NCERT Exemplar: Carbon & its Compounds | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
(a) carbon monoxide only
(b) carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) carbon dioxide only
(d) coal
Ans: c
Q.2. Which of the following statements are usually correct for carbon compounds? These
(i) are good conductors of electricity
(ii) are poor conductors of electricity
(iii) have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(iv) do not have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: d
Explanation:
Carbon compounds form covalent bonds hence they have very weak force of attraction. Carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity.
Q.3. A molecule of ammonia (NH3 ) has
(a) only single bonds
(b) only double bonds
(c) only triple bonds
(d) two double bonds and one single bond
Ans: a
Explanation:
Nitrogen has three electrons in its outermost shell and hydrogen has 1. 3 hydrogen atoms combine with 1 nitrogen atom to make ammonia. These bonds are single bonds.
Q.4. Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of
(a) phosphorus
(b) sulphur
(c) carbon
(d) tin
Ans: c
Explanation:
Diamond, Graphite, Lonsdaleite, C60 (Buckminsterfullerene or buckyball), C540, C70, Amorphous carbon, and a single-walled carbon nanotube, or buckytube. Are the allotropes of Carbon.
Q.5. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
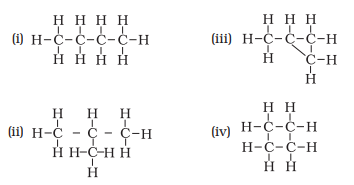
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: c
Explanation:
Chemical formula of Butane isC4H10, here option iii) and iv) have 8 hydrogen atoms, hence they are wrong.
Q.6. CH3 – CH2 – OH Alkaline KMnO Heat 4 + → CH3 – COOH
In the above-given reaction, alkaline KMnO4 acts as
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) dehydrating agent
Ans: b
Explanation:
Two Hydrogen atoms are replaced by an atom of oxygen making oxidation of ethanol. Here addition of oxygen is provided by potassium.
Q.7. Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form fats. This is an example of
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Substitution reaction
(c) Displacement reaction
(d) Oxidation reaction
Ans: a
Explanation:
Here Hydrogen is added to oil, hence it is an addition reaction.
Q.8. In which of the following compounds, — OH is the functional group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanol
(c) Butanoic acid
(d) Butanal
Ans: b
Explanation:
Compound with OH Functional group will have a suffix ol in them hence answer is (b) Butanol.
Q.9. The soap molecule has a
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(b) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(c) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(d) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Ans: a
Explanation:
Because of hydrophobic tail Oil and grease is trapped inside a micelle. Hydrophobic head makes the outer surface of micelle. Hence micelle is easily washed by water.
Q.10. Which of the following is the correct representation of the electron dot structure of nitrogen?
(a) 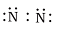
(b) 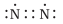
(c) 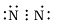
(d) 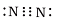
Ans: d
Explanation:
In this structure Nitrogen atoms get 8 electrons whereas in other options it is different.
Q.11. Structural formula of ethyne is
(a) H - C ≡ C - H
(b) H3 - C ≡ C - H
(c) 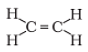
(d) 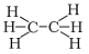
Ans: a
Explanation:
Chemical formula of Ethyne is C2H2, Hence answer is a)
Q.12. Identify the unsaturated compounds from the following
(i) Propane
(ii) Propene
(iii) Propyne
(iv) Chloropropane
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans: d
Explanation:
Propene has double bond and Propyne is having a triple bond. Hence they are unsaturated compounds.
Q.13. Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
Ans: b
Explanation:
In the presence of sunlight, Chlorine reacts with Hydrocarbons and displaces Hydrogen atoms.
Q. 14. In the soap micelles
(a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
(b) ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
(c) both ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster
(d) both ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster
Ans: a
Explanation:
A micelle is a spherical aggregate soap molecules in soap solution. In the soap micelles, the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
Q.15. Pentane has the molecular formula C5 H12. It has
(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Ans: c
Q.16. Structural formula of benzene is
(a)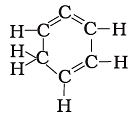
(b)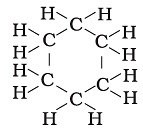
(c)
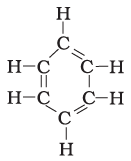
(d)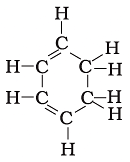
Ans: c
Explanation:
Chemical formula of Benzene is C6H6. In option call the arms of carbon atoms are occupied hence it is the right answer.
