NCERT Exemplar: Redox Reactions | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions - I |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions- II |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Matching Type Questions |

|
| Assertion and Reason Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions - I
Q.1. Which of the following is not an example of a redox reaction?
(i) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(ii) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(iii) 2K + F2 → 2KF
(iv) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Ans. (d)
Solution.
BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl is not a redox reaction. It is an example of double displacement reactions.
Q.2. The more positive the value of Eθ, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
Eθ values: Fe3+/Fe2+ = + 0.77; I2(s)/I– = + 0.54;
Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34; Ag+/Ag = + 0.80V
(1) Fe3+
(2) I2(s)
(3) Cu2+
(4) Ag+
Ans.(4)
Solution.
Since Ag+/Ag has highest positive value of E°, therefore, Ag+ is the strongest oxidizing agent with highest tendency to get reduced.
Q.3. Eθ values of some redox couples are given below. On the basis of these values choose the correct option.
Eθ values : Br2/Br– = + 1.90; Ag+ /Ag(s) = + 0.80
Cu2+/Cu(s) = + 0.34; I2(s)/I– = + 0.54
(1) Cu will reduce Br–
(2) Cu will reduce Ag
(3) Cu will reduce I–
(4) Cu will reduce Br2
Ans.(4)
Solution.
Copper will reduce Br2, if the E° of the redox reaction, 2Cu + Br2
CuBr2 is +ve.
Now,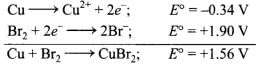
Since E° of this reaction is +ve, therefore, Cu can reduce Br2 and hence option (d) is correct.
Q.4. Using the standard electrode potential, find out the pair between which redox reaction is not feasible.
Eθ values : Fe3+/Fe2+ = + 0.77; I2/I– = + 0.54;
Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34; Ag+/Ag = + 0.80 V
(1) Fe3+ and I–
(2) Ag+ and Cu
(3) Fe3+ and Cu
(4) Ag and Fe3+
Ans. (4)
Solution.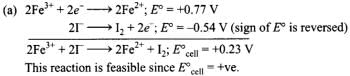
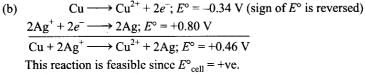
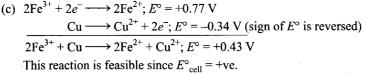
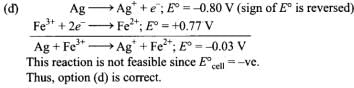
Q.5. Thiosulphate reacts differently with iodine and bromine in the reactions given below: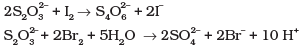
Which of the following statements justifies the above dual behavior of thiosulphate?
(1) Bromine is a stronger oxidant than iodine.
(2) Bromine is a weaker oxidant than iodine.
(3) Thiosulphate undergoes oxidation by bromine and reduction by iodine in these reactions.
(4) Bromine undergoes oxidation and iodine undergoes reduction in these reactions.
Ans.(1)
Solution.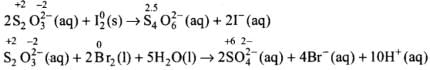
Bromine being stronger oxidizing agent than I2, it oxidises S of S2O2-3 to SO2-4 whereas I2 oxidises it only into S4O62- ion.
Q.6. The oxidation number of an element in a compound is evaluated on the basis of certain rules. Which of the following rules is not correct in this respect?
(1) The oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1.
(2) The algebraic sum of all the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero.
(3) An element in the free or the uncombined state bears oxidation number zero.
(4) In all its compounds, the oxidation number of fluorine is – 1.
Ans. (1)
Solution.
Oxidation number of hydrogen is -1 in metal hydrides like NaH.
Q.7. In which of the following compounds, an element exhibits two different oxidation states.
(1) NH2OH
(2) NH4NO3
(3) N2H4
(4) N3H
Ans.(2)
Solution.
NH4NO3 is an ionic compound consisting of NH4+ and NO3- ion.
The oxidation number of N in two species is different as shown below:
In NH,
Let the oxidation state of N in NH4+ be x.
x + 4x(+1) = +1
x = -3
In NO3-
Let the oxidation state of N in NO3- be y,
y + 3 x (-2) = -1
y = +5
Q.8. Which of the following arrangements represent increasing oxidation number of the central atom?
(1) CrO2– , ClO3– , CrO42– , MnO4–
(2) ClO3– , CrO42– , MnO4– , CrO2–
(3) CrO2– , ClO3– , MnO4– , CrO42–
(4) CrO42–, MnO4– , CrO2– , ClO3–
Ans. (1)
Solution.
