Modals Class 10 PDF Download
Modals
Modals are auxiliary verbs used to form the tenses, moods, voices, etc. of other verbs. They are helping verbs that cannot be used on their own but to be used along with other main verbs mainly to express attitudes.
1. When something happens, they form a tense of the main verb.
Examples:
- I shall go.
- He was going.
2. They express permission, necessity, or possibility to do something.
Examples:
- They may go.
- You must go.
- I can’t go.
- I might go.
- She would go if she could.
Observe the highlighted words in these sentences:
- We can make our nation a superpower by the year 2020.
- Kalam says that we need to do things ourselves. We must not import equipment from other nations.
- In twenty years, each one of us ought to have our destiny worked out.
All the highlighted words are Modal Auxiliaries that are used with another verb, and express the mood of the speaker:
- The main MODALS are: can, could; may, might; shall, should; will, would; must; ought to; need to; have to.
- The negative modals are: couldn’t, wouldn’t, shouldn’t, mustn’t, needn’t, oughtn’t.
Some Important Modals
1. Must and have to:
- Must is used for all persons in the present and the future tenses.
- The negative is must not (mustn’t).
- The interrogative form is, must I?
- Must has no infinitive and no past tense. It is followed by the infinitive without ”to’.
(i) Must is used to express obligation.
Examples:
- You must obey your parents.
- You must go to school in time.
(ii) It is used to express compulsion, e. ordering someone to do something because it is necessary or important to do so.
Examples:
- You must answer all questions.
- You must return by the evening.
(iii) It is used for saying that something is probably true because nothing else seems possible.
Examples:
- You must be tired after your long journey (inference).
- There must be some mistakes.
(iv) The negative form of must (must not) is used for prohibition.
Examples:
- You must not come here.
- You must not use the office phone for private calls.
(v) It is used to give emphatic advice.
- She must consult a doctor at once.
- You must work hard if you want to get good marks.
Must and have to: Have to, like must, expresses obligation in the present while had to does so in the past. Must expresses an obligation imposed by the speaker. Have to/Had to expresses external obligations—an obligation by some authority or circumstances.
Examples:
- I must reach there in time (the speaker himself feels so).
- You must reach in time (ordered to do so by some external authority).
Had to is used when describing something belonging to the past.
Example:
- He had to go early to catch the train.
These two verbs have the following forms: 
Have to and had to have alternative negative and interrogative forms:
Examples:
- Have you to obey his orders? or Do you have to obey his orders?
- Had you to work on Sundays? or Did you have to work on Sundays?
- Do you have to mind your watch every day? or Did you have to pay customs duty on your watch?
2. Have to/Had to:
(i) Have to express obligation and necessity in the present. Had to does so in the past.
Examples:
- She has to look after her mother.
- He had to finish his work before 5 p.m.
(ii) Have to and had to are used for giving advice.
Examples:
- First you have to mix the water and the sugar.
- She had to take those pills to get better.
(iii) Have to and had to are used to draw a logical conclusion.
Examples:
- There has to be some reason for his mischief.
- This has to be a part of the whole plan.
(iv) Have to is used for supposition or to describe something based on possible ideas or situations.
Examples:
- You will have to work very hard to stand first.
- If she has to choose, she won’t marry him.
(v) Have to is used to indicate that something is very important or necessary.
Examples:
- We have to be more careful in the future.
- They will have to clear all their debts before December.
3. Should:
(i) Should is the past tense of shall. In the indirect form of speech ‘shall’ changes into should.
Examples:
- I said, “I shall go to school tomorrow.”
- I said that I should go to school the next day.
(ii) Should is used to express obligation, duty, etc.
Examples:
- You should look after your old parents.
- You should pay all your taxes.
(iii) Should is used to give advice or suggestion.
Examples:
- You should consult a doctor.
- She should do yoga exercises daily.
- He should learn English if he wants to get a good job.
(iv) Should is used to express purpose.
Examples:
- Mohan walked fast so that he should catch the train.
- Satish worked hard so that he should stand first in the class.
(v) Should is used to state imaginary results.
Examples:
- He should get angry if he had come to know about it.
(vi) Should is used to express polite requests.
Examples:
- I should be thankful if you give me some money.
4. Need: As a modal verb, need is usually followed by an infinitive without ‘to’. The modal verb need is mainly used in questions and negatives, which are formed without ‘do’.
Examples:
- Need I go now?
- You need not go.
The negative need not is often shortened to needn’t in the conversation and informal writing. Need does not change its form, so the third person singular of the present tense does not end in’ —s’.
Example:
- He need not go there.
The modal verb need has no past tense. But it can be used in the pattern followed by a past participle.
Examples:
- Need not have/needn’t have
- You needn’t have waited for me.
The negative and interrogative forms of the past tense are:
- Did not (didn’t) need and did I need?
In the present and future tenses, the negative and interrogative can be formed in either of the two ways:
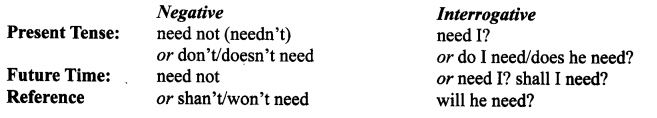
(i) The negative need expresses absence of obligation.
Examples:
- They need not send the letter now.
- You need not go. (i.e., It is not necessary for you to go).
- He need not come now.
(ii) Need is used to express obligation or necessity.
Examples:
- Need I attend the class today?
- Need he solve all the sums?
(iii) Need not + perfect infinitive is used to express an unnecessary action which was performed.
Examples:
- You needn’t have gone to see the doctor. He was on leave today.
- You needn’t have carried an umbrella as it was not raining.
5. Ought: Ought is usually followed by ‘to’ and an infinitive.
Example:
- You ought to tell the truth.
It does not change its form so that the third person singular form does not end in ‘-s’.
Example:
- She ought to work a little harder.
It can be used as a present, past, or future tense.
The negative is ought not (oughtn’t) and the interrogative is ought I?, Ought you?, Ought he?, etc:
Examples:
- Ought I do it at once?
- He ought not disobey his teachers.
(i) Ought to is used for expressing what is the right or sensible thing to do, or the right way to behave.
Examples:
- You ought to get up earlier.
- We ought to exercise daily.
- Teachers ought not smoke before students.
(ii) Ought to is used when we believe strongly or expect that something will happen.
Examples:
- The Indian team ought to win.
- Satish ought to pass.
- The meeting ought to have finished by 2 o’clock.
(iii) Ought to see/hear/meet, is used for emphasising how good, impressive or unusual something or someone is.
Examples:
- You ought to see their new house.
- You ought to meet his elder brother.
(iv) Ought to have is used when we realise that we did not do the right thing in the past.
Examples:
- You ought to have listened to my advice.
- She ought to have taken the money.
Ought, must, have to, and should
Note: Ought is used to express the subject’s obligation or duty. But it indicates neither the speaker’s authority as with must nor an outside authority as with have to. The speaker is only reminding the subject of his duty. Besides this, he is giving advice or indicating a correct or sensible action.
Ought can be used in exactly the same way as should:
- You ought to/should obey your parents.
- Have to and must:
- You have to be regular. (These are the rules.)
- You must obey your teachers. (The speaker insists on it.)
- You have to take this medicine. (The doctor insists on it.)
- You must take this medicine. (The speaker insists on it or It is the speaker’s emphatic advice.)
- You mustn’t drink this, it is poison, (prohibition)
- You oughtn’t to smoke so much. (It is not right or sensible.)



