Q.17. Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are
(a) sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) sodium ethoxide and oxygen
Ans: c
Explanation:
2Na+2CH3CH2OH →2CH3CH2ONa+H2
Q.18. The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is
(a)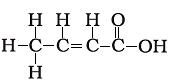
(b)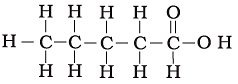
(c)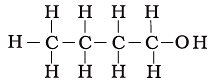
(d)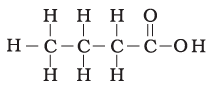
Ans: d
Q.19. Vinegar is a solution of
(a) 50% – 60% acetic acid in alcohol
(b) 5% – 8% acetic acid in alcohol
(c) 5% – 8% acetic acid in water
(d) 50% – 60% acetic acid in water
Ans: c
Q.20. Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
(i) mineral acids are completely ionised
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionised
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionised
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionised
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: a
Explanation:
Mineral acids are completely ionized whereas carboxylic acids are partially ionized. Hence mineral acids are stronger than carboxylic acids.
Q. 21. Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g. hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
(a) helium
(b) neon
(c) argon
(d) krypton
Ans: b
Explanation:
After sharing four valence electrons with univalent atoms. Electronic configuration of Carbon becomes 2.8 which is same as the electronic configuration of Neon.
22. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is electron dot structure of a water molecule
Ans: c
Explanation:
Option c) represents a complete octet configuration. Hence it is the right answer.
23. Which of the following is not a straight-chain hydrocarbon?
(a)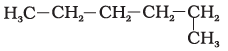
(b)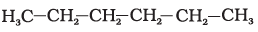
(c)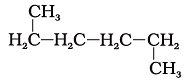
(d)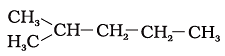
Ans: d
Q. 24. Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons?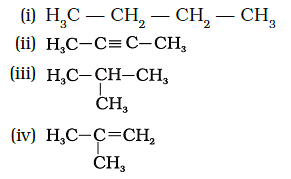
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: c
Explanation:
Option (ii) and (iv )having double and triple bonds, hence they are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Q.25. Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH4
(b) C2 H6
(c) C3 H8
(d) C4 H8
Ans: d
Explanation:
General formula for C4H8 is CnH2n and for other option it is CnH2n+2
Q.26. The name of the compound CH3 — CH2 — CHO is
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
Ans: a
Explanation:
This compound has 3 carbon atoms and an aldehyde which add suffix al to 3 carbon compound.
Q.27. The heteroatoms present in CH3 — CH2 — O — CH2— CH2 Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: d
Explanation:
Oxygen and chlorine are not among essential components of Hydrocarbon hence they are heteroatoms.
Q.28. Which of the following represents the saponification reaction?
(a) CH3COONa + NaOH → CH4 + Na2CO3
(b) CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 +H2O
(c) 2CH3COOH + 2Na → 2CH3 COONa + H2
(d) CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3 COONa + C2H5OH
Ans: d
Explanation:
Saponification is a reaction in which ethanol and sodium ethanoate are produced upon treatment of ester with an alkali.
Q.29. The first member of the alkyne homologous series is
(a) ethyne
(b) ethene
(c) propyne
(d) methane
Ans: b
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.30. Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne and also draw its structural formula.
Ans.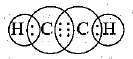
It is the electron dot structure of ethyne (C2H2)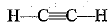 is its structural formula.
is its structural formula.
Q.31. Write the names of the following compounds.
(a)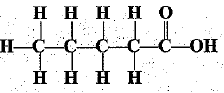
(b)
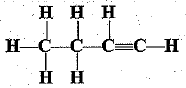
(c)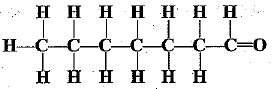
(d)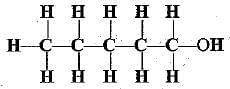
Ans.
