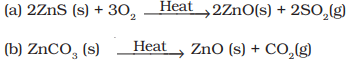NCERT Exemplar: Metals & Non-metals | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which of the following property is generally not shown by metals?
(a) Electrical conduction
(b) Sonorous in nature
(c) Dullness
(d) Ductility
Ans. (c)
Q2. The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wire is known as
(a) ductility
(b) malleability
(c) sonorousity
(d) conductivity
Ans. (a)
- Ductility is the property of metals to be drawn into thin wire.
- Malleability is the property of metals to be drawn into a thin wire
- Sonorousity is the ability of a metal to be sonorous in nature, which means it is capable of making a deep, ringing sound.
- Conductivity is the ability to conduct electricity
Q3. Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
(i) Good thermal conductivity
(ii) Good electrical conductivity
(iii) Ductility
(iv) High melting point
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans. (d)
Ductility and electric conductivity have no relation to cooking hence thermal conductivity, and high melting point are the right answers.
Q4. Which one of the following metals do not react with cold as well as hot water?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Mg
(d) Fe
Ans. (d)
Sodium and Calcium react vigorously with water and Magnesium reacts with hot water to form Magnesium Oxide. Iron does not react with cold and hot water, but it reacts with steam.
Q5. Which of the following oxide(s) of iron would be obtained on prolonged reaction of iron with steam?
(a) FeO
(b) Fe2O3
(c) Fe3O4
(d) Fe2O3 and Fe3O4
Ans. (c)
3Fe+4H2O →Fe3O4+4H2
Q6. What happens when calcium is treated with water?
(i) It does not react with water
(ii) It reacts violently with water
(iii) It reacts less violently with water
(iv) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (d)
Calcium reacts vigorously with water and forms hydrogen, which will make calcium to float.
Q7. Generally metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen gas.
Which of the following acids does not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg)?
(a) H2SO4
(b) HCl
(c) HNO3
(d) All of these
Ans. (c)
Nitric acid is a powerful oxidizing agent. It reacts with the metal to form water.
Q8. The composition of aqua-regia is
(a) Dil.HCl : Conc. HNO3 = 3 : 1
(b) Conc.HCl : Dil. HNO3 = 3 : 1
(c) Conc.HCl : Conc.HNO3 = 3 : 1
(d) Dil.HCl : Dil.HNO3 = 3 : 1
Ans. (c)
Q9. Which of the following are not ionic compounds?
(i) KCl
(ii) HCl
(iii) CCl4
(iv) NaCl
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans. (b)
HCl and CCl4 are covalent compounds; hence they cannot be ionic.
Q10. Which one of the following properties is not generally exhibited by ionic compounds?
(a) Solubility in water
(b) Electrical conductivity in solid state
(c) High melting and boiling points
(d) Electrical conductivity in molten state
Ans. (b)
In an ionic compound, free ions are not available in a solid-state; hence solid ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity.
Q11. Which of the following metals exist in their native state in nature?
(i) Cu
(ii) Au
(iii) Zn
(iv) Ag
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (c)
Gold and silver are non-reactive metals because of they are non-reactive they exist in their native state in nature.
Q12. Metals are refined by using different methods. Which of the following metals are refined by electrolytic refining?
(i) Au
(ii) Cu
(iii) Na
(iv) K
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (a)
Sodium and potassium are at the top in the reactivity series hence they can be refined by electrolytic refining.
Q13. Silver articles become black on prolonged exposure to air. This is due to the formation of
(a) Ag3N
(b) Ag2O
(c) Ag2S
(d) Ag2S and Ag3N
Ans. (c)
Silver metal reacts with sulphur present in the atmosphere to form Ag2S. Ag2S is responsible for black colouration of silver articles.
Q14. Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating with a thin layer of
(a) Gallium
(b) Aluminium
(c) Zinc
(d) Silver
Ans. (c)
Galvanization is a process of applying a layer of Zinc on iron by using electrolysis.