Writing the O.N. of Cr, Cl and Mn on each species in the four set of ions, we have,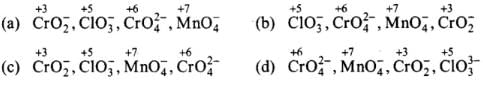
Q.9. The largest oxidation number exhibited by an element depends on its outer electronic configuration. With which of the following outer electronic configurations the element will exhibit largest oxidation number?
(1) 3d14s2
(2) 3d34s2
(3) 3d54s1
(4) 3d54s2
Ans.(4)
Solution.
Highest O.N. of any transition element = (n – 1)d electrons +ns electrons. Therefore, larger the number of electrons in the 3d orbitals, higher is the maximum O.N.
(a) 3d14s2 = 3;
(b) 3d24s2 = 3 + 2 = 5;
(c) 3d54s1 = 5 + 1=6
(d) 3d54s2 = 5 + 2 = 7
Q.10. Identify disproportionation reaction
(1) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
(2) CH4 + 4Cl2 → CCl4 + 4HCl
(3) 2F2 + 2OH– → 2F– + OF2 + H2O
(4) 2NO2 + 2OH– → NO2– + NO3– + H2O
Ans.(4)
Solution.
Reactions in which the same substance is oxidized as well as reduced are called disproportionation reactions. Writing the O.N. of each element above its symbol in the given reactions,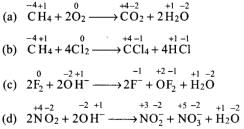
Thus, in reaction (d), N is both oxidized as well as reduced since the O.N. of N increases from +4 in NO2 to +5 in NO–3 and decreases from +4 in N02 to +3 in N0–2.
Q.11. Which of the following elements does not show disproportionation tendency?
(1) Cl
(2) Br
(3) F
(4) I
Ans. (3)
Solution.
Being the most electronegative element, F can only be reduced and hence it always shows an oxidation number of-1. Further, due to the absence of d-orbitals, it cannot be oxidized and hence it does not show +ve oxidation numbers. In other words, F cannot be simultaneously oxidized as well as reduced and hence does not show disproportionation reactions. Thus, option (3) is correct.
Multiple Choice Questions- II
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Q.12. Which of the following statement(s) is/are not true about the following decomposition reaction.
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
(1) Potassium is undergoing oxidation
(2) Chlorine is undergoing oxidation
(3) Oxygen is reduced
(4) None of the species are undergoing oxidation or reduction
Ans.(1, 2, 3, 4)
Solution.
Writing the oxidation number of each element above its symbol,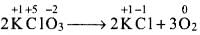
(a) The O.N. of K does not change, K. undergoes neither reduction nor oxidation. Thus, option (a) is not correct.
(b) The O.N. of chlorine decreases from +5 in KClO3 to -l in KCl, hence, Cl undergoes reduction.
(c) Since, O.N. of oxygen increases from -2 in KClO3 to O in O2, oxygen is oxidized.
(d) This statement is not correct because Cl is undergoing reduction and O is undergoing oxidation.
Q.13. Identify the correct statement (s) in relation to the following reaction:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
(1) Zinc is acting as an oxidant
(2) Chlorine is acting as a reductant
(3) Hydrogen ion is acting as an oxidant
(4) Zinc is acting as a reductant
Ans.(3, 4)
Solution.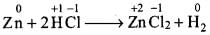
(a) The O.N. of Zn increases from 0 to +2 (in ZnCl2) and therefore, Zn acts as a reductant and not as an oxidant. Hence, option (a) is not correct.
(b) The O.N. of Cl does not change and therefore, it neither acts as a reductant nor an oxidant. Hence, option (b) is not correct.
(c) The O.N. of H decreases from +1 in H+ to O in H2. Therefore, H+ acts an oxidant. This option is correct.
(d) Zinc acts as reductant because its O.N. changes from 0 to +2. This option is correct.
Q.14. The exhibition of various oxidation states by an element is also related to the outer orbital electronic configuration of its atom. Atom(s) having which of the following outermost electronic configurations will exhibit more than one oxidation state in its compounds.
(1) 3s1
(2) 3d14s2
(3) 3d24s2
(4) 3s23p3
Ans. (2, 3, 4)
Solution.
Elements which have only s-electron in the valence shell do not show more than one oxidation state. Thus, element with 3s1 as outer electronic configuration shows only one oxidation state of +1.
