NCERT Exemplar: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field
(a) The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points
(b) Magnetic field lines are closed curves
(c) If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength
(d) Relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines
Correct Answer is Option (c)
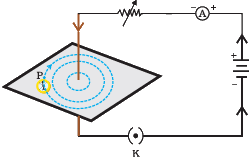
Q.2. If the key in the arrangement (Figure 13.1) is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are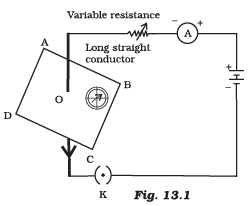 (a) concentric circles
(a) concentric circles
(b) elliptical in shape
(c) straight lines parallel to each other
(d) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.3. A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the key is ON. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anti clockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to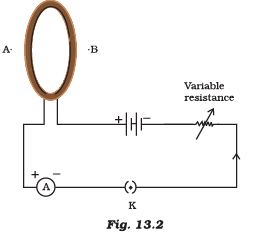 (a) A
(a) A
(b) B
(c) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small and A if the current is large
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.4. For a current in a long straight solenoid N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
(a) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
(b) The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the coil
(c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
(d) The N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.5. A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper pointing from left to right as shown in Figure 13.3. In the field an electron and a proton move as shown. The electron and the proton experience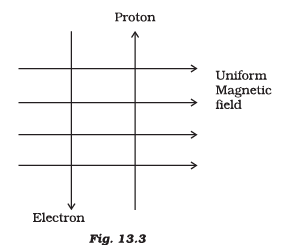 (a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
(a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
(b) forces both pointing out of the plane of paper
(c) forces pointing into the plane of paper and out of the plane of paper, respectively
(d) force pointing opposite and along the direction of the uniform magnetic field respectively
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.6. Commercial electric motors do not use
(a) an electromagnet to rotate the armature
(b) effectively large number of turns of conducting wire in the current carrying coil
(c) a permanent magnet to rotate the armature
(d) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound
Correct Answer is Option (c)
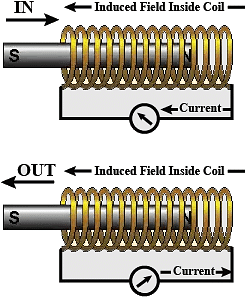
Q.7. In the arrangement shown in Figure 13.4 there are two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed. Then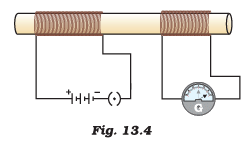 (a) the deflection in the galvanometer remains zero throughout
(a) the deflection in the galvanometer remains zero throughout
(b) there is a momentary deflection in the galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is no effect when the key is removed
(c) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in the same direction
(d) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in opposite directions
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.8. Choose the incorrect statement
(a) Fleming’s right-hand rule is a simple rule to know the direction of induced current
(b) The right-hand thumb rule is used to find the direction of magnetic fields due to current carrying conductors
(c) The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the direct current always flows in one direction, whereas the alternating current reverses its direction periodically
(d) In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/50 second
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.9. A constant current flows in a horizontal wire in the plane of the paper from east to west as shown in Figure 13.5. The direction of magnetic field at a point will be North to South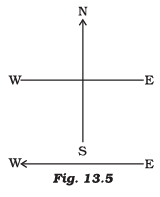 (a) directly above the wire
(a) directly above the wire
(b) directly below the wire
(c) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the north side of the wire
(d) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the south side of the wire
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.10. The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is
(a) more at the ends than at the centre
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) same at all points
(d) found to increase from one end to the other
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.11. To convert an AC generator into DC generator
(a) split-ring type commutator must be used
(b) slip rings and brushes must be used
(c) a stronger magnetic field has to be used
(d) a rectangular wire loop has to be used
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.12. The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is
(a) earthing
(b) use of fuse
(c) use of stabilizers
(d) use of electric meter
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.13. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane of paper near point A as shown in Figure 13.6. In which plane should a straight current carrying conductor be placed so that it passes through A and there is no change in the deflection of the compass? Under what condition is the deflection maximum and why?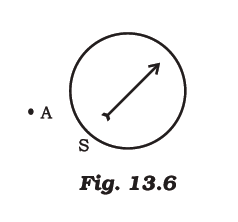
In the plane of the paper itself. The axis of the compass is vertical and the field due to the conductor is also vertical. It could result in a dip of compass needle which is not possible in this case (dips result only if axis of compass is horizontal). The deflection is maximum when the conductor through A is perpendicular to the plane of paper and the field due to it is maximum in the plane of the paper.
Q.14. Under what conditions permanent electromagnet is obtained if a current carrying solenoid is used? Support your answer with the help of a labelled circuit diagram.
