NCERT Exemplar: Our Environment | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which one of the following is an artificial ecosystem?
(a) Pond
(b) Crop field
(c) Lake
(d) Forest
Soln: The answer is (b) Crop field
Explanation: The crop field is an artificial ecosystem because people make it and take care of it. They plant the crops, give them water, and add things to help them grow. It doesn't happen by itself, like a forest or lake.
A pond, lake, and forest are natural ecosystems because they happen naturally and don’t need people to take care of them.
Q2: In a food chain, the third trophic level is always occupied by
(a) Carnivores
(b) Herbivores
(c) Decomposers
(d) Producers
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The first trophic level is producers, the second trophic level are herbivores, the third trophic level is occupied by carnivores.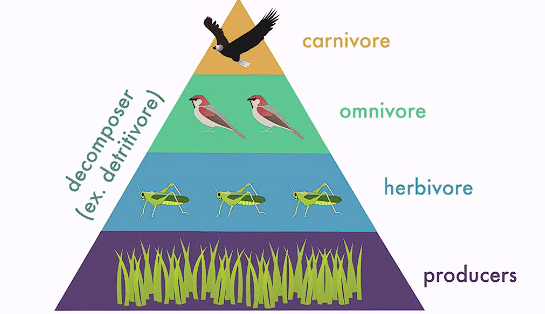
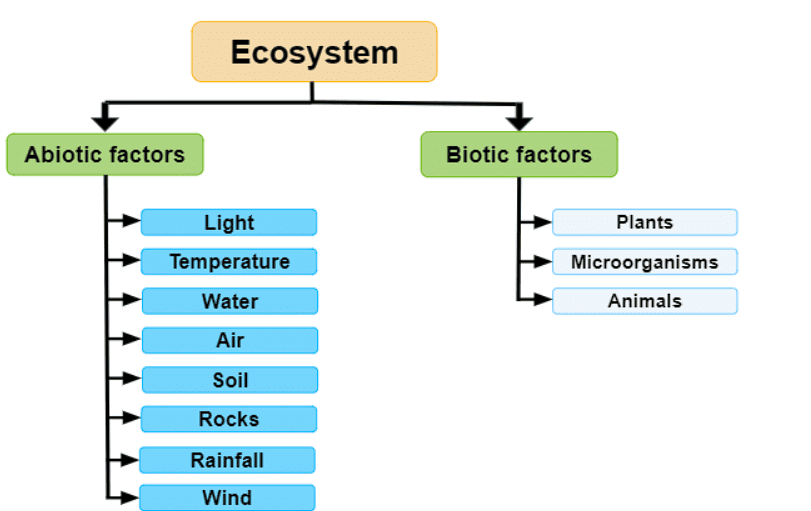
Q3: An ecosystem includes
(a) All living organisms
(b) Non-living objects
(c) Both living organisms and non-living objects
(d) Sometimes living organisms and sometimes non-living objects
Ans: (c)
Explanation: An ecosystem is a complex of living( biotic) and non-living (abiotic) organisms and their interactions.
Q4: In the given food chain, suppose the amount of energy at the fourth trophic level is 5 kJ, what will be the energy available at the producer level?
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
(a) 5 k J
(b) 50 k J
(c) 500 k J
(d) 5000 k J
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Available energy level at a particular trophic level is 10 times the energy level at next tropic level. Hence, energy at a third level trophic level is 50kj. Second level trophic has 500 KJ energy and 1st level trophic level (Producer) has energy of 5000 KJ.
Q5: Accumulation of non-biodegradable pesticides in the food chain in increasing amount at each higher trophic level is known as
(a) Eutrophication
(b) Pollution
(c) Biomagnification
(d) Accumulation
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
- Eutrophication is richness of nutrient beyond optimum level. Eutrophication occurs due to runoff from land.
- Introduction of an undesired substance into the environment. Pollution leads to harmful effects on living organisms.
Q6: Depletion of ozone is mainly due to
(a) Chlorofluorocarbon compounds
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Methane
(d) Pesticides
Ans: (a)
The depletion of the ozone layer is mainly caused by chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances (ODS) like halons, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform. These chemicals are used in products such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and aerosol sprays.
Q7: Organisms which synthesise carbohydrates from inorganic compounds using radiant energy are called
(a) Decomposers
(b) Producers
(c) Herbivores
(d) Carnivores
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Producers use solar energy to synthesize food from water and carbon dioxide. Plants and few micro-organisms are the producers.