Transition elements, i.e., elements (2, 3) having incompletely filled orbitals in the penultimate shell show variable oxidation states. Thus, element with outer electronic configuration as 3d1 4s2 shows variable oxidation states of +2 and +3 and the element with outer electronic configuration as 3d24s2 shows variable oxidation states of +2, +3 and +4.
p-Block elements also show variable oxidation states due to a number of reasons such as involvement of J-orbitals and inert pair effect. For example, element (4) with 3s2 3p3 as (i.e., P) as the outer electronic configuration shows variable oxidation states of +3 and +5 due to involvement of d-orbitals.
Q.15. Identify the correct statements with reference to the given reaction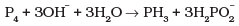
(1) Phosphorus is undergoing reduction only.
(2) Phosphorus is undergoing oxidation only.
(3) Phosphorus is undergoing oxidation as well as reduction.
(4) Hydrogen is undergoing neither oxidation nor reduction.
Ans. (3, 4)
Solution.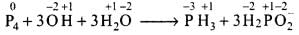
Because O.N. of P increases from 0 (P4) to +1 (H2P0–2) and decreases from 0 (P4) to -3 (PH3), therefore, P has undergone both oxidation as well as reduction. So, option (c) is correct. Option (d) is also correct because O.N. of H remains +1 in all the compounds and hence hydrogen is undergoing neither oxidation nor reduction.
Q.16. Which of the following electrodes will act as anodes, when connected to Standard Hydrogen Electrode?
| Al/Al3+ | Eθ = –1.66 |
| Fe/Fe2+ | Eθ = – 0.44 |
| Cu/Cu2+ | Eθ = + 0.34 |
| F2 (g)/2F– (aq) | Eθ = + 2.87 |
Ans.(1, 2)
Solution.
The electrodes having negative electrode potentials are stronger reducing agents than H2 gas and therefore, will act as anodes.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.17. The reaction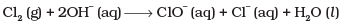 represents the process of bleaching. Identify and name the species that bleaches the substances due to its oxidising action.
represents the process of bleaching. Identify and name the species that bleaches the substances due to its oxidising action.
Ans.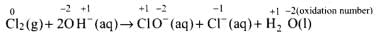
In this reaction, O.N. of Cl increases from 0 (in Cl2) to +1 (in ClO–) and decreases to -1 (in Cl–). Therefore, Cl2 is both oxidized to ClO– and reduced to Cl–. Since Cl– ion cannot act as an oxidizing agent (because it cannot decrease its O.N. lower than -1), therefore, Cl2 bleaches substances due to oxidizing action of hypochlorite, ClO ion.
Q.18. Mn042- undergoes disproportionation reaction in acidic medium but MnO4– does not. Give reason.
Ans.In Mn0–4, Mn is in the highest oxidation state of+7 (i.e.. cannot be oxidized further) and hence it cannot undergo disproportionation.
In contrast, the O.N. of Mn in Mn042- is +6. Therefore, it can increase its O.N. to+7 or decrease its O.N. to some lower value. Thus, Mn042- undergoes disproportionation according to the following reaction.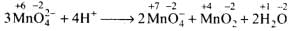
Here, the O.N. of Mn increases from +6 in Mn042- to +7 in Mn0–4 and decreases to +4 in MnO2. Thus, Mn042- undergoes disproportionation in acidic medium.
Q.19. PbO and PbO2 react with HCl according to following chemical equations :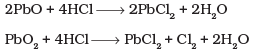
Why do these compounds differ in their reactivity?
Ans.(i)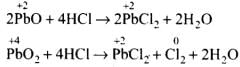
In reaction (i), O.N. of none of the atoms undergo a change. Therefore, it is not a redox reaction. It is an acid-base reaction, because PbO is a basic oxide which reacts with HCl acid. The reaction (ii) is a redox reaction in which PbO2 gets reduced and acts as an oxidizing agent.
Q.20. Nitric acid is an oxidising agent and reacts with PbO but it does not react with PbO2. Explain why?
Ans.Nitric acid is an oxidizing agent and reacts with PbO to give a simple acid- base reaction without any change in oxidation state. In PbO2, Pb is in +4 oxidation state and cannot be oxidized further, hence no reaction takes place between PbO2 and HNO3.