Q15. Stainless steel is very useful material for our life. In stainless steel, iron is mixed with
(a) Ni and Cr
(b) Cu and Cr
(c) Ni and Cu
(d) Cu and A
Ans. (a)
Stainless steel is an alloy of Iron, Nicker and chromium. This alloy makes the metal strong, durable and corrosion-resistant.
Q16. If copper is kept open in air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of
(a) CuSO4
(b) CuCO3
(c) Cu(NO3)2
(d) CuO
Ans. (b)
On exposure to air, copper reacts to atmospheric oxygen to form copper oxide layer which is green in colour.
Q17. Generally, metals are solid in nature. Which one of the following metals is found in liquid state at room temperature?
(a) Na
(b) Fe
(c) Cr
(d) Hg
Ans. (d)
Q18. Which of the following metals are obtained by electrolysis of their chlorides in molten state ?
(i) Na
(ii) Ca
(iii) Fe
(iv) Cu
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Ans. (d)
Sodium and Calcium are in the top, in reactivity series
Q19. Generally, non-metals are not lustrous. Which of the following nonmetal is lustrous?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Iodine
Ans. (d)
Q20. Which one of the following four metals would be displaced from the solution of its salts by other three metals?
(a) Mg
(b) Ag
(c) Zn
(d) Cu
Ans. (b)
Reactivity series Mg> Zn> Cu> Ag
Q21. 2 mL each of concentrated HCl, HNO3 and a mixture of concentrated HCl and concentrated HNO3 in the ratio of 3 : 1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metal got dissolved in test tube C respectively. The metal could be
(a) Al
(b) Au
(c) Cu
(d) Pt
Ans. (b)
Answer is gold because solution C is a mixture of Concentrated HCL and Concentrated HNO3 which is called aqua regia. Aqua Regia dissolves gold.
Q22. An alloy is
(a) an element
(b) a compound
(c) a homogeneous mixture
(d) a heterogeneous mixture
Ans. (c)
An Alloy is a homogeneous mixture because its composition is uniform.
Q23. An electrolytic cell consists of
(i) positively charged cathode
(ii) negatively charged anode
(iii) positively charged anode
(iv) negatively charged cathode
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) ad (iv)
Ans. (b)
Q24. During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets
(a) deposited on cathode
(b) deposited on anode
(c) deposited on cathode as well as anode
(d) remains in the solution
Ans. (a)
Zinc is positively charged hence it moves towards the negatively charged cathode.
Q25. An element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) P
(d) Ca
Ans. (b)
Sodium is soft which can be cut with a knife. Sodium reacts with water and air vigorously hence it is kept in kerosene.
Q26. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or nonmetal. Which among the following alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
(a) Brass
(b) Bronze
(c) Amalgam
(d) Steel
Ans. (d)
Steel is an alloy made up of carbon and iron where carbon is a non-metal.
Q27. Which among the following statements is incorrect for magnesium metal?
(a) It burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame
(b) It reacts with cold water to form magnesium oxide and evolves hydrogen gas
(c) It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves hydrogen gas
(d) It reacts with steam to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves hydrogen gas
Ans. (b)
Magnesium reacts with cold water to form magnesium oxide and evolves hydrogen gas is a wrong statement because Magnesium Hydroxide is formed, not Magnesium oxide.
Q28. Which among the following alloys contain mercury as one of its constituents?
(a) Stainless steel
(b) Alnico
(c) Solder
(d) Zinc amalgam
Ans. (d)
Zinc amalgam is an alloy of Mercury and Zinc
Q29. Reaction between X and Y, forms compound Z. X loses electron and Y gains electron. Which of the following properties is not shown by Z?
(a) Has high melting point
(b) Has low melting point
(c) Conducts electricity in molten state
(d) Occurs as solid
Ans. (b)
Here Z is an ionic compound and Ionic compounds have melting point hence option b) is a wrong statement.
Q30. The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are X — 2, 8; Y — 2, 8, 7 and Z —2, 8, 2. Which of the following is correct?