(a) Pentanoic acid
(b) But-1-yne
(c) Heptanal
(d) pentan-1-ol
Q.32. Identify and name the functional groups present in the following compounds.
(a)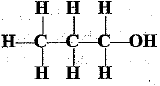
(b)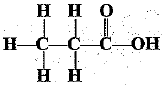
(c)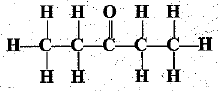
(d)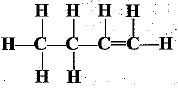
Ans.
| Functional group | Name |
(a)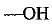 | Alcohol |
(b)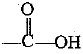 | Carboxylic acid |
(c) 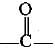 | Ketone |
(d)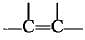 | Alkene |
Q.33. A compound X is formed by the reaction of a carboxylic acid C2H4O2 and an alcohol in presence of a few drops of H2SO4. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid as used in this reaction. Give the names and structures of
(a) Carboxylic acid
(b) Alcohol and
(c) The compound X.
Also write the reaction.
Ans.
(a) Carboxylic acid is ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
(b) Alcohol is ethanol (C2H5OH).
(c) ‘X’ is ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H5)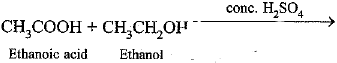
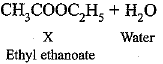

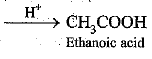
Q.34. Why are detergents better cleansing agents than soaps? Explain.
Ans. It is because detergents form a lot of lather even with hard water. Hard water contains Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions which react with soap to form insoluble salts of calcium and magnesium called scum and soap goes waste. Detergents do not form insoluble compounds with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, therefore these are more effective.
Q.35. Name the functional groups present in the following compounds.
(a) CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
(b) CH3CH2CH2COOH
(c) CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2CHO
(d) CH3CH2OH
Ans.
(a) Ketone
(b) Carboxylic acid
(c) Aldehyde
(d) Alcohol
Q.36. How is ethene prepared from ethanol? Give the reaction involved in it.
Ans. Ethanol is heated at 443k along with excess Sulphuric acid to obtain Ethene.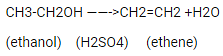
Q.37. Intake of small quantity of methanol can be lethal. Comment.
Ans. Methanol is oxidised to methanal in liver. Methanal is highly reactive and good reducing agent. It causes protoplasm to coagulate. It also affects the optic nerve and leads to blindness.
Q.38. A gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and also write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Ans: When ethanol reacts with sodium it gives Sodium ethoxide with the liberation of hydrogen gas.
2CH3- CH2-OH +2Na——>2 CH3- CH2- ONa + H2
Q.39. Ethene is formed when ethanol at 443K is heated with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid. What is the role of sulphuric acid in this reaction? Write the balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
Ans: Sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst and a dehydrating agent in the formation of ethene.
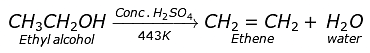
Q.40. Carbon, Group (14) element in the Periodic Table is known to form compounds with many elements. Write an example of a compound formed with:
(a) Chlorine (Group 17 of Periodic Table)
(b) Oxygen (Group 16 of Periodic Table)
Ans.
(a) CCl4 (Carbon tetrachloride)
(b) CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
Q.41. In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
(a) The atomic number of chlorine is 17.
Write its electronic configuration.
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule.
Ans.
(a) Cl(17)
Electronic configuration:
(b) 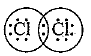
Q.42. Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Ans. Carbon shows catenation to a large extent as compared to silicon as well as any other element due to smaller size of carbon. C—C bond is stronger than Si-Si bond because Si is larger in size, so it forms a weaker bond.
Q.43. Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain multiple bonds between the two C-atoms and show addition reactions. Give the test to distinguish ethane from ethene.
Ans. Add bromine water. Ethane will not react. Ethene will decolourise bromine water.
Alternative Method:
Combustion test:
Ethane, a saturated hydrocarbon, will bum with blue flame which is non-smoky, whereas ethene, an unsaturated hydrocarbon, will bum with yellow flame which is smoky due to the presence of unburnt carbon particles.
Q.44. Match the reactions given in Column (A) with the names given in Column (B).
