NCERT Exemplar: Heredity | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Exchange of genetic material takes place in
(a) vegetative reproduction
(b) asexual reproduction
(c) sexual reproduction
(d) budding
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Apart from sexual reproduction, other options are a type of asexual reproduction where only single parent is involved. Hence exchange of genetic material takes place in sexual mode of reproduction.
Q.2. Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be
(a) double fertilisation
(b) self-pollination
(c) cross-fertilisation
(d) no fertilization
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
The progeny ratio 1 red : 2 pink : 1 white suggests incomplete dominance, where neither allele is completely dominant. This ratio comes from a cross between two heterozygous (pink) plants (Rr × Rr), which happens through cross-fertilisation — the fusion of male and female gametes from different flowers.
Q.5. If a round, green seeded pea plant (RR yy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rr YY) the seeds produced in the F1 generation are
(a) round and yellow
(b) round and green
(c) wrinkled and green
(d) wrinkled and yellow
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Round and yellow are the dominant characters hence in f1 generation all seeds will be round and yellow.
Q.6. In human males, all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. This/these unpaired chromosome is/are
(i) large chromosome
(ii) small chromosome
(iii) Y-chromosome
(iv) X-chromosome
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Explanation: These are sex-determining chromosomes that are not paired perfectly due to half size of the Y chromosome.
Q.9. Select the incorrect statement
(a) Frequency of certain genes in a population change over several generations resulting in evolution
(b) Reduction in weight of the organism due to starvation is genetically controlled
(c) Low weight parents can have heavyweight progeny
(d) Traits which are not inherited over generations do not cause evolution
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Option b) is a wrong statement because weight loss and gain are controlled by external factors and they are not controlled genetically.
Q.10. New species may be formed if
(i) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells
(ii) chromosome number changes in the gamete
(iii) there is no change in the genetic material
(iv) mating does not take place
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Evolution will not take place without change and variation the genetic material. Hence change in genetic material and variation in chromosome is required for the evolution of new species.
Q.11. Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have a new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following
(i) Round, yellow
(ii) Round, green
(iii) Wrinkled, yellow
(iv) Wrinkled, green
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Q.14. If the fossil of an organism is found in the deeper layers of earth, then we can predict that
(a) the extinction of organism has occurred recently
(b) the extinction of organism has occurred thousands of years ago
(c) the fossil position in the layers of earth is not related to its time of extinction
(d) time of extinction cannot be determined
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Older fossils are found deep in the earth. Hence option b) is the right answer.
Q.15. Which of the following statements is not true with respect to variation?
(a) All variations in a species have an equal chance of survival
(b) Change in genetic composition results in variation
(c) Selection of variants by environmental factors forms the basis of evolutionary processes.
(d) Variation is minimum in asexual reproduction
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Statement a) is wrongs because only useful variation have a chance of survival. Nature choose the fittest variation to survive.
Q.16. A trait in an organism is influenced by
(a) paternal DNA only
(b) maternal DNA only
(c) both maternal and paternal DNA
(d) neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA
Ans: (c)
Explanation: DNA is contributed to an offspring by both the parents hence traits are contributed by both the parents.
Q.17. Select the group which shares the maximum number of common characters
(a) two individuals of a species
(b) two species of a genus
(c) two genera of a family
(d) two genera of two families
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Species is the lowest taxon hence members of same species share a maximum number of common characteristics.
Q.20. The two versions of a trait (character) which are brought in by the male and female gametes are situated on
(a) copies of the same chromosome
(b) two different chromosomes
(c) sex chromosomes
(d) any chromosome
Ans: (b)
Explanation: This is the reason behind the expression of one progeny in one version and other versions in another progeny.
Q.21. Select the statements that describe characteristics of genes
(i) genes are a specific sequence of bases in a DNA molecule
(ii) a gene does not code for proteins
(iii) in individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome
(iv) each chromosome has only one gene
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Statement ii) is wrong because genes code for specific proteins. Statement 4 is wrong because chromosomes have any number of genes.
Q.22. In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2 is
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3: 1
(c) 1: 1
(d) 2: 1
Ans: (b)
Explanation: A cross between pure tall plant (TT) and short plant (tt) would produce progenies with following genotypes. TT(Pure tall), tt( Pure short) andTt ( Mixed tall). This makes the ratio between tall and short plants is 3:1.
