Mollusca | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Introduction
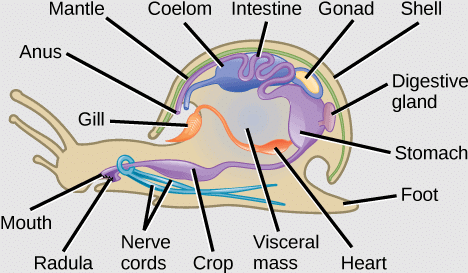
Animals belonging to the phylum Mollusca have soft-bodies, triploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical and coelomate. The study of Mollusca is called Malacology. They are sluggish invertebrates, with a thin fleshy envelope or mantle covering the visceral organs.

Characteristics of Mollusca
– It is the second largest Phylum.
– Mollusca (Soft bodied) are marine or freshwater or terrestrial.
Johnston coined the name Mollusca.
– Study of this phylum is known as Malacology & study of shells of molluscan is known as Conchology.
– Body is unsegmented with a variety of shapes. Neopilina is exceptionally segmented. (connecting link).
– Molluscas are usually bilateral. Few are secondarily asymmetrical (snail) due to twisting (Torsion) during growth.
– Triploblastic with Organ system level.
– Body wall includes one layered epidermis (usually cilited) with unstripped muscles found in bundles.
Body parts consist of:
(i) Head with sense organ. Head is absent in Pelecypoda & Scaphopoda.
(ii) Dorsal visceral mass containing organ system.
(iii) Ventral foot for locomotion.
(iv) Thin fleshy fold or outgrowth of dorsal body wall covers the body. This fold is called mantle or pallium. It encloses a space mantle or pallial cavity between itself and the body. The mantle usually secretes an external limy shell. Shell is made up of Calcium carbonate and Concheolin protein.
Shell may also be internal (Cuttle fish), reduced and even absent (Octopus).
 Mollusca
Mollusca
– Coelom is greatly reduced. It is represented by cavities in the pericardium, kidneys and gonads. Space among the viscera contain blood and form haemocoel.
– Digestive tract is complete. Buccal cavity contain a rasping organ the Radula, with transverse row of teeth.
– Anus opens into the mantle cavity.
– Digestive glands are known as hepatopancreas.
– Respiration is usually by gills i.e., Ctenidia. But respiration may takes place by body surface also.
Dentalium respire by Mantle.
– Pila respire by pulmonary sac on land and by gills in water.
– The circulatory system is open. It includes dorsal pulsatile heart and a few arteries that open into sinuses.
– Cephalopoda has closed type of circulatory system
– Blood has a copper containing, blue respiratory pigment Haemocyanin. Blood is colourless with amoebocytes.
– Excretory system includes 1 or 2 pairs of sac like kidneys, which open into the mantle cavity. Kidney of molluscans are Metanephridia known as Kaber's organs or Organ of Bojanus. Excretory matter is ammonia or uric acid.
Nervous system comprises three paired ganglia:
(1) Cerebral (above the mouth) (2) Pedal (In the foot) (3) Visceral (in visceral mass)
These are interconnected by
(1) Commissure (Joins similar ganglia)
(2) Connectives (Joins dissimilar ganglia)
Senses organ includes
(1) Eye - Present over a stalk called ommatophore (Gastropoda).
(2) Statocyst/Lithocyst - For equilibrium in foot
(3) Osphradia - Chemoreceptor/Olfactory as well as for testing chemical & physical nature of water.
– Sexes usually separate (snail has ovotestis). Gonads have ducts.
– Fertilization may be external or internal. – Cleavage is spiral, determinate, unequal and holoblastic.
– Development is - Direct or indirect.
– Trochophore is very common larva of Mollusca phylum.
– Larva - Glochidium (Fresh water mussel) and Veliger (Pila)
– Precious pearl of the size of tennis - ball is made by a mollusk - Tridekna
– ‘‘Nacre layer’’ is called ‘‘Mother of Pearl’’. This layer is made up of CaCO3 and choncheolin protein.
– Father of pearl industry - Kokichi Mikimoto
Classification of Mollusca
Molluscs are classified on the basis of shell, Foot, Nervous system and Gills into seven classes.
1. Cephalopoda - Marine
Shell-Internal and reduced it may be external (Nautilus) or absent (Octopus)
Redula - Present
Foot - Modified into a funnel and partly into 8 or 10 sucker bearing arms that surround the mouth
Locomotion is by expelling water in jet through siphon (Jet propulsion). Ink glands in some squids for offense and defense. When the squid is attacked, it emits a cloud of inky fluid through its siphon. This 'smoke screen' interferes with the vision and chemoreceptor of the predator and thereby helps the squid to escape.
- Closed blood circulation.
- Hectocotyle for sperm transfer
- Larva absent
e.g. Sepia-Cuttle fish*
10 arms having Chromatophores.
Tethys - Sea-fly
Loligo - Squid
(Radula absent)
*Octopus - Devil fish 8 arms
Nautilus - Tiger shell
2. Pelecypoda Bivalvia or Lamellibranchiata
- Marine/fresh water
Head-Absent
Shell-Consist of two valves Movably hinged dorsally.
Redula-Absent Foot-Plough or Wedge shaped for burrowing
Redula-absent
Larva-Glochidium Trochophore
Unio-Mussel (fresh water)
Mytilus-Mussel (marine)
Lamellidens-mussel
Ostrea
Teredo-Ship worm.
Pinctada-Pearl oysters.
Pteria- Indian pearl oyster.
Tridekna-Highest economic value
Pecten - Scallop
3. Gastropoda
- Marine/fresh water/moist soil. largest class.
- embryo grows into an asymmetrical adult due to twisting/torsion of visceral mass during development. mouth & anus lie on same side.
Head-With eyes & tentacles.Shell - Spirally coiled
Radula – Present
Foot - Large & flat
Larva - Trochophore or Veliger.
e.g.- Pila-Apple-snail (Shell used in but-tons)
Cypraea-Old currency
Limex-Slug (shell-less)
Helix
Turbinella-Shankh
Doris-Sea lemon
Aplysia- Sea hare*
Planorbis-Land snail
Lymnea-Land snail
4. Scaphopoda
- Marine
Head - absent. Shell-Tubular, open at both end.
Redula-Present
Foot - Conical and use for digging
Larva - Trochophore
e.g.
Dentalium-Tusk shell. (Respire by mantle)
5. Polyplacophora/ Amphineura - Marine
Head - reduced without eyes and tentacles.
Shell - Present or absent. 8 dorsal plates present. (Multivalved)
Radula – Present
Foot - Reduced/absent.
Larva-Trochophore
e.g.
Chiton-The coat of mail shell (Sea-mica)
Chaetopleura-*
6. Aplacophora
- Marine, Worm-like
Head-Small without eyes & tentacles
Shell - Absent.
Redula - Present
Foot-Reduce/absent.
Larva-Trochophore
e.g.
- Neomenia
7. Monoplacophora - Marine, common character of Annelida and Arthropoda.
Head - Indistinct
Shell - Dome-shaped with mantle.
Radula - Present
Foot - Flat muscular
Larva - Trochophore
e.g.- Neopilina
Living fossils Connecting link of Annelida and Mollusca and only segmented mollusk with nephridia.
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Mollusca - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are some common characteristics of mollusks? |  |
| 2. How are mollusks classified? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of mollusks in the ecosystem? |  |
| 4. What are some economic uses of mollusks? |  |
| 5. How do mollusks reproduce? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|

