Q.21. Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
(1) Permanganate ion (MnO4–) reacts with sulphur dioxide gas in acidic medium to produce Mn2+ and hydrogensulphate ion. (Balance by ion electron method)
(2) Reaction of liquid hydrazine (N2H4) with chlorate ion (ClO3–) in basic medium produces nitric oxide gas and chloride ion in gaseous state. (Balance by oxidation number method)
(3) Dichlorine heptaoxide (Cl2O7) in gaseous state combines with an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide in acidic medium to give chlorite ion (ClO2–) and oxygen gas. (Balance by ion electron method)
Ans.(1) 2MnO–4 + 5SO2 + 2H2O + H+→5HS0–4 + 2Mn2+
Balancing by ion-electron method: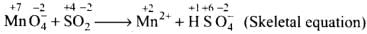
Oxidation half: SO2 → HSO-4
Reduction half: MnO4- →Mn2+
Oxidation half: SO2 → HSO-4 + 2e-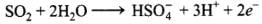 ...........(i)
...........(i)
(Add 2H2O molecules to balance O atoms)
Reduction half: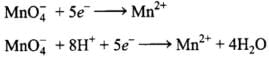
(Add 4H2O molecules to balance O atoms and H atoms)
Add oxidation and reduction half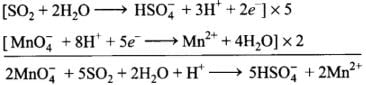
(2)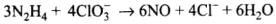
Balancing by oxidation number method: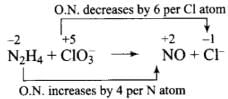
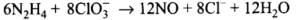
(3) 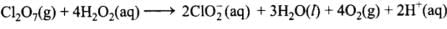
Balancing by ion-electron method:
Oxidation half:
H2O2 → O2 + 2e-
Adding 2H+ on right side to balance H atoms and charge.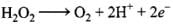
Reduction half: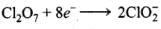
Adding H2O and H+ to balance H and O atoms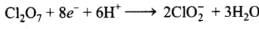
Adding oxidation and reduction half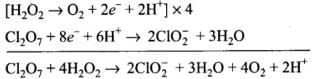
Q.22. Calculate the oxidation number of phosphorus in the following species.
(1) HPO2-3 and
(2) PO3-4
Ans.(1) Let the oxidation number of P in HPO2-3 be x. So, + 1 + x + (-6) = -2 x = +3
(2) Let the oxidation number of P in P03-4 be x. So, x + (-8) = -3
x = +5
Q.23. Calculate the oxidation number of each sulphur atom in the following compounds:
(1) Na2S2O3
(2) Na2S4O6
(3) Na2SO3
(4) Na2SO4
Ans. (1)
Solution. (a)
Structure of Na2S2O3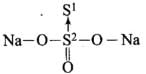
The oxidation state of S1 is -2
Let oxidation state of S2 be x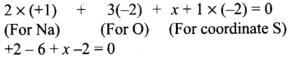
Thus, the oxidation states of two S atoms in Na2S2O3 are -2 and +6.
(b) Na2S4O6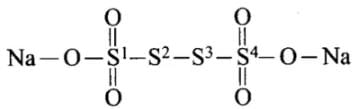
From the left, S1 = (-2) + (-2) + (-1) = +5
S2 = 0
S3 = 0
S4 = +5
(c) Na2SO3
2 x (+1) + x + 3 x (-2) = 0
x = +4
(d) Na2SO4
+2 + x + (-8) = 0
x = +6
Q.24. Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
(i)
(ii)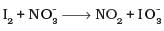
(iii)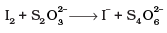
(iv)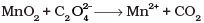
Ans.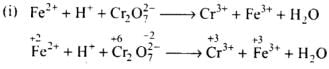
(a) Balance the increase and decrease in O.N.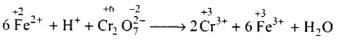
(b) Balancing H and O atoms by adding H+ and H2O molecules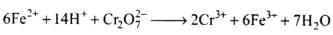
(ii)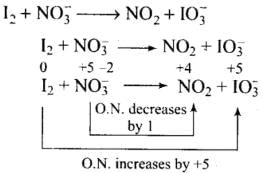
Total increase in O.N. = 5 × 2 = 10
Total decrease in O.N. = 1
To equalize O.N. multiply NO3-, by 10
I2 + 10no3- → 10no2 + IO3-
Balancing atoms other than O and H
I2 + 10no3-→ 10NO2 + 2 IO3-
Balancing O and H
I2 + lO no3- + 8H+→ 10NO2 + 2 IO3- + 4H20
(iii) 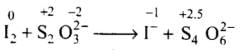
Total increase in O.N. = 0.5 x 4 = 2
Total decrease in O.N. = 1x2 = 2
To equalize O.N. multiply S2O2-3 and I- by 2.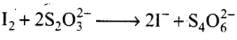
(iv) 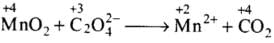
Total increase in O.N. = 1 x 2 = 2
Total decrease in O.N. = 2
To equalize O.N. multiply CO2 by 2.