- Organisms that decompose organic material are called decomposers.
- Herbivores are the organisms that feed on plants and its products.
- Carnivores are the ones that feed on other organisms.
Q.8. In an ecosystem, the 10% of energy available for transfer from one trophic level to the next is in the form of
(a) Heat energy
(b) Light energy
(c) Chemical energy
(d) Mechanical energy
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Energy is available for transfer from one trophic level to the next in the form of food. Food is a chemical form of energy.
Q.9. Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several types of organisms belonging to a lower trophic level constitute the
(a) food web
(b) ecological pyramid
(c) ecosystem
(d) food chain
Ans: (a)
Explanation: A series of organisms through which food energy flows in an ecosystem is called a food chain. An ecosystem consists of all the living beings of an area and non-living components of their environment. The graphic summary of the trophic structure and energy transfer in an ecosystem is called ecological pyramids. Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several types of organisms belonging to a lower trophic level constitute the food web.
Q.10. Flow of energy in an ecosystem is always
(a) Unidirectional
(b) Bidirectional
(c) Multidirectional
(d) No specific direction
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The flow of energy is from prey to predator and it cannot be in the reverse direction. Hence the flow of energy is uni-directional.
Q.11. Excessive exposure of humans to U V-rays results in
(i) damage to the immune system
(ii) damage to lungs
(iii) skin cancer
(iv) peptic ulcers
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Explanation: UV rays affect upper surface of our body. UV rays lead to skin cancer and effect on skin will affect our immune system as skin is considered as the primary level of the immune barrier.
Q.12. In the following groups of materials, which group (s) contains only non-biodegradable items?
(i) Wood, paper, leather
(ii) Polythene, detergent, PVC
(iii) Plastic, detergent, grass
(iv) Plastic, bakelite, DDT
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Group i) has wood and leather which are biodegradable. Group iii) has grass which is biodegradable hence the answer is d) (ii) and (iv)
Q.13. Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
(a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b) Sufficient food supply
(c) Polluted air
(d) Water
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Available energy level at a particular trophic level is 10 times the energy level at next tropic level. When we reach the fourth trophic level; a minute portion of energy from producer is available.
Q.14. Which of the statement is incorrect?
(a) All green plants and blue-green algae are producers
(b) Green plants get their food from organic compounds
(c) Producers prepare their own food from inorganic compounds
(d) Plants convert solar energy into chemical energy
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Green plants produce their food by harnessing solar energy. Solar energy is used to prepare carbohydrate with the help of CO2 and water which are inorganic substances.
Q.15. Which group of organisms are not constituents of a food chain?
(i) Grass, lion, rabbit, wolf
(ii) Plankton, man, fish, grasshopper
(iii) Wolf, grass, snake, tiger
(iv) Frog, snake, eagle, grass, grasshopper
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Explanation: In option ii) plankton does not eat grass. In option iii) none of them eat grass hence option c) is the right answer.
Q.16. The percentage of solar radiation absorbed by all the green plants for the process of photosynthesis is about
(a) 1 %
(b) 5 %
(c) 8 %
(d) 10 %
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Green plants utilize 1% of the radiation absorbed by the leaf and use it for photosynthesis.
Q.17. In the given Figure 15.1 the various trophic levels are shown in a pyramid. At which trophic level is maximum energy available?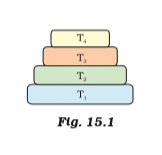 (a) T4
(a) T4
(b) T2
(c) T1
(d) T3
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Maximum energy is available for producers. Only 10% of the energy is consumed by an organism at the next level. Hence T1>T2>T3>T4
Q.18. What will happen if deer is missing in the food chain given below?
Grass → Deer → Tiger
(a) The population of tiger increases
(b) The population of grass decreases
(c) Tiger will start eating grass
(d) The population of tiger decreases and the population of grass increases
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Lack of predators will increase the population of grass. Population of tiger will reduce due to lack of food.
Q.19. The decomposers in an ecosystem
(a) Convert inorganic material, to simpler forms
(b) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
(c) Convert inorganic materials into organic compounds
(d) Do not breakdown organic compounds
Ans: (b)
Q.20. If a grasshopper is eaten by a frog, then the energy transfer will be from
(a) Producer to decomposer
(b) Producer to primary consumer
(c) Primary consumer to secondary consumer
(d) Secondary consumer to primary consumer
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Grasshopper is a primary consumer because it feeds on grass. If grasshopper is getting eaten by a frog. Frog will be the secondary consumer.
