Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 5
MORPHOLOGY
Gr. Morphos = Form, logos = Study
Morphology is the branch of science which deals with the study of form and structure. In botany, it generally means the study of external features, forms and relative positions of different organs on plants.
Angiosperms or flowering plants show a great variety of shape, size and form. The size ranges from the minute Wolffia and Lemna (0.1cm) to the tall Eucalyptus (up to 100 metre) and large sized Banyan (Ficus benghalensis).
PARTS OF A FLOWERING PLANT
The Root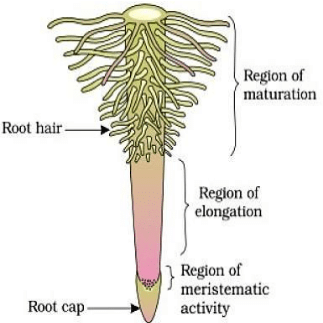
The root is usually an underground part of the plant which helps in fixation and absorption of water. The root with its branches is known as the root system.
(i) Characteristics of the root
- The root is the descending portion of the plant axis and is positively geotropic.
- It is non-green or brown in colour.
- The root is not differentiated into nodes and internodes.
- As per the rule the root does not bear leaves and true buds.
- Usually, the root tip is protected by a root cap.
- The root hairs unicellular root hairs.
- Lateral roots arise from the root which are endogenous in origin (arises from pericycle).
(ii) Types of root system:
The root system is generally of two types:
- Tap root system: The tap root system develops from radicle of the germinating seed. It is also called the normal root system. The tap root system is present in dicotyledonous plants.
- Adventitious root system: The root system that develops from any part of the plant body other than the radical is called the adventitious root system. It is mostly seen in monocotyledonous plants.
THE STEM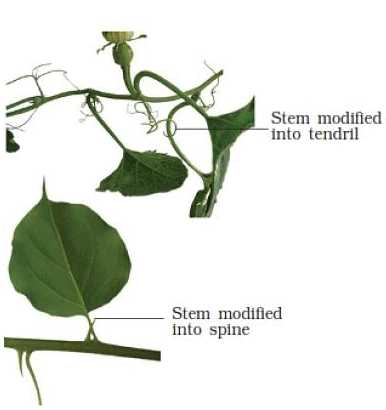
(i) The stem develops from the plumule of the germinating seed.
(ii) The stem shows the differentiation of nodes and internodes.
(iii) The place where the leaf develops on the stem is called the node.
(iv) The portion of the stem between two successive nodes is called the internode.
(v) Characteristics of stem:
- Stem is an ascending axis of the plant and develops from the plumule and epicotyl of the embryo.
- It is generally erect and grows away from the soil towards light. Therefore, it is negatively geotropic and positively phototropic.
- The growing apex of stem bears a terminal bud for growth in length.
- In flowering plants, stem is differentiated into nodes and internodes.
- The lateral organs of stem (i.e., leaves and branches) are exogenous in origin (from cortical region).
- The young stem is green and photosynthetic.
- Hair, if present, are generally multicellular.
- In mature plants, stem and its branches bear flowers and fruits.
(vi) Diverse forms of stem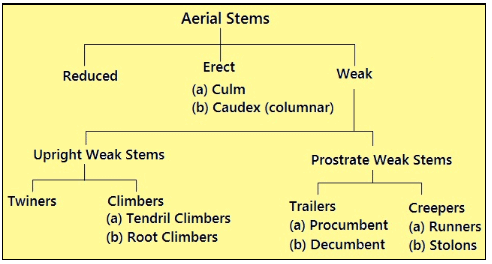
THE LEAF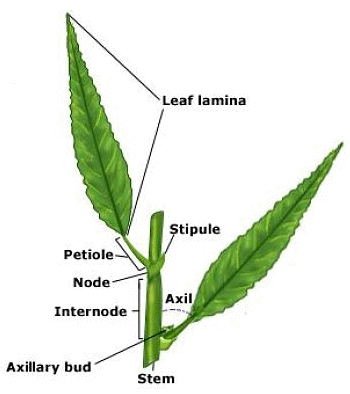
The leaf is a green, flat, thin, expanded lateral appendages of stem which is borne at a node and bears a bud in its axil. It is exogenous in origin and develops from the leaf primordium of shoot apex. The green colour of leaf is due to presence of the photosynthetic pigment – chlorophyll which helps plants to synthesize organic food. The green photosynthetic leaves of a plant are collectively called foliage. They are borne on stem in acropetal succession.
(i) Characteristics of leaf
- The leaf is a lateral dissimilar appendage of the stem.
- A leaf is always borne at the node of stem.
- Generally, there is always an axillary bud in the axil of a leaf.
- It is exogenous in origin and develops from the swollen leaf primordium of the growing apex.
- The growth of leaf is limited.
- The leaves do not possess any apical bud or a regular growing point.
- A leaf has three main parts – Leaf base, petiole and leaf lamina. In addition, it may possess two lateral outgrowths of the leaf base, called stipules.
- The leaf lamina is traversed by prominent vascular strands, called veins.
(ii) Types of leaf
- Acicular type - Needle shaped leaves.
