identities to simplify.
3. Find all possible angles that satisfy the equation, often using the unit circle.
4. Consider the periodic nature of trigonometric functions to find additional solutions within the given interval.
Related Searches





