Q.21. Disposable plastic plates should not be used because
(a) they are made of materials with lightweight
(b) they are made of toxic materials
(c) they are made of biodegradable materials
(d) they are made of non-biodegradable materials
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Plastics are non-biodegradable hence they start accumulating in nature harming living organisms.
Short Answer Questions
Q.22. Why is improper disposal of waste a curse to the environment?
Ans: Wastes pollute our environment, air, soil, and water, and cause harmful effects on all living organisms.
Q.23. Write the common food chain of a pond ecosystem.
Ans:
Phyto planktons
↓
Small aquatic animals larvae, shrimps, Insects
↓
Fish
↓
Bird
Q24: What are the advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping
Ans: The advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping are as follows
- They can carry more weight than plastic bags
- They are bio-degradable
- They can be reused.
- They do not cause environmental pollution.
Q25: Why are crop fields known as artificial ecosystems?
Ans: Crops fields are known as artificial ecosystems because they are manmade where certain biotic and abiotic components are manipulated.
Q26: Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances. Cite examples.
Ans: : Substances that can be broken into pieces by the biological process are known as biodegradable substances. Substances that cannot be broken into pieces by the biological process are known as non-biodegradable substances.
Q27: Suggest one word for each of the following statements/ definitions
(a) The physical and biological world where we live in
(b) Each level of the food chain where the transfer of energy takes place
(c) The physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind and soil of an ecosystem
(d) Organisms which depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for food
Ans:
- Environment
- Trophic level
- Abiotic factors
- Consumers or heterotrophs
Q28: Explain the role of decomposers in the environment?
Ans: : Decomposers breakdown dead and decaying living matter and helps in the nutrient recycling. This will clean the environment by removing dead material.
Q29: Select the mismatched pair in the following and correct it.
(a) Biomagnification — Accumulation of chemicals at the successive trophic levels of a food chain
(b) Ecosystem — Biotic components of environment
(c) Aquarium — A man-made ecosystem
(d) Parasites — Organisms which obtain food from other living organisms
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Ecosystem — Biotic components of environment
Both biotic and abiotic components of the environment constitute an ecosystem.
Q30: We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned. Why
Ans: An aquarium is an artificial ecosystem which is incomplete ecosystem when compared to pond or lake which is a natural and complete ecosystem.
Long Answer Questions
Q31: Indicate the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Why is it unidirectional? Justify.
Ans: Flow of energy in an ecosystem is as follows.
- Green plants in ecosystems capture about 1% of sunlight and convert it into food energy.
- Primary consumers lose most energy as heat, and only 10% is passed on to the next level.
- Due to energy loss, food chains usually have only three or four levels.
- There are more organisms at lower levels, with producers being the most numerous.
- Food chains are complex, often forming interconnected food webs instead of straight chains.
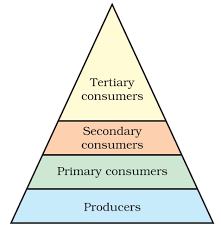
- The flow of energy is unidirectional because the energy captured by autotrophs does not return to the Sun.
- Energy that is passed from autotrophs to herbivores does not go back to the autotrophs.
- As energy moves through the different trophic levels, it becomes unavailable to the previous level.
- Additionally, energy diminishes at each trophic level due to losses as it moves upward in the food chain.
Q32: What are decomposers? What will be the consequence of their absence in an ecosystem?
Ans:
- Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi decompose dead remains and waste products of organisms.
- These decomposers break down complex organic substances into simple inorganic ones, which return to the soil and are reused by plants.
- Without decomposers, recycling of materials in the biosphere would not occur, leading to the buildup of dead plants and animals.
- Over time, the environment would be depleted of essential resources required to sustain life.
Q33: Suggest any four activities in daily life which are eco-friendly
Ans: Activities in daily life which are eco-friendly are as follows
- Using of bicycles and electrical bikes instead of vehicles run by fossil fuels.
- Avoid using plastic bags, instead we can use bags made of clothes and papers.
- Plant trees in our surroundings.
- Stop usage of old items and recycle them.
Q34: Give two differences between the food chain and the food web.