Ans.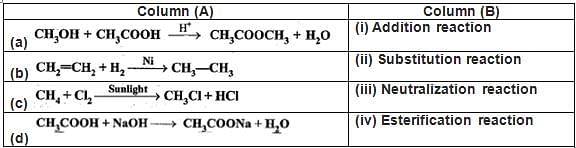
Ans.
(a) - (iv) Esterification reaction because ester is being formed from carboxylic acid and alcohol.
(b) - (i) Addition reaction as hydrogen is being added.
(c) - (ii) Substitution reaction because hydrogen of methane is being substituted by chlorine atom.
(d) - (iii) Neutralisation reaction because acetic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form salt and water.
Q.45. Write the structural formulae of all the isomers of hexane.
Ans.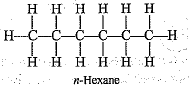
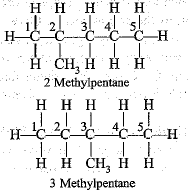
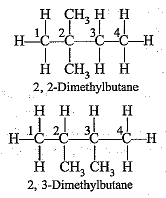
Q.46. What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?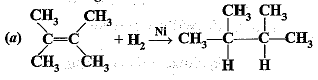
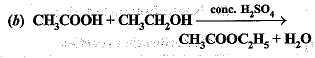
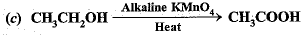
Ans.
(a) Ni is used as a catalyst
(b) Cone. H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent.
(c) Alkaline KMnO4 is an oxidising agent.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.47. A salt ‘X’ is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. Name the salt ‘X’ and the gas evolved.
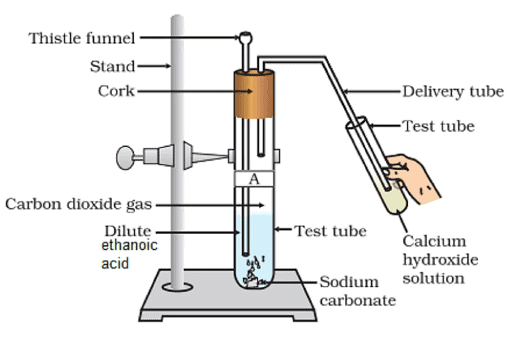
Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Ans.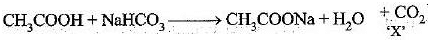
The salt ‘X’ is sodium ethanoate. The gas evolved is CO2.
Pass the gas through lime water. It will turn milky. It shows that gas evolved is CO2.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2→ CaCO3 + H2O
Aim: To demonstrate the reaction of carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Materials Required: Ethanoic acid , sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen-carbonate, lime water.
Procedure:
1. Set the apparatus as shown in diagram.
2. Take 1g of Na2CO3 and add 2 ml of ethanoic acid into it.
3. Pass the gas formed through lime water and note down the observations.
4. Repeat the same procedure with sodium hydrogen-carbonate and record your observations.
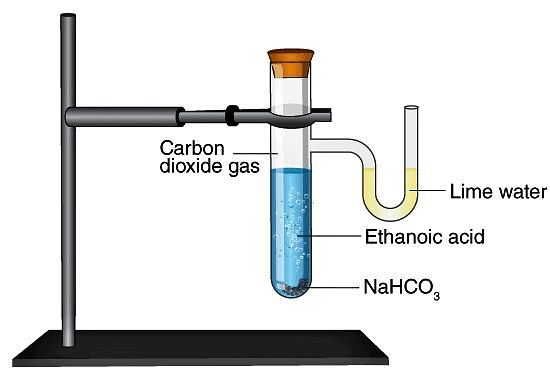
Fig: Evolution of Carbon dioxide Gas by Reaction of Ethanoic Acid with Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
Observation: Brisk effervescence due to carbon dioxide formed which turns lime water milky.
Chemical Reaction:
2CH3COOH(l) + Na2CO3(s) → 2CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
CH3COOH(l) + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)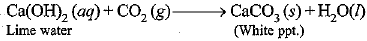
Conclusion: Carboxylic acid reacts with sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate to liberate CO2 gas which turns lime water milky.
Q.48.
(a) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples.
(b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
(c) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Ans.
(a) Hydrocarbons are the compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms only, e.g. CH4 (methane), C2H6 (ethane), CH2= CH2 (ethene), etc.