(a) X is a metal
(b) Y is a metal
(c) Z is a non-metal
(d) Y is a non-metal and Z is a metal
Ans. (d)
Element Y has 3 electrons in its outer, which is electronegative in nature. Z has 2 electrons in its outermost shell hence it is electropositive. Hence it is a metal.
Q31. Although metals form basic oxides, which of the following metals form an amphoteric oxide?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Al
(d) Cu
Ans. (c)
Oxides of Aluminum are both acidic and basic in nature. Hence aluminium oxides are amphoteric in nature.
Q32. Generally, non-metals are not conductors of electricity. Which of the following is a good conductor of electricity?
(a) Diamond
(b) Graphite
(c) Sulphur
(d) Fullerene
Ans. (b)
Q33. Electrical wires have a coating of an insulting material. The material, generally used is
(a) Sulphur
(b) Graphite
(c) PVC
(d) All can be used
Ans. (c)
Sulphur is brittle in nature; hence it can be used and Graphite is a good conductor of electricity hence it cannot be used as an insulator.
Q34. Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
(a) Carbon
(b) Bromine
(c) Phosphorus
(d) Sulphur
Ans: (b)
Q35. Which of the following can undergo a chemical reaction?
(a) MgSO4 + Fe
(b) ZnSO4 + Fe
(c) MgSO4 + Pb
(d) CuSO4 + Fe
Ans. (d)
Iron is more reactive than copper hence it displaces copper in the reaction to form Feso4.
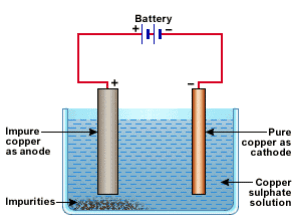
Q36. Which one of the following figures correctly describes the process of electrolytic refining?
(a)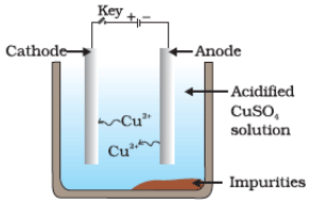
(b)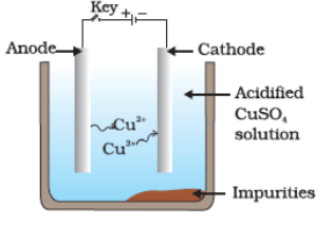
(c)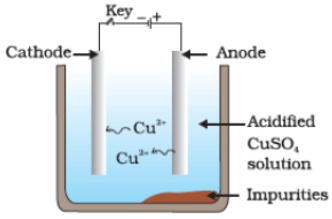
(d)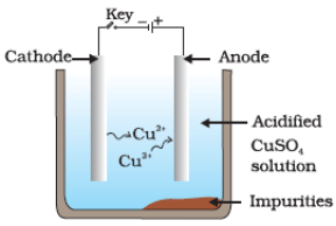
Ans. (c)
Copper ions are dispersed from the positively charged anode and deposited on the negatively charged cathode.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q37. Iqbal treated a lustrous, divalent element M with sodium hydroxide. He observed the formation of bubbles in the reaction mixture. He made the same observations when this element was treated with hydrochloric acid. Suggest how can he identify the produced gas. Write chemical equations for both the reactions.
Ans.
- M + 2NaOH → Na2MO2 + H2(g)
- M + 2HCl → MCl2 + H2(g)
- Bring a burning candle near the gas.
- If it burns with a pop sound, the gas is hydrogen, and the element is a metal.
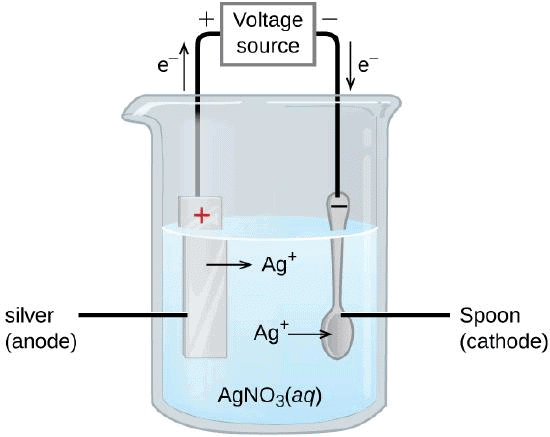
Q38. During the extraction of metals, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals.