Q.23. The number of pair (s) of sex chromosomes in the zygote of humans is
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Ans: (a)
Explanation: 23rd pair of chromosome determines the sex of the offspring hence it is called a sex chromosome.
Short Answer Questions
Q.26. How is the sex of a newborn determined in humans?
Solution: Sex of the individual is determined the genes inherited from the parents. If a newborn acquires X chromosomes from father-child will be a female and if newborn receives Y chromosome from father it will be a male.
Q.27. Do genetic combination of mothers play a significant role in determining the sex of a newborn?
Solution: No Sex of a newborn will be determined by the chromosome donated by the father. Mothers have XX in their 23rd chromosome pair and they always donate One X. But fathers have X And Y in their 23rd chromosome pair. If father donates X child will be a girl and if father donates Y child will be a boy.
Q.28. Mention three important features of fossils which help in the study of evolution.
Solution:
- Fossils are the preserved ancient species
- Fossils help determine evolutionary differences between organisms and their ancestors.
- Fossils determine the living period of specific species.

Q.29. Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome
Solution: Females possess XX in their 23 pair of chromosome. During meiosis one X chromosome enters each gamete hence all females gametes possess X chromosome.
Q.30. In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 : 50. Give a suitable explanation.
Solution: Sex of the offspring is determined by the gamete donated by male. Male possess X and Y chromosomes in their 23rd pair. The ration between X and Y is 1:! Hence the probability of getting either a male or female child is 50: 50.
Q.31. A very small population of a species faces a greater threat of extinction than a larger population. Provide a suitable genetic explanation.
Solution: A very small population of a species faces a greater threat of extinction than a larger population because of the following reasons
Inbreeding: Small population promotes inbreeding. Inbreed results in lesser variations.
Genetic drift: Small population is vulnerable to a sudden changes in the environment. Because of genetic drift chances of species with a small populations may wipe out.
Inbreeding depression: This lead to negative population growth which is detrimental to the survival of the species with a smaller population.
Q.32. What are homologous structures? Give an example. Is it necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor?
Solution: Homologous structures are those which has a common basic structure and performs different functions. e.g. forelimbs of reptiles, amphibians and mammals. If they don’t have common ancestry they are called as analogous structure.
Q.33. Does the occurrence of the diversity of animals on earth suggest their diverse ancestry also? Discuss this point in the light of evolution.
Solution: In spite of the fact that animals have a different variety of structures, they do not have a common ancestry. This is because common ancestry may greatly limit the extent of diversity. Many of the animals are inhabiting the same habitat, their evolution by geographical isolation and speciation is also not likely. Hence common ancestry for all the animals is not the likely theory.
Q.34. Give the pair of contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and recessive
(i) yellow seed (ii) round seed
Solution: (i) Yellow- dominant, Green- Recessive
(ii) Round-dominant, Wrinkled-Recessive
Q.35. Why did Mendel choose pea plant for his experiments?
Solution:
Mendel chosen pea plant for his experiments for the following reasons:
- Pea plants are easy to grow
- They have a short life span
- They got larger size flower
- Pea plants are self-pollinated
Q.36. A woman has only daughters. Analyse the situation genetically and provide a suitable explanation.
Solution: A woman has only daughter; it means egg always received X chromosome from the sperm. If sperm donates X chromosomes the resultant child will be female and if Sperm donates y chromosome baby will be a male.
Long Answer Questions
Q.37. Does geographical isolation of individuals of a species lead to the formation of a new species? Provide a suitable explanation.
Solution: Geographical isolation of individual of a species leads to genetic drift. This limits the sexual reproduction of the separated population. This results in separated individuals reproducing among themselves. This leads to the formation of a new variation. Accumulation and transfer of these variations through generation will lead to the formation of new species.
Q.38. Bacteria have a simpler body plan when compared with human beings. Does it mean that human beings are more evolved than bacteria? Provide a suitable explanation.
Solution: This is an issue of debate. It depends on the way we evaluate evolution. If the complexity of the body is a parameter then Human are far superior than bacteria. Bacteria has a cellular level of organization and humans have an organ level organization. On the other hand, if we consider the ability of survival bacteria have evolved more than human beings. Humans can live in any environment but with artificial protection. Humans cannot live in a harsher climate whereas bacteria can be found anywhere on earth. They can survive even harsh climates such as Hydrothermal vents, sulphur springs.