(b) Saturated hydrocarbons contain single covalent bonds only, 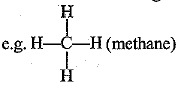 and
and 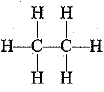 (ethane) are saturated hydrocarbons.
(ethane) are saturated hydrocarbons.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain double or triple covalent bonds, e.g.
(c) Functional group is an atom or group of atoms or reactive part of the compound which determines chemical properties of the those compounds, e.g.
(i) —OH (Alcohol)
CH3CH2OH (Ethanol)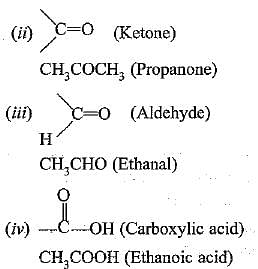
Q.49. Name the reaction which is commonly used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction involved in detail.
Ans:
Addition reaction is involved in the conversion of oils into fats. This process is known as Hydrogenation. Here Unsaturated vegetable are converted to saturated fats which have saturated carbons.
Nickel is used as a catalyst in the hydrogenation process and the reaction is given below
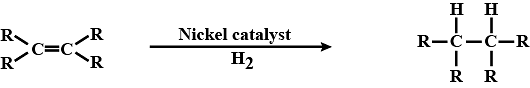
Q.50. (a) Write the formula and draw the electron dot structure of carbon tetrachloride.
(b) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process.
Ans:
(a) Carbon tetrachloride- CCl4
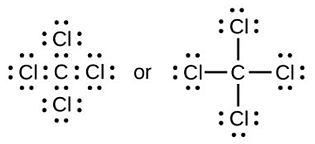
(b) When an ester is heated with sodium hydroxide solution, ester gets hydrolyzed (breaks down) to form the parent alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid.
CH3COOCH3 + NaOH → CH3COONa+CH3OH
Q.51. Esters are sweet smelling substances and are used in making perfumes. Suggest one activity and the reaction involved for the preparation of ester with a well labelled diagram.
Ans.
Aim:
Materials Required : Beaker, water, test tube, ethanol, acetic acid, conc. H2SO4, tripod stand, burner, wire gauze, etc.
Method:
1. Take 2 ml of ethanol in a test tube.
2. Add 2 ml of ethanoic acid (acetic acid) into it.
3. Add few drops of cone. H2SO4.
4. Warm it in a beaker containing water.
5. Observe the smell of the products formed.
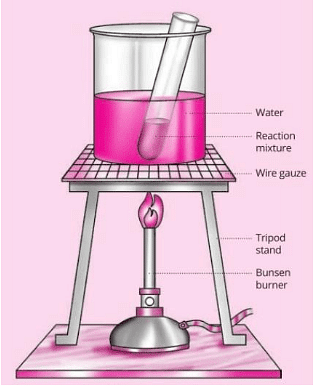
Fig: Reaction of dil. CH3COOH and Ethonal in the presence of conc. H2SO4 - formation of ester
Observations: Pleasant fruity smelling compound (called ester) is formed.
Chemical Reaction Involved:
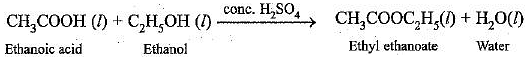
Conclusion: Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in presence of conc. H2SO4, which acts as a dehydrating agent to form esters.
Q.52. A compound ‘C’ (molecular formula, C2H4O2) reacts with Na-metal to form a compound ‘R’ and evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound.
Compound ‘C' on treatment with an alcohol ‘A’ in presence of an acid forms a sweet smelling compound ‘S’ (molecular formula C3H6O2). On addition of NaOH to ‘C’, it also gives R’ and water. ‘S’ on treatment with NaOH solution gives back ‘R’ and 'A'. Identify ‘C’, ‘R' ‘A’, ‘S ’ and write down the reactions involved.
Ans.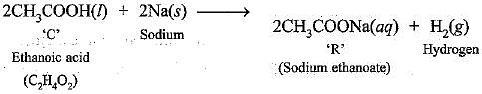
H2 gas burns with ‘pop’ sound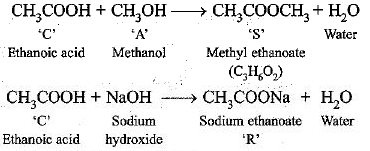

‘C’ is ethanoic acid, ‘R’ is sodium ethanoate, ‘A’ is methanol and ‘S’ is methyl ethanoate.