(a) Which material will be used as anode and cathode for refining of silver metal by this process?
(b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte also.
(c) In this electrolytic cell, where do we get pure silver after passing electric current?
Ans.
(a) Pure silver rod will be used as cathode, and impure silver rod will be used as the anode.
Electrolyte Refining(b) AgNO3(aq) can be used as the electrolyte.
(c) Pure silver will be formed at the cathode.
At anode : Ag → Ag+ + e-
At cathode : Ag+ + e- → Ag
Q39. Why should the metal sulphides and carbonates be converted to metal oxides in the process of extraction of metal from them?
Ans.
It is because it is easier to reduce metal oxides to get free metals as compared to metal sulphides and metal carbonates.
Q40. Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated, but when metals (except Mn and Mg), treated with HNO3, hydrogen is not liberated. Why?
Ans.
It is because HNO3 is an oxidising agent and it gets reduced to NO if it is dilute and NO2 if HNO3 is concentrated, it oxidises H2 to H2O.
Q41. Compound X and aluminium are used to join railway tracks.
(a) Identify the compound X.
(b) Name the reaction.
(c) Write down its reaction.
Ans.
(a) ‘X ’ is Fe2O3.
(b) It is called thermite reaction.(c)
Molten iron is used to form broken railway tracks.
Q42. When a metal X is treated with cold water, it gives a basic salt Y with molecular formula XOH (molecular mass = 40) and liberates a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X, Y and Z and also write the reaction involved.
Ans.
- Both sodium (Na) and potassium (K) react with cold water to give basic salt NaOH and KOH respectively. Since the molecular mass of XOH is 40, therefore, the metal X is Na. Since, the molecular mass of NaOH is 40 (23 + 16 + 1 = 40).
- Therefore, Y is NaOH and the gas liberated during the reaction is hydrogen. Thus, Z is H2.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 + Heat energy
Q43. A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z
Ans.
X — Carbon; Y — Diamond and Z — Graphite
Q.44. The following reaction takes place when aluminium powder is heated with MnO2
(a) Is aluminium getting reduced?
(b) Is MnO2 getting oxidised?
Ans.
(a) No, aluminium is getting oxidised.
(b) No, MnO2 is getting reduced.
Q45. What are the constituents of solder alloy? Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Ans.
- Solder is made up of lead and tin.
- It has low melting point, therefore, it is used for soldering (welding) electrical wires.
Q46. A metal 'A', which is used in thermite process, when heated with oxygen gives an oxide B, which is amphoteric in nature? Identify A and B. Write down the reactions of oxide B with HCl and NaOH.
Ans.
- ‘A’ is aluminium.
4Al(s) + 3O22Al2O3(s)
- 'B' is amphoteric in nature(Al2O3).
► Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
► Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Q47. A metal that exists as liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide in the presence of air. Identify the metal and its ore and give the reaction involved.
Ans.
The metal is mercury.
► 2HgS(s) + 3O2 → 2HgO + 3SO2(g)
► HgS(s) + 2HgO → 3Hgl(l) + SO2(g)
Q48. Give the formulae of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of following pairs of elements:
(a) Mg and N2
(b) Li and O2
(c) Al and Cl2
(d) K and O2
Ans.
(a) 3Mg + Mg3N2 → Mg3N2
(b) 4Li + O2 → 2Li2O
(c) 2Al + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3
(d) 4K + O2 → 2K2O
Q49. What happens when
(a) ZnCO3 is heated in the absence of oxygen?
(b) a mixture of Cu2O and Cu2S is heated?
Ans.
(a)
- Zinc oxide(s) and CO2(g) are formed.
ZnCO3ZnO + CO2
- Blister copper(s) and SO2(g) are formed.