Q.39. All the human races like Africans, Asians, Europeans, Americans and others might have evolved from a common ancestor. Provide a few evidences in support of this view.
Solution: All humans races appear to be different but they have evolved from common ancestry. Following are the evidence to support this view.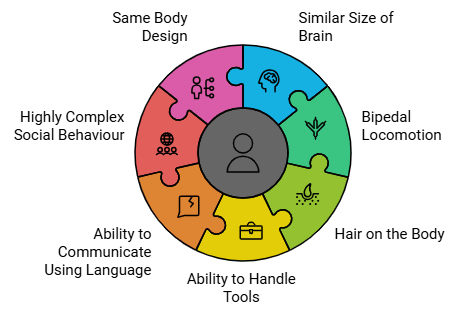
Q.40. Differentiate between inherited and acquired characters. Give one example for each type.
Solution:
Inherited Characters | Acquired Characters |
Characters that are passed on from parents to offspring | Characters appearing in an individual’s lifetime but cannot be transmitted to next generation |
Alters Genotype and Phenotype | Alters Phenotype only |
Transmitted to further generation | Cannot be transmitted to further generation |
Results in genetic recombination | Results in response to environmental changes |
Ex: colour of seeds, colour of eyes. | Ex: obese body, loss of a finger in an accident. |
Q.41. Give reasons why acquired characters are not inherited.
Solution: Acquired characters are the results of our body’s response to external stimuli such as food, disease, climate change. This results in the development of a particular trait where a change of phenotype is observed. But for characters to get inherited to generation Genotype of an organism should be changed. In acquired characters, there is no change in the DNA of germ cells. Hence acquired characters cannot be inherited.
Q.42. Evolution has exhibited a greater stability of molecular structure when compared with morphological structures. Comment on the statement and justify your opinion.
Solution: Structure which are apparent to our eyes are called morphological structures. Molecular structures are those biomolecules which are the integral components of organisms. We see a lot of diversity all around us. This diversity is possible because of diversity in morphological structures. This shows that morphological structures are the least stable. Life which began as simple forms on the earth is now composed of many complex forms. Life has evolved for millions of years but the structure of basic biomolecules such as DNA remains the same. A DNA is the same in a human and in a mouse. A protein has the same structure in a bird and in a fungi. So, the molecular basis of life has not changed through all these years. This proves that evolution has exhibited a greater stability of molecular structure when compared with morphological structure.