Ans: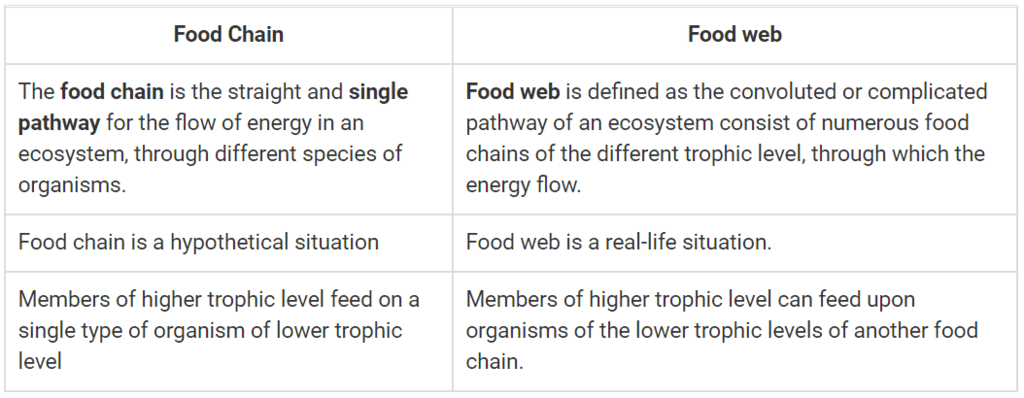
Q35: Name the wastes which are generated in your house daily. What measures would you take for their disposal?
Ans: Wastes generated in our house daily are as follows
(a) Kitchen wastes
(b) Paper waste like newspapers, bags, envelopes
(c) Plastic bags
(d) Vegetable/fruit peels/rind Measures for disposal
Measures to take to dispose of house waste are
(a) Segregation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes.
(b) Safe disposal of plastic bags.
(c) Vegetable/fruit peels can be placed near trees/plants, which on decomposition will enrich the soil with nutrients.
(d) Give paper wastes for recycling.
(e) Prepare a compost pit for kitchen wastes.
Q36: Suggest suitable mechanism (s) for waste management in fertiliser industries.
Ans: To manage waste in the fertiliser industry following steps must be taken:
For control of gaseous pollutants combustion equipments are used which can be oxidised. The pollutants are exposed to a high temperature in the process. Air pollutants, such as certain gases and vapour and inflammable compounds are controlled through the use’ of adsorption equipment. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon, and it needs the presence of a large solid surface area. This process removes toxic and odoriferous compounds are efficiently.
Three options available for controlling the effluents are:
- Control can take place at the point of generation within the factory.
- Wastewater can be pre-treated for discharge to municipal treatment systems.
- Wastewater can be treated completely at the factory and either reused or discharged directly for receiving water.
Q37: What are the by-products of fertiliser industries? How do they affect the environment?
Ans: The most common byproduct of fertilizer industries are oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. They pass into the atmosphere and spread to all nearby places. The gases have a corrosive effect on several items besides being harmful to living beings. They also give rise to acid rain. Acid rain is highly destructive to forests, crops and aquatic biota.
Oxides of Nitrogen and Sulphur are the most common by-product of fertilizer industries. These oxides pass into the atmosphere and spread to all nearby places. Sulphur and nitrogen oxides have a corrosive effect on several items besides being harmful to living beings. Sulphur oxides lead to acid rain which causes harms to forests, crops and aquatic biota.
Q38: Explain some harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment.
Ans: Following are the harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment
Soil degradation Extensive cropping causes loss of soil fertility. Also, over time it can lead to soil erosion and finally to desertification.
Pollution
Use of synthetic fertilisers and pesticides leads to soil, water and air pollution. •
Water shortage
Excess use of groundwater for agriculture lowers the water level. This results in acute water shortage at many places.
Bio-magnification
The chemical pesticides, being non-biodegradable accumulate in organisms in increasing amounts at each trophic level.
Deforestation
Indiscriminate cutting of trees for agriculture has resulted in loss of habitat for wildlife. Thus, it also causes damage to the natural ecosystem.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Our Environment - Science Class 10
| 1. How do human activities impact the environment? |  |
| 2. What are the major causes of air pollution? |  |
| 3. How can we help reduce plastic pollution? |  |
| 4. What are the effects of water pollution on aquatic life? |  |
| 5. How does deforestation contribute to climate change? |  |






