(b) 2Cu2O + Cu2S(s)
6Cu(s) + SO2(g)
Q50. A non-metal A is an important constituent of our food and forms two oxides B and C. Oxide B is toxic whereas oxide C causes global warming,
(a) Identity A, B and C.
(b) To which group of periodic table does A belong?
Ans. (a)
- ‘A’ is carbon.
- It forms two oxides:
(i) CO (B) is toxic
(ii) Whereas CO2 (C) causes global warming as it absorbs heat radiations from atmosphere.
(b) ‘A’ belongs to group 14 of periodic table.
Q51. Give two examples each of the metals that are good conductors and poor conductors of heat respectively.
Ans.
(a) Good conductor : Ag and Cu
(b) Poor conductor : Pb and Hg
Q52. Name one metal and one non-metal that exist in liquid state at room temperature. Also name two metals having melting point less than 310 K (37°C)
Ans.
Metal – Mercury (Hg); Non-metal – Bromine (Br) Two metals with melting points less than 310K are Cesium (Cs) and Gallium (Ga)
Q53. An element A reacts with water to form a compound B which is used in whitewashing. The compound B on heating forms an oxide C which on treatment with water gives back B. Identify A, B and C and give the reactions involved.
Ans.
Q54. An alkali metal A gives a compound B (molecular mass = 40) on reacting with water. The compound B gives a soluble compound C on treatment with aluminium oxide. Identify A, B and C and give the reaction involved.
Ans.
Alkali metal sodium when reacting with water gives a chemical compound sodium hydroxide. When sodium hydroxide is treated with aluminium oxide gives a soluble compound sodium aluminate.
Hence, A is sodium, B is sodium hydroxide and C is sodium aluminate.
Al2O3 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) → NaAlO2 (aq)+ H2O (l)
Q55. Give the reaction involved during extraction of zinc from its ore by
(a) roasting of zinc ore
(b) calcination of zinc ore
Ans.
Q56. A metal M does not liberate hydrogen from acids but reacts with oxygen to give a black colour product. Identify M and black coloured product and also explain the reaction of M with oxygen.
Ans.
M is 'Cu' It does not liberate hydrogen with dilute acid as it is less reactive than hydrogen gas.
Q57. An element forms an oxide A2O3 which is acidic in nature. Identify A as a metal or non-metal.
Ans.
Since an oxide of element is acidic in nature, therefore, A will be a non-metal.
Q58. A solution of CuSO4 was kept in an iron pot. After a few days, the iron pot was found to have a number of holes in it. Explain the reason in terms of reactivity. Write the equation of the reaction involved.
Ans.
- Iron is more reactive than copper.
- Therefore, it displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
- A portion of the iron pot got dissolved in this process and caused holes in it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q59. A non-metal A which is the largest constituent of air, when heated with H2 in 1 : 3 ratio in the presence of catalyst (Fe) gives a gas B. On heating with 0 2, it gives an oxide C. If this oxide is passed into water in the presence of air, it gives an acid D which acts as a strong oxidising agent.
(a) Identify A, B, C and D.
(b) To which group of periodic table does this non-metal belong?
Ans. (a)
- N2 is largest constituent of air when heated with H2 in the ratio of 1 : 3 in the presence of a catalyst (Fe) gives a gas NH3(B).
- Nitrogen reacts with oxygen on heating to form nitrogen monoxide 'C' which gets oxidised in the presence of O2 to nitrogen dioxide. Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water in the presence of oxygen to form nitric acid, which is an oxidising agent.
- 'A' is N2, 'B' isNH3, 'C' is NO and 'D' is HN03.
(b) Group 15
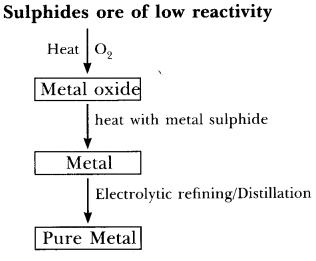
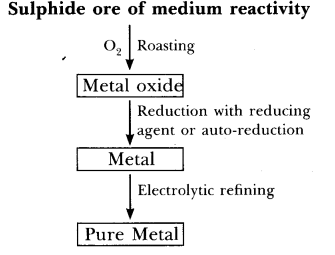
Q60. Give the steps involved in the extraction of metals of low and medium reactivity from their respective sulphide ores.
