Friction: Its Types and Problems | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Friction? |

|
| Types of Friction |

|
| Angle of Friction |

|
| Angle of Repose (θ) |

|
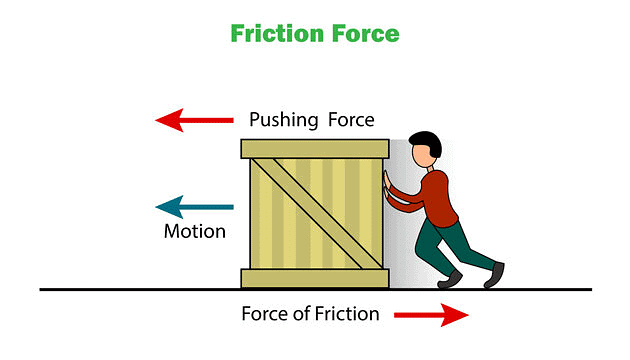
"Friction is like a silent force that affects everything around us. It's the resistance that objects experience when they slide, roll, or move against each other. Imagine trying to push a heavy box across a rough floor - you can feel the force pushing back against your hands. That force is friction.
Do you know who formulated the concept of friction for the first time? It was the legend, Leonardo da Vinci. In this document, we will study friction, its types, and important terms related to it.
What is Friction?
Friction, or the force of friction, is characterized as the force that opposes the movement of an object on a surface, whether the object is at rest or in motion relative to the surface.
- Contact Force: Friction takes place at the point where the object makes contact with the surface, essentially occurring between two surfaces and therefore classified as a contact force.
- Resistance to movement: Surfaces, by nature, are not perfectly smooth; they contain bumps and irregularities. When these surfaces come into contact, the bumps adhere and interlock, creating resistance to movement. This resistance is what defines friction as a force.
It's important to note that frictional force is non-conservative. As an object moves from one position to another against friction, energy is not conserved, as a portion of it is dissipated in the form of heat.
Types of Friction
Before we proceed further into a detailed account of frictional phenomena, it is advisable to become familiar with different types of frictional forces.
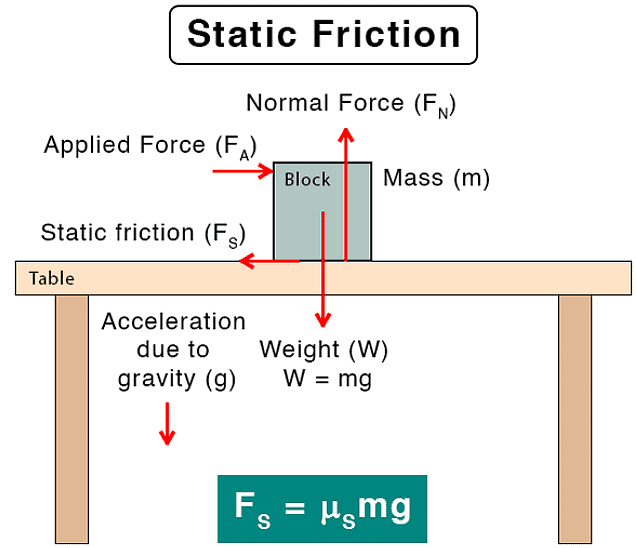
Static Friction
- Static friction occurs when an object is at rest relative to a surface.
- This friction prevents the object from moving when a force is applied until a maximum static friction value is reached.
- Once the applied force surpasses this threshold, the object starts moving, and static friction no longer applies.
- It can have a value maximum up to the limiting friction (fsm).
fs ≤ fsm - The limiting friction is experimentally observed proportional to the normal reaction between surfaces in contact. f= μsN
Here μs is the constant of proportionality. It is known as the coefficient of static friction
for the two surfaces involved.
Examples:
- Preventing a person from slipping while walking or running.
- Keeping a heavy object stationary while pushing or pulling.
 Static Friction
Static Friction
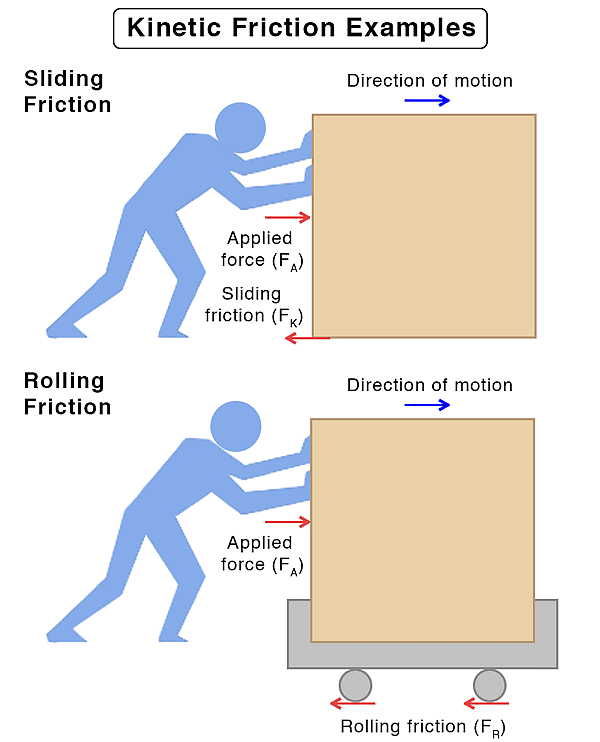
Kinetic Friction
- Kinetic friction comes into play when an object moves relative to a surface after overcoming static friction.
