Mnemonics: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction
These mnemonics provide a fun and effective way to grasp essential concepts in chemical bonding, from the Octet Rule to hydrogen bonding. They help simplify complex ideas and make them easier to recall for studying and exams.
Octet Rule
Describes: Atoms achieve a stable configuration of 8 valence electrons.
- Mnemonic: "Only Eight Stay Awesome."
- Only: Octet
- Eight: 8 valence electrons
- Stay: Stable configuration
- Awesome: Atoms

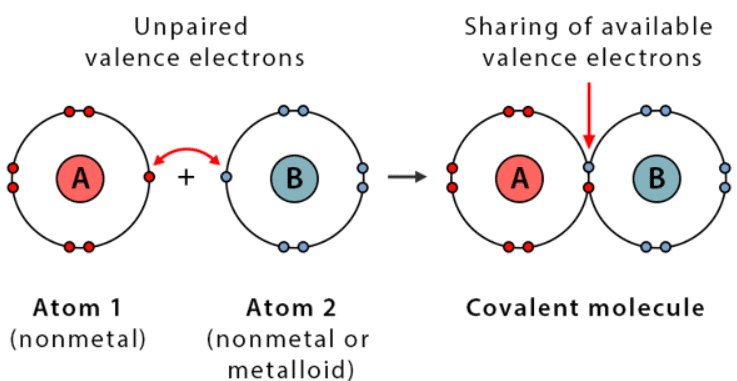
Covalent Bond
Describes: Sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Mnemonic: "Couples Value Equal Sharing."
- Couples: Covalent bond
- Value: Valence electrons
- Equal Sharing: Sharing electrons equally

Isoelectronic Species
Describes: Species with the same number of electrons.
- Mnemonic: "Identical Electrons Share Charge."
- Identical: Isoelectronic
- Electrons: Same electrons
- Share Charge: Equal charge distribution

Resonance Structure
Describes: Delocalization of electrons in molecules with multiple valid structures.
- Mnemonic: "Resonance Redefines Real Bonding."
- Resonance: Resonance in molecules
- Redefines: Multiple forms for the same molecule
- Real: The true bonding situation is a hybrid of all forms
- Bonding: Refers to bond formation in resonance

Polarity of NH₃ and NF₃
Describes: NH₃ is polar due to lone pair dipole aligning with bonds, while NF₃ is less polar due to lone pair dipole opposing bond dipoles.
- Mnemonic: "Nitrogen Holds, Fluorine Fights."
- Nitrogen Holds: NH₃ has aligned dipoles
- Fluorine Fights: NF₃ has opposing dipoles

Geometry (VSEPR Theory)
Describes: Shape of molecules based on electron-pair repulsion.
- Mnemonic: "Valence Shell Shapes Predict Reality."
- Valence Shell: VSEPR theory
- Shapes: Geometries/ Shapes
- Predict Reality: Actual/ Real molecular shapes

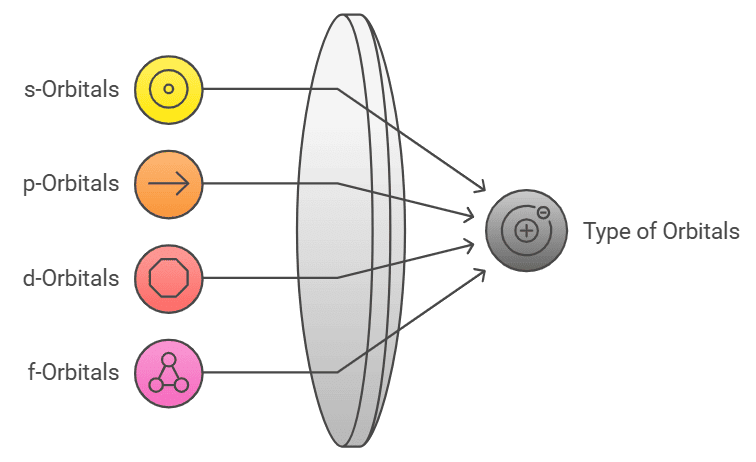
Types of Orbitals
Describes: s, p, d, and f orbitals.
- Mnemonic: "Simple People Draw Flowers."
- Simple: s-orbitals
- People: p-orbitals
- Draw: d-orbitals
- Flowers: f-orbitals

Conditions for Hybridisation
- Mnemonic: "Hybridization Depicts Same Energy, No Promotion Required."
- Hybridization: Process of hybridization.
- Same Energy: The orbitals involved in hybridization must have nearly the same energy.
- No Promotion: Promotion of electrons is not necessary before hybridization.
Hydrogen Bonding
Describes: Attraction between hydrogen and highly electronegative atoms (F, O, N).
- Mnemonic: "FONs Hold Hydrogen Tightly."
- FONs: Fluorine, Oxygen, and Nitrogen (the electronegative atoms involved in hydrogen bonding).
- Hold: Indicates the attraction.
- Hydrogen: Refers to the hydrogen atom involved in the bond.
- Tightly: Emphasizes the strong nature of the bond.

Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Describes: Hydrogen bonding within the same molecule between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom (F, O, N).
- Mnemonic: "Inside Attractions Bind Molecules."
- Inside: Refers to the bonding happening within the same molecule (intra-).
- Attractions: Refers to the hydrogen bonds formed.
- Bind: Highlights how the hydrogen atoms are bound within the same molecule.
- Molecules: Refers to the molecule in which these bonds are formed.

Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Describes: Hydrogen bonding between hydrogen of one molecule and an electronegative atom (F, O, N) in a different molecule.
- Mnemonic: "Between Molecules, Hydrogen Bridges."
- Between: Refers to the connection between two or more molecules.
- Molecules: Refers to the separate molecules.
- Hydrogen: Refers to the hydrogen atom involved in the bond.
- Bridges: Refers to the bridging action of the hydrogen bonds between molecules.

These mnemonics simplify complex concepts, making them easy to understand and remember for exams!
|
129 videos|238 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the octet rule and why is it important in chemical bonding? |  |
| 2. How do covalent bonds form between atoms? |  |
| 3. What are isoelectronic species and can you provide examples? |  |
| 4. How does molecular geometry affect the polarity of NH₃ and NF₃? |  |
| 5. What are the conditions required for hybridization to occur? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|