Mnemonics: Print Culture and the Modern World | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Introduction to Print |

|
| 2. First Printed Books |

|
| 3. Gutenberg’s Printing Press |

|
| 4. Print Revolution |

|
| 5. Print in India |

|
1. Introduction to Print
Mnemonic: "PRINT"
Interpretations:
- P: Paper and printing materials spread
- R: Reading public emerged
- I: Interaction with information changed
- N: New institutions influenced
- T: Technology (printing press) transformed book production
Explanation: The spread of Paper and printing materials led to a growing Reading audience. This changed how people Interacted with information and influenced New institutions. The Technology of the printing press transformed book production and accessibility.
 Print Culture
Print Culture
2. First Printed Books
Mnemonic: "Chinese Kings Just Praise Literature"
Interpretations:
- C: China started printing (AD 594)
- K: Korea, Japan adopted printing
- J: Japanese Diamond Sutra (868 AD)
- P: Printing for civil service exams in China
- L: Literature for scholars and public expanded
Explanation: China pioneered printing (AD 594), followed by Korea and Japan. The Printing of books initially supported scholars and civil service exams, but later, Literature expanded to include trade and leisure reading.
3. Gutenberg’s Printing Press
Mnemonic: "GUTENBERG"
Interpretations:
- G: Goldsmith skills helped Gutenberg
- U: Unprecedented speed (180 Bibles in 3 years)
- T: Text production increased
- E: Enabling mass literacy
- N: New movable type revolutionized print
- B: Book trade expanded
- E: Economical books encouraged learning
- R: Reading public transformed
- G: Gutenberg’s Bible changed history
Explanation: Goldsmith Gutenberg adapted existing tools for printing. This led to Unprecedented speed, making Text production faster. Enabling mass literacy, it introduced New movable type. The Book trade expanded, Economical books became widely available, and the Reading public grew. Gutenberg’s Bible became a historical milestone.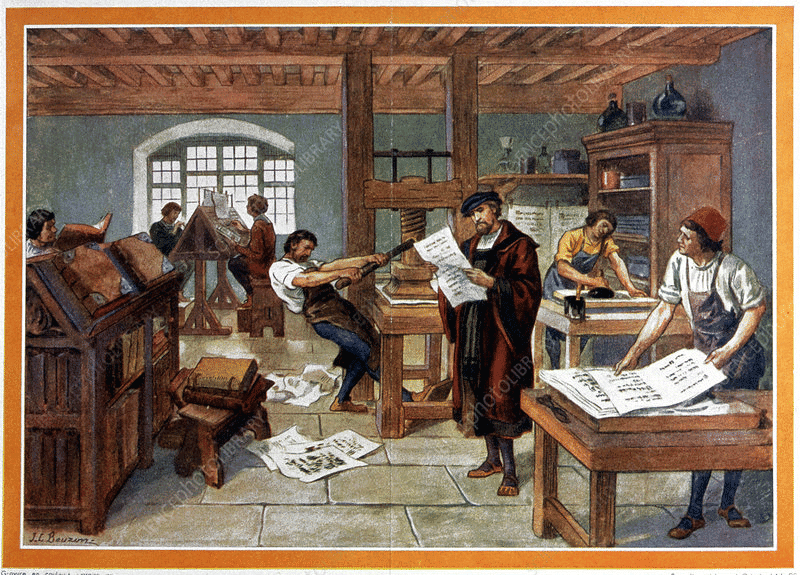 Printing Press
Printing Press
4. Print Revolution
Mnemonic: "PRESS"
Interpretations:
- P: Production of books increased
- R: Reading culture spread
- E: Enlightenment ideas circulated
- S: Society engaged in debates
- S: Social movements like Reformation emerged
Explanation: Printing increased book production, making knowledge widely accessible. Reading culture expanded beyond the elite. Enlightenment ideas spread, sparking reforms. Society engaged in public debates, and Social movements like the Reformation gained momentum.
5. Print in India
Mnemonic: "Portuguese British Indians Revolutionized Newspapers"
Interpretations:
- P: Portuguese introduced the printing press in Goa
- B: British controlled press freedom (Vernacular Press Act 1878)
- I: Indian newspapers emerged (Bengal Gazette by Hickey)
- R: Religious debates flourished through print
- N: Nationalist newspapers criticized colonial rule
Explanation: Portuguese missionaries introduced the first printing press in Goa. British colonial rulers later controlled the press through laws like the Vernacular Press Act. Indian newspapers emerged, challenging colonial rule. Religious debates flourished in print, shaping societal change. Nationalist newspapers spread anti-colonial sentiments. Print in India
Print in India
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Print Culture and the Modern World - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What was the significance of Gutenberg’s printing press in the history of print culture? |  |
| 2. How did the first printed books impact society? |  |
| 3. What role did print culture play in India during the colonial period? |  |
| 4. How did the print revolution contribute to the modern world? |  |
| 5. What were the differences between manuscript culture and print culture? |  |