- Kinetic friction is experimentally found proportional to the normal reaction between surfaces in contact. fk = μkN
- Two types of kinetic friction exist: sliding friction for objects sliding over a surface and rolling friction for objects rolling on a surface.
Examples:
- Causing a car to skid.
- Bringing a skier to a stop.
 Kinetic Friction
Kinetic FrictionFluid Friction:
- Fluid friction arises when an object moves through a fluid or between layers of moving fluid.
- Fluids can be gases (e.g., air) or liquids (e.g., water), and the friction in some fluids, like oil and water, depends on viscosity.
Examples:
- Creating resistance for a swimmer moving through a pool.
- Impeding the motion of a ship sailing in the ocean.
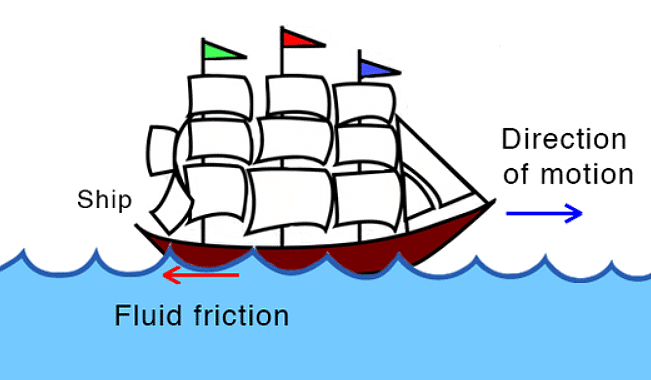 Fluid Friction
Fluid Friction
Static and Kinetic Friction in a Box on a Horizontal Surface
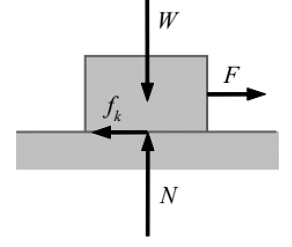
To understand the nature of friction let us consider a box of weight W placed on a horizontal rough surface.
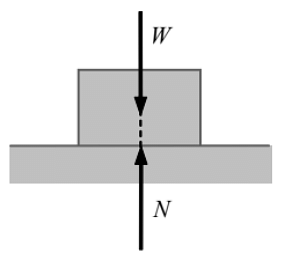
- The forces acting on the box are its weight and reaction from the horizontal surface. They are shown in the figure.
- The weight does not have any horizontal component, so the reaction of the horizontal surface on the box is normal to the surface. It is represented by N in the figure.
- The box is in equilibrium therefore both W and N are equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, and collinear. Now suppose the box is being pulled by a gradually increasing horizontal force F to slide the box.
- Initially, when the force F is small enough, the box does not slide. This can only be explained if we assume a frictional force, which is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the applied force F acts on the box.
- The force F produces in the box a tendency of sliding and the friction force is opposing this tendency of sliding. The frictional force developed before sliding initiates is defined as static friction. It opposes the tendency of sliding.
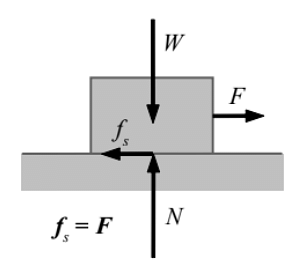 Static Friction
Static Friction
- As we increase F, the box remains stationary until a value of F is reached Kinetic friction when the box starts sliding.
- Before the box starts sliding, the static friction increases with F and counterbalances F until the static friction reaches its maximum value known as limiting friction or maximum static friction fsm.
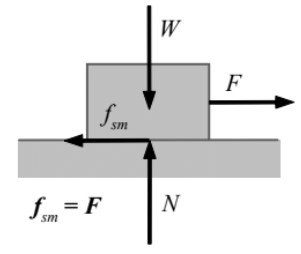 Limiting Friction: The maximum Static Friction
Limiting Friction: The maximum Static Friction
- When the box starts sliding, to maintain it sliding still a force F is needed to overcome frictional force. This frictional force is known as kinetic friction (fk ). It always opposes sliding.
 Kinetic Friction
Kinetic Friction
Coefficients of Friction:
- In fk = μkN, μk is the constant of proportionality. It is known as the coefficient of kinetic friction for the two surfaces involved. The frictional forces between any pair of surfaces are decided by the respective coefficients of friction.
- The coefficients of friction are dimensionless constants and have no units. The coefficient of static friction (μs) is generally larger than the coefficient of kinetic friction (μk) but never becomes smaller; at the most, both of them may be equal.
Therefore, the magnitude of kinetic friction is usually smaller than the limiting static friction (fsm), and sometimes kinetic friction becomes equal to the limiting static friction but it can never exceed the limiting friction.