Q.43. In the following crosses write the characteristics of the progeny
Cross | Progeny |
| |
| |
| |
|
Solution:
Cross | Progeny |
| Round, yellow |
| Round, yellow Round, green Wrinkled, yellow Wrinkled, green |
| Wrinkled, green |
| Round, yellow |
Q.44. Study the following cross and showing self- pollination in F1, fill in the blank and answer the question that follows
Parents RRYY x rryy
Round, yellow wrinkled green
F1 — Rr Yy x ?
Round, yellow
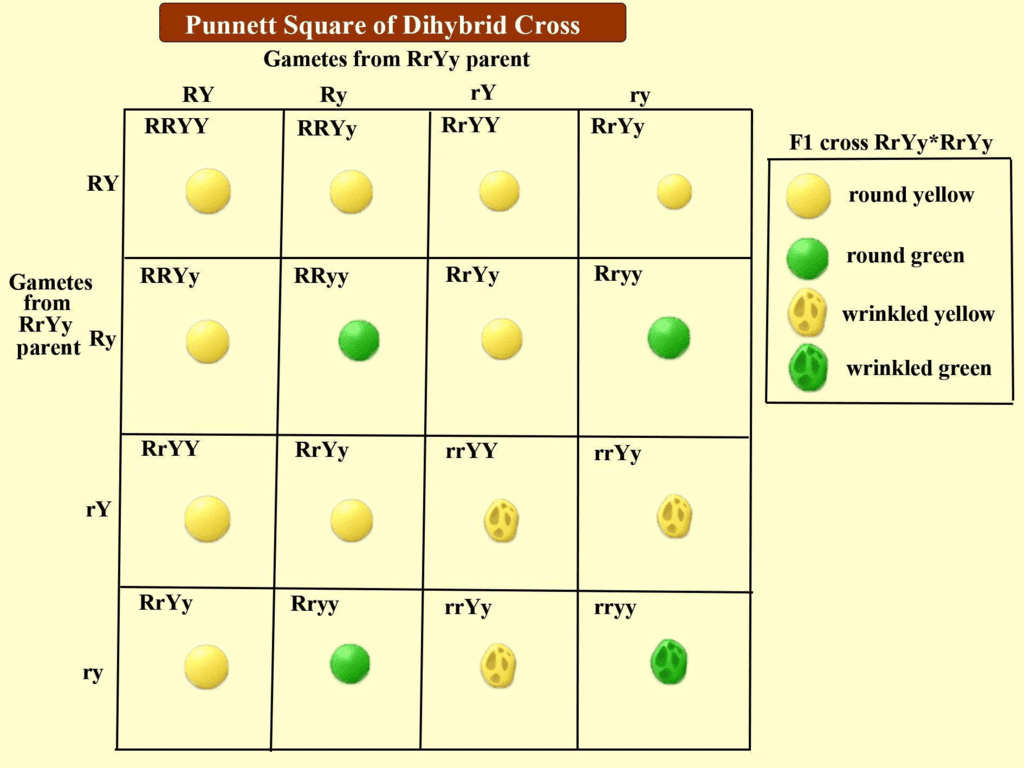
Solution: RrYy- Round yellow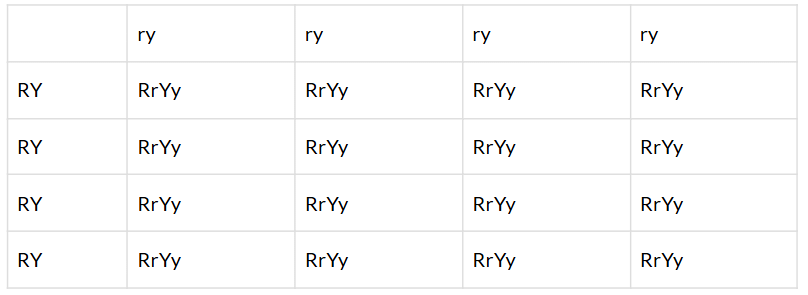 Q.45. In question 44, what are the combinations of character in the F2 progeny? What are their ratios?
Q.45. In question 44, what are the combinations of character in the F2 progeny? What are their ratios?
Solution: 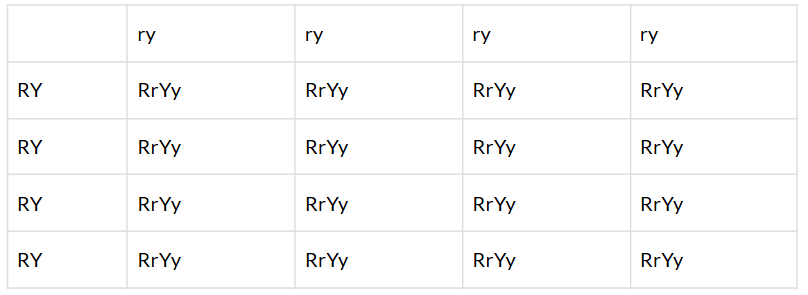 (i) Round yellow — 9(ii) Round green — 3
(i) Round yellow — 9(ii) Round green — 3
(iii) Wrinkled yellow — 3
(iv) Wrinkled green — 1
9 : 3 : 3: 1
Q.46. Give the basic features of the mechanism of inheritance.
Solution: Basic features of the mechanism of inheritance are as follows
- Genes control the characters
- Genes are present in two or more forms
- One form of a gene may be dominant over other
- Genes are present on chromosomes
- Individual genes exist in two forms may be similar or dissimilar
- Two forms of the gene separate at the time of gamete formation
- Two forms of genes are brought together in the zygote
Q.47. Give reasons for the appearance of new combinations of characters in the F2 progeny.
F1 plants have round and yellow seeds. Cross between generations can give rise to new combinations in F2 generation with round-yellow, round green, wrinkled yellow and wrinkled green in the ratio of 9 : 3 : 3: 1.
This shows that the chances for the pea seed to be round or wrinkled do not depend on their chances to be yellow or green. Hence each pair of alleles is independent of the other pair. This is called an independent assortment.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Heredity - Science Class 10
| 1. What is heredity and why is it important in biology? |  |
| 2. How do dominant and recessive traits work in heredity? |  |
| 3. What are the key differences between genotype and phenotype? |  |
| 4. Can environmental factors influence heredity? |  |
| 5. What role do mutations play in heredity? |  |