Ans.
(a)
- Metal sulphide like HgS reacts with O2 on heating to form mercuric oxide, HgO and sulphur dioxide, SO2.
2HgS + 3O22HgO + 2SO2
- Mercuric oxide on further heating gives Hg which can be refined by distillation.
2HgO2Hg + O2
- In the same manner, copper in copper glance, Cu2S is found in nature and can be obtained from its ore by heating in air:
2Cu2S + 3O22Cu2O + 2SO2
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2- Pure copper is obtained from electrolytic refining.
(b)
- Sulphide ore like zinc blende (ZnS) on roasting in the presence of O2 gives metal oxide. On reduction with suitable reducing agent gives metal which is impure.
- Impure metal on electrolytic refining gives pure metal.
- Pure zinc is obtained by electrolytic refining.
Q61. Explain the following
(а) Reactivity of Al decreases if it is dipped in HNO3.
(b) Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg.
(c) NaCl is not a conductor of electricity in solid state whereas it does conduct electricity in aqueous solution as well as in molten state.
(d) Iron articles are galvanised.
(e) Metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg are never found in their free state in nature.
Ans.
(a) It is due to the formation of oxide layer on its surface.
(b) It is because Na or Mg are strong reducing agents, therefore, carbon cannot reduce their oxides.
(c) NaCl does not conduct electricity in solid state as it does not have free ions to move in solid-state but in aqueous solution and in molten states ions are free to move.
(d) Iron articles are galvanised to protect them from rusting.
(e) It is because these metals are highly reactive and occur in the form of their compounds.
Q62. (i) Given below are the steps for extraction of copper from its ore. Write the reaction involved.
(a) Roasting of copper (1) sulphide
(b) Reduction of copper (1) oxide with copper (1) sulphide.
(c) Electrolytic refining
(ii) Draw a neat and well labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper
Ans.
(i) (a) Roasting of sulphide ore:
2Cu2S(s) + 3O2(s) → 2Cu2O(s) + 2SO2(g)
(b) Reduction of copper (I) oxide with copper (I) sulphide:
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu(s) + SO2(g)
This reaction is known as auto - reduction.
(c) Reaction for electrolytic refining:
At anode : Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
At cathode : Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-(ii) A neat and well-labeled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper.
Q63. Of the three metals X, Y and Z. X reacts with cold water, Y with hot water and Z with steam only. Identify X, Y and Z and also arrange them in order of increasing reactivity.
Ans.
X is alkali metal, Na or K
Y is alkaline earth metal, Mg or CaZ is Fe
Increasing reactivity series: Na > Mg> Fe
Q64. An element A burns with golden flame in air. It reacts with another element B, atomic number 17, to give a product C. An aqueous solution of product C on electrolysis gives a compound D and liberates hydrogen. Identify A, B, C and D. Also write down the equations for the reactions involved.
Ans.
- ‘A’ is sodium as it bums with golden flame in air.
- ‘B ’ (17) has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7 so ‘B ’ is chlorine
‘A’ is Na, ‘B’ is Cl2, ‘C’ is NaCl and ‘D’ is NaOH.
Q65. Two ores A and B were taken. On heating ore A gives CO2 whereas, ore B gives SO2. What steps will you take to convert then into metals?
Ans.
- Ore A gives CO2, therefore, it is a carbonate ore. Ore ‘A’ is first subjected to calcination, followed by reduction.
MCO3MO + CO2
MO + CM + CO
- Ore B gives SO2, therefore, it is a sulphide ore. Ore B is first subjected to roasting followed by reduction.
2MS + 3O22MO + 2SO2
MO + CM + CO
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Metals & Non-metals - Science Class 10
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How are metals and non-metals different in terms of their physical properties? |  |
| 4. What is the reactivity series? |  |
| 5. How do metals and non-metals react with oxygen? |  |