A solenoid is a simple electromagnetic device consisting of a coiled electric wire, wrapped in a 3D circular pattern. When electric current is passed through the wire, the solenoid acts like a magnet with N and S poles at the ends of the coil.
When a ferromagnetic material rod is permanently placed inside the solenoid, the metal greatly increases the magnetic effect and becomes a permanent electromagnet. Moreover, it can also be used as an electrical switch by drawing in or pushing out a ferromagnetic material like an iron rod. Depending on the directions of the rod and the electrical current the switching action takes place.
Given figure represents the solenoid as electromagnet and the switching action.
Q.15. AB is a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown in Figure 13.7. What are the directions of magnetic fields produced by it at points P and Q? Given r1 > r2, where will the strength of the magnetic field be larger?
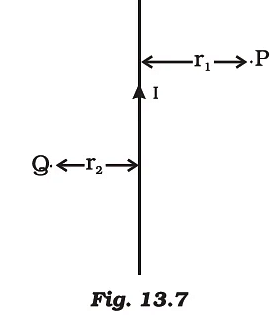
Apply right-hand thumb rule, the direction of magnetic field produced by a current carrying conductor at Point
P - into the plane of paper Point
Q - out of the plane of paper.
As magnetic field is inversely proportional to distance, the field at Q will be larger than the field at P (r1 > r2).
Q.16. A magnetic compass shows a deflection when placed near a current carrying wire. How will the deflection of the compass get affected if the current in the wire is increased? Support your answer with a reason.
The deflection increases. The strength of magnetic field is directly proportional to the magnitude of current passing through the straight conductor.
Q.17. It is established that an electric current through a metallic conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Is there a similar magnetic field produced around a thin beam of moving (i) alpha particles, (ii) neutrons?
Justify your answer.
Since an electric current through a metallic conductor produces a magnetic field around it, the requirement is to check if the given beam gives rise to an electric current.
(i) Alpha particles are positively charged. Thus, they would give rise to an electric current opposite to the direction of the movement of the particles and this would produce a magnetic field.
(ii) Neutrons lack any type of charge and hence, would not give rise to any electric current thus resulting in no magnetic field.
Q.18. What does the direction of thumb indicate in the right-hand thumb rule. In what way this rule is different from Fleming’s left-hand rule?
The thumb indicates the direction of current in the straight conductor held by curled fingers, whereas the Fleming’s left-hand rule gives the direction of force experienced by current carrying conductor placed in an external magnetic field.
Q.19. Meena draws magnetic field lines of field close to the axis of a current carrying circular loop. As she moves away from the centre of the circular loop, she observes that the lines keep on diverging. How will you explain her observation?
Strength of the magnetic field falls as distance increases. This is indicated by the decrease in degree of closeness of the lines of field.
Q.20. What does the divergence of magnetic field lines near the ends of a current carrying straight solenoid indicate?
The divergence, that is, the falling degree of closeness of magnetic field lines indicates the fall in strength of magnetic field near and beyond the ends of the solenoid.
Q.21. Name four appliances wherein an electric motor, a rotating device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, is used as an important component. In what respect motors are different from generators?
Electric fans, mixers, washing machines, computer drives, etc.
Motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy whereas generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Q.22. What is the role of the two conducting stationary brushes in a simple electric motor?
The brushes are connected to the battery and touch the outer side of two halves of the split ring whose inner sides are insulated and attached to the axle.
Q.23. What is the difference between a direct current and an alternating current? How many times does AC used in India change direction in one second?
Direct current always flows in one direction but the alternating current reverses its direction periodically. The frequency of AC in India is 50 Hz and in each cycle it alters direction twice. Therefore AC changes direction 2 × 50 = 100 times in one second.
Q.24. What is the role of fuse, used in series with any electrical appliance? Why should a fuse with defined rating not be replaced by one with a larger rating?
Fuse is used for protecting appliances due to short-circuiting or overloading. The fuse is rated for a certain maximum current and blows off when a current more than the rated value flows through it. If a fuse is replaced by one with larger ratings, the appliances may get damaged while the protecting fuse does not burn off. This practice of using fuse of improper rating should always be avoided.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.25. Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing North and South in the absence of a nearby magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept.
When electric current passes through the conductor it behaves like a bar magnet and an induced EMF is created which generates magnetic lines of force around it. Thus, when a magnetic compass that is pointing in the north-south direction according to the earth's magnetic field, shows deflection with respect to the strength of the magnetic field that is superposition of magnetic field created by the current carrying conductor and of earth. Features of magnetic lines of force, The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude.