- Linear type - Long and slightly broader leaves.
- Lanceolate type - Lance shaped leaves.
- Orbicular type - More or less circular leaves.
- Elliptical type - Leaves are like an ellipse.
- Ovate type - Egg shaped (oval) leaves.
- Spathulate type - Spoon like leaves.
- Oblique type - Leaf lamina is with unequal half.
- Oblong type - Rectangular leaves
- Reniform type - Kidney shaped leaves
- Cordate type - Heart shaped (with a deep notch at the base) leaves.
- Saggitate type - Leaves shaped like an arrow head.
- Hastate type - Leaves like sagittate but the two basal lobes are directed outwards.
- Lyrate type - Leaves shaped like a lyre.
- Centric type - Hollow and cylindrical leaves.
- Cuneate type - Wedge shaped leaves.
FLOWER
It can be defined as modified dwarf shoot which is meant for sexual reproduction.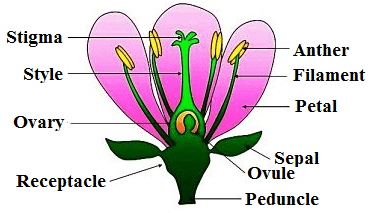
Floral Parts of a typical flower
(i) Calyx: It is the outermost whorl composed of sepals.
The calyx may show number of modifications. They are:
- Campanulate: Bell shaped, e.g., Althaea.
- Cupulate: Cup like, e.g., Gossypium.
- Urceolate: Urn shaped, e.g., Hyoscyamus.
- Infundibuliform: Funnel shaped, e.g., Atropa belladonna.
- Tubular: Calyx tube like, e.g., Datura.
- Bilabiate: Calyx forms two lips, e.g., Ocimum.
- Spread: One or two sepals forming a beak like structure, e.g., Larkspur.
- Pappus: Calyx are modified into hairs e.g., Sonchus, Tridax (Asteraceae).
- Spines: When calyx forms spines, e.g., Trapa.
- Hooded: When sepals enlarged to form a hood over the flower, e.g., Aconitum.
- Petaloid: Enlarged and brightly coloured sepals, e.g., Clerodendron, Mussaenda
(ii) Corolla: It is composed of petals and is the second whorl. The corolla may undergo modification or possess some special appendages.
- Sepaloid: Green or dark coloured sepal. e.g., Annona, Polyalthia and Artabotrys.
- Saccate: The corolla tube may form a pouch on one side. e.g., Antirrhinum.
- Spurred: Sometimes one or two petals or the entire corolla tube grow downwards forming a spur that usually stores nectar. e.g., Aquilegia vulgaris.
- Corona: Special appendages of different kinds like scales, hairs develop from the corolla. Such appendages are called corona. e.g., Passiflora, Oleander and Nerium.
(iii) Androecium: It is the third whorl composed of stamens. The mode of attachment of a filament to anther by connective is called fixation.
It is of following types:
- Adnate: Filament attached to the total length of the anther on the back. e.g., Michelia (Champaca).
- Basifixed: Filament is attached to the base of the anther e.g., Datura, Mustard, Radish
- Dorsifixed: Filament is attached to the anther on the dorsal side at middle portion e.g., Passiflora.
- Versatile: Filament is attached to the anther at a point so that anther can swing freely in all direction. e.g., Grasses.
(iv) Gynoecium: It is the innermost whorl and is also called pistil. It shows carpels.
Accordingly the gynoecium may be described as follows:
- Monocarpellary: It is a ovary with a single carpel, e.g., Bean.
- Bicarpellary: It is presence of two carpels in a ovary, e.g., Helianthus.
- Tricarpellary: It is presence of three carpels, e.g., Cocos.
- Tricarpellary: It is presence of four carpels, e.g., Cotton.
- Pentacarpellary: It is presence of five carpels, e.g., Hibiscus.
- Multicarpellary: It is presence of many carpels, e.g., Annona.
AESTIVATION
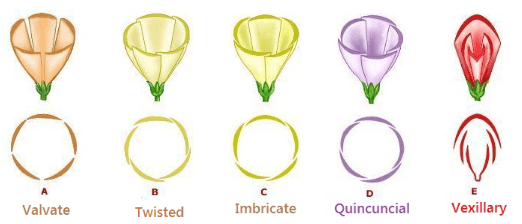
The arrangement of sepals and petals in bud condition of the flower is called “aestivation”. It is may be of following types:
- Open
- Valvate
- Twisted
- Imbricate
- Quincuncial
- Vexillary
FLORAL FORMULA
It is an expression summarizing the information given in a floral diagram. It represents the information given in a floral diagram in the form of an equation. Following symbols are used in constructing a floral formula.
FAQs on Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 5
| 1. What is the importance of studying the morphology of flowering plants for the NEET exam? |  |
| 2. How can the study of the morphology of flowering plants help in taxonomy? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of root systems found in flowering plants? |  |
| 4. How does the structure of leaves contribute to plant survival? |  |
| 5. What is the role of flowers in the reproductive process of flowering plants? |  |






