Q.53. Look at figure and answer the following questions:
(a) What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube ‘B' ?
(b) Write the reaction involved in test tubes ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively.
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?
 Ans.
Ans.
(a) Lime water will turn milky.
(b) Test tube A:
2CH3COOH(l) + Na2CO3(s) → 2CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Test tube B:
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
(c) Ethanol will not react with Na2CO3.
(d) Add Ca(OH)2 in water, shake it well. Filter the solution. The filtrate is lime water.
Q.54. How would you bring about the following conversions? Name the process and write the reaction involved.
(a) Ethanol to ethene
(b) Propanol to propanoic acid
Ans.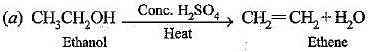
The reaction is called dehydration.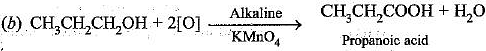
The reaction is called oxidation.
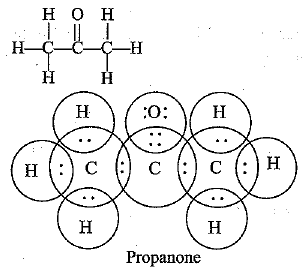
Q.55. Draw the possible isomers of compound with molecular formula C3H6O and also give their electron dot structures. [CBSE Sample Paper 2018]
Ans: C3H6O represents aldehyde as well as ketone.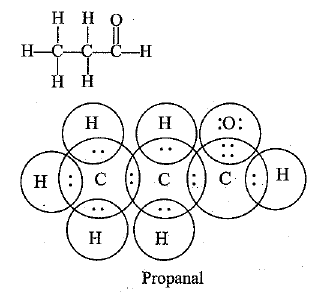
Q.56. Explain the given reactions with the examples
(a) Hydrogenation reaction
(b) Oxidation reaction
(c) Substitution reaction
(d) Saponification reaction
(e) Combustion reaction
Ans.
(a) Hydrogenation reaction: When hydrogen is added to unsaturated hydrocarbons having double or triple bond in presence of Ni as catalyst, the reaction is called hydrogenation, e.g.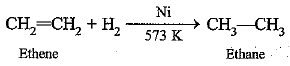
(b) Those reactions in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed are called oxidation reactions, e.g.
(c) Substitution reaction: The reaction in which one or more atoms of compound is replaced by another atom or group of atoms, it is called substitution reaction, e.g.
(d) Saponification reaction: When an ester reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol, it is called saponification, e.g.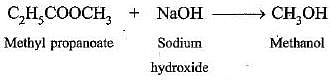
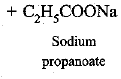
(e) Combustion reaction : When an organic compound burns in presence of air to form CO2 and H2O along with heat and light is called combustion reaction, e.g.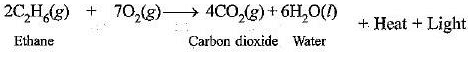
Q.57. An organic compound ‘A’ on heating with conc. H2SO4 forms a compound B, which on addition with 1 mole of hydrogen in presence of Ni forms a compound ‘C' One mole of compound ‘C’ on combustion forms two moles of CO2 and 3 moles of H2O. Identify the compounds A, B and C and write the chemical equation of the reactions involved. [HOTS]
Ans. The compounds are as follows:
A—Ethanol, B—Ethene, C—Ethane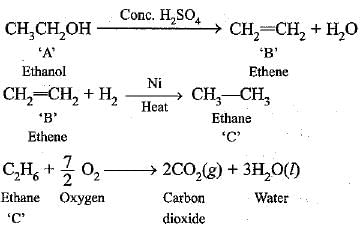
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Carbon & its Compounds - Science Class 10
| 1. What is carbon and its compounds? |  |
| 2. Why is carbon considered unique? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of carbon compounds? |  |
| 4. How are carbon compounds classified? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of carbon compounds in our daily lives? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