Magnetic lines of force start from the North Pole and end at the South Pole. Two magnetic lines of force cannot intersect each other and they are continuous along the axis of the electromagnetic conductor. The magnetic lines of force are uniform and strong at the center or inside of the conductor and they diverge as they move away from the conductor and as the distance increases. Eventually, the strength of the magnetic field is strong inside and they weaken as they closeness decreases.
Q.26. With the help of a labelled circuit diagram illustrate the pattern of field lines of the magnetic field around a current carrying straight long conducting wire. How is the right hand thumb rule useful to find direction of magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor?
Right hand thumb rule states that if a current carrying straight conductor is supposedly held in the right hand with the thumb pointing towards the direction of current, then the fingers will wrap around the conductor in the direction of the field lines of the magnetic field.
Q.27. Explain with the help of a labelled diagram the distribution of magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop. Why is it that if a current carrying coil has n turns the field produced at any point is n times as large as that produced by a single turn?
The magnetic field pattern due to a circular coil is as shown in the given figure.
At every point of current carrying circular loop, the concentric circles representing the magnetic field around it becomes larger and larger as we move away from the wire. At the center of the loop, the field appears as a straight line.
The magnetic field produced by current-carrying circular wire at a given point depends on:
(1) Amount of current flowing through the wire, I
B ∝ I ..........(1)
(2) The number of turns, N
B ∝ N ..........(2)
There is a circular coil having N turns, the field produced is n times as a large as that produced by a single turn. It happens because the current in each circular turns has the same direction and the field due to each turn just adds up.
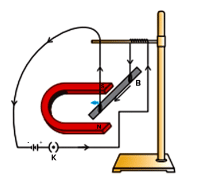
Q.28. Describe the activity that shows that a current-carrying conductor experiences a force perpendicular to its length and the external magnetic field. How does Fleming’s left-hand rule help us to find the direction of the force acting on the current carrying conductor?
Activity for a current-carrying conductor:
- Take a little aluminium rod and write AB on it of about 5 centimeter.
- Suspend it horizontally from a stand using two connecting cables.
- Place a powerful horseshoe magnet between the two poles with the magnetic field pointing upwards.
- Place the north pole of the magnet vertically below the aluminium rod and the south pole vertically above it for this.
- Connect the aluminium rod to a battery, a key, and a rheostat in series.
- Now, from end B to end A, run a current through the aluminium rod.
- It is observed that the rod is displaced towards the left.
- Reverse the direction of the stream flowing through the rod to see which way it is displaced. It's moving right now.
Fleming Left-hand rule:
- When an electric current flows through a straight wire and an external magnetic field is put across it, the wire experiences a force that is perpendicular to both the field and the direction of the current flow, according to Fleming's left-hand rule.
- The direction of the force, magnetic field, and current may all be determined using this rule.
- The thumb, first finger, and second finger of the left hand can all be held perpendicular to each other. The direction of motion arising from the force on the conductor is represented by the thumb. The first finger represents the magnetic field's direction. The current's direction is represented by the second finger.
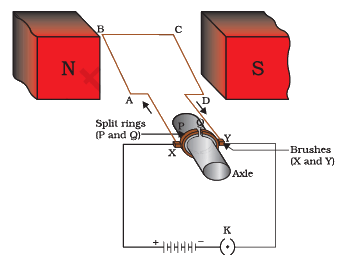
Q.29. Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a simple electric motor and explain its working. In what way these simple electric motors are diffferent from commercial motors?
Principle of a simple electric motor is when a rectangular coil carrying current is placed in a magnetic field, a torque acts on the coil which rotates it continuously. When the coil rotates, the shaft attached to it also rotates and thus it is able to do mechanical work. The main parts of electric motor are the magnets, armature, split ring commutators and brushes. The armature consists of a rectangular coil made of insulated copper wire wound on a soft iron core. The coil is mounted on an axle and is placed between the cylindrical concave poles of a magnet. The commutator is used to reverse the direction of flow of current. It is a copper ring split into two parts P and Q. The split rings are insulated from each other and mounted on the axle of the motor. The two ends of the coil are soldered to these rings. They rotate along with the coil. Commutator rings are connected to a battery. The wires from the battery are not connected to the rings but to the brushes which are in contact with the rings. The brushes are two small strips of carbon, which press slightly against the two split rings, and the split rings rotate between the brushes. The carbon brushes are connected to a D.C. source.
Working of the Electric motor:
When the coil is powered, a magnetic field is generated around the armature. The left side of the armature is pushed away from the left magnet and drawn towards the right, causing rotation. When the coil turns through 90 degrees, the brushes lose contact with the commutator and the current stops flowing through the coil. However, the coil keeps turning because of its own momentum. Now when the coil turns through 180 degrees, the sides get interchanged. As a result the commutator ring P is now in contact with brush Y and commutator ring Q is in contact with brush X. Therefore, the current continues to flow in the same direction.