Note:
The limiting static friction and the kinetic friction between any pair of solid surfaces follow these two empirical laws:
(i) Frictional forces are independent of measured area of contact.
(ii) Both the limiting static friction and kinetic friction are proportional to the normal force pressing the surfaces in contact.
Angle of Friction
The angle of friction is the angle between the resultant contact force and normal reaction N, when sliding is initiating. It is denoted by λ
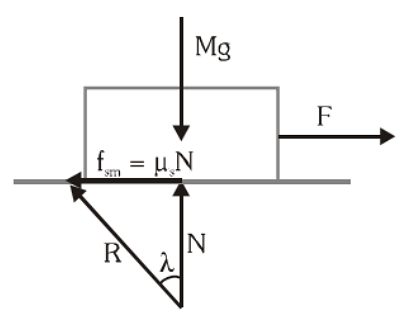 Angle of Friction (λ)
Angle of Friction (λ)
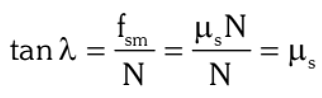
For smooth surface λ = 0
Angle of Repose (θ)
A body is placed on an inclined plane and the angle of inclination is gradually increased. At some angle of inclination θ the body starts sliding down the plane due to gravity. This angle of inclination is called the angle of repose (θ).
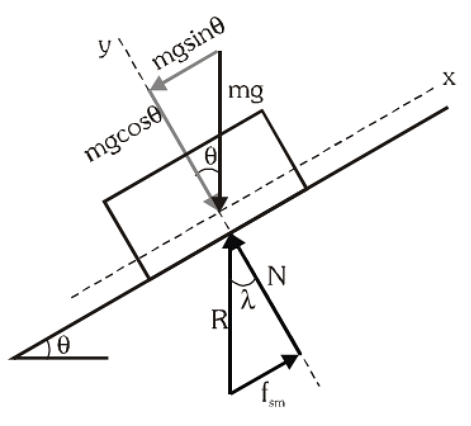 Angle of Repose(θ)
Angle of Repose(θ)
The angle of repose is the minimum angle of inclination at which a body placed on the inclined starts sliding down due to its own weight. Thus, the angle of repose = the angle of friction.
Example 1: A block of mass 1 kg is at rest on a rough horizontal surface, where coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.2 and 0.15.
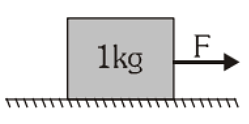 Find the frictional forces if a horizontal force
Find the frictional forces if a horizontal force
(a) F = 1N (b) F = 1.96 N (c) F = 2.5 N is applied on a block
Solution: Maximum force of friction is the limiting friction fsm = 0.2 × 1 × 9.8 N = 1.96 N
(a) For F = 1 N, F < fsm
So, the body is at rest means static friction is present, and hence fs = F = 1 N
(b) For F = 1.96 N, F = fsm = 1.96 N. The block is about to slide, therefore f = 1.96 N
(c) For F = 2.5 N, So F > fsm
Now the body is sliding and kinetic friction acts.
Therefore f = fk = μkN = μk mg = 0.15 × 1 × 9.8 = 1.47 N
Example 2. The length of a uniform chain is L and the coefficient of static friction is μ between the chain and the tabletop. Calculate the maximum length of the chain that can hang from the table without sliding.
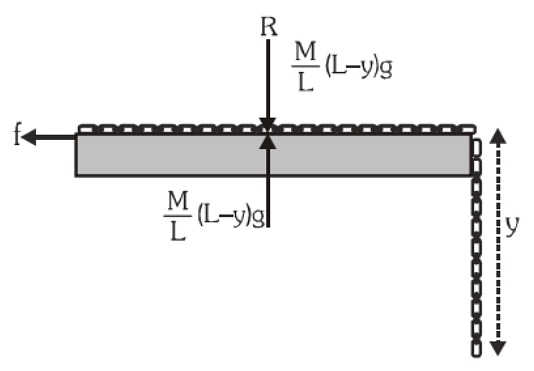 Solution: Let y be the maximum length of the chain that can hang without causing the portion of chain on the table to slide.
Solution: Let y be the maximum length of the chain that can hang without causing the portion of chain on the table to slide.
Length of chain on the table = (L – y)
Weight of part of the chain on table =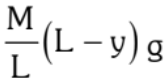
Weight of hanging part of the chain =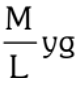
For equilibrium with a maximum portion hanging,
limiting friction = weight of hanging part of the chain
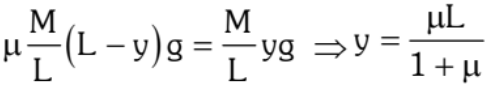
|
97 videos|378 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on Friction: Its Types and Problems - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is friction and why is it important in everyday life? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of friction? |  |
| 3. How is the angle of friction defined and what does it signify? |  |
| 4. What is the angle of repose and how is it different from the angle of friction? |  |
| 5. How can problems involving friction be solved in physics? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