Difference between simple electric motors and commercial electric motors:
In commercial electric motors, field coils are used for producing magnetic fields and not a permanent magnet as in simple electric motors. These coils become magnetized when current is passed through them. Field coils give a stronger, more easily shaped magnetic field than permanent magnets. More the number of turns in the field coil, more the magnetic field. Therefore, the suitable field coil sizes are used for various commercial purposes.
Q.30. Explain the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Describe an experiment to show that a current is set up in a closed loop when an external magnetic field passing through the loop increases or decreases.
Definition:
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force across a conductor when it is exposed to a varying magnetic field.
Experiment:
Two different coils of copper wire having large number of turns (say 50 and 100 turns respectively) are taken. They are now inserted over a non-conducting cylindrical roll, as shown in figure below.The coil-1, having larger number of turns, is connected in series with a battery and a plug key. Also, the other coil-2 is connected with a galvanometer as shown.The key is initiated and the galvanometer is observed. We will observe that the needle of the galvanometer instantly jumps to one side and then quickly returns to zero, indicating a momentary current in coil-2.
The coil-1 is now disconnected from the battery. Now we will observe that the needle momentarily moves, but to the opposite side. It means that now the current flows in the opposite direction in coil-2.
Observations:
From these observations, we conclude that a potential difference is induced in the coil-2 whenever the electric current through the coil1 is changing (starting or stopping). As the current in the first coil changes, the magnetic field associated with it also changes. Thus the magnetic field lines around the secondary coil also change. Hence the change in magnetic field lines associated with the secondary coil is the cause of induced electric current in it. This process, by which a changing magnetic field in a conductor induces a current in another conductor, is called electromagnetic induction.
In practice we can induce current in a coil either by moving it in a magnetic field or by changing the magnetic field around it. It is convenient in most situations to move the coil in a magnetic field.
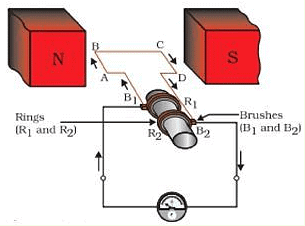
Q.31. Describe the working of an AC generator with the help of a labelled circuit diagram. What changes must be made in the arrangement to convert it to a DC generator?
Working of an AC generator:
- The coil ABCD is rotated clockwise in the arrangement shown in the figure. By applying Fleming’s right-hand rule, the induced currents are set up in these arms along the directions AB and CD. Thus an induced current flows in the direction ABCD.
- If there are larger numbers of turns in the coil, the current generated in each turn adds up to give a large current through the coil. This means that the current in the external circuit flows from B2 to B1.
- After half a rotation, arm CD starts moving up and AB moving down. As a result, the directions of the induced currents in both the arms change, giving rise to the net induced current in the direction DCBA.
- The current in the external circuit now flows from B1 to B2. Thus after every half rotation the polarity of the current in the respective arms changes.
To get a direct current (DC, which does not change its direction with time), a split-ring type commutator must be used. With this arrangement, one brush is at all times in contact with the arm moving up in the field, while the other is in contact with the arm moving down.
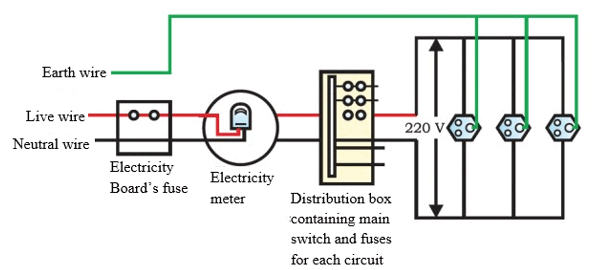
Q.32. Draw an appropriate schematic diagram showing common domestic circuits and discuss the importance of fuse. Why is it that a burnt out fuse should be replaced by another fuse of identical rating?
- A schematic diagram for common domestic circuit:
- Importance of fuse: It is the most important safety device, used for protecting the circuit from short circuiting or overloading.
- Burnt fuse in the live wire acts as an open circuit. So, to maintain the flow of current in the circuit and to prevent the circuit from damage due to some fault, a burnt out fuse should be replaced by another fuse of identical rating.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the magnetic effects of electric current? |  |
| 2. How is an electromagnet different from a permanent magnet? |  |
| 3. What is the right-hand thumb rule? |  |
| 4. How does an electric motor work? |  |
| 5. What is electromagnetic induction? |  |