MnO2 + C2O2-4 → Mn2+ + 2CO2
Balance H and O by adding 2H2O on right side, and 4H+ on left side of equation.
MnO2 + C2O2-4 + 4H+ → Mn2+ + 2CO2 + 2H2O
Q.25. Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.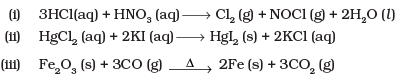
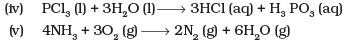
Ans.(i)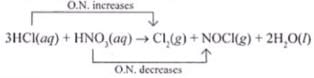
Oxidising agent - HNO3
Reducing agent - HCl
(ii) This is not a redox reaction.
(iii)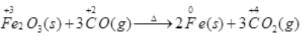
Fe - Oxidising agent
CO - Reducing agent
(iv)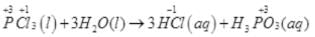
Above reaction is not a redox reaction.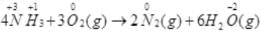
Reducing agent — NH3
Oxidising agent — O2
Q.26. Balance the following ionic equations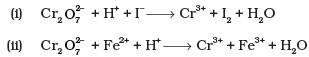
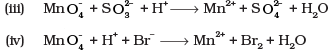
Ans.(i)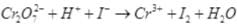
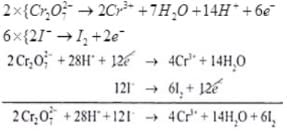
Dividing eq. by 2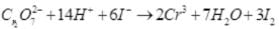
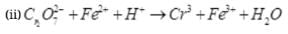
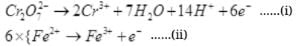
On adding (i) and (ii)
(iii) 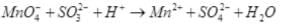
Reduction half: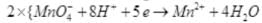
Oxidation half: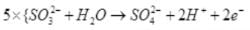
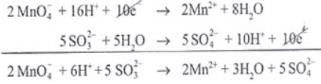
(iv) 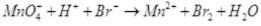
Reduction half: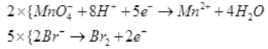

Matching Type Questions
Q.27. Match Column I with Column II for the oxidation states of the central atoms.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Cr2O72- | (a) +3 |
| (ii) MnO4- | (b) +4 |
| (iii) VO3- | (c) +5 |
| (iv) FeF63- | (d) +6 |
| (e) +7 |
Ans. (i) → (d); (ii) → (e); (iii) → (c); (iv) → (a)
Q.28. Match the items in Column I with relevant items in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Ions having positive charge | (a) +7 |
| (ii) The sum of oxidation number of all atoms in a neutral molecule | (b) –1 |
| (iii) Oxidation number of hydrogen ion (H+) | (c) +1 |
| (iv) Oxidation number of fluorine in NaF | (d) 0 |
| (v) Ions having negative charge | (f) Cation |
| (g) Anion |
Ans. (i) → (e); (ii) → (d); (iii) → (c); (iv) → (b); (v) → (f)
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Q.29. Assertion (A) : Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason (R) : Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(3) A is true but R is false.
(4) Both A and R are false.
Ans.(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation.
Fluorine is most electro-negative element that is why it is best oxidant among halogens.
Q.30. Assertion (A): In the reaction between potassium permanganate and potassium iodide, permanganate ions act as oxidising agent.
Reason (R) : Oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7 during the reaction.
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(3) A is true but R is false.
(4) Both A and R are false.
Ans.(3) A is true but R is false.
Explanation.
As permanganate ion changes to MnO2.
Q.31. Assertion (A) : The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen is an example of disproportionation reaction.
Reason (R) : The oxygen of peroxide is in -1 oxidation state and it is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 and -2 oxidation state in H2O.
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(3) A is true but R is false.
(4) Both A and R are false.
Ans. (1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation.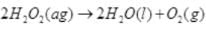
Here the oxygen of peroxide, which is present in -1 state, is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 undergoing oxidation and decreases to -2 oxidation state in H2O undergoing reduction.
Q.32. Assertion (A) : Redox couple is the combination of oxidised and reduced form of a substance involved in an oxidation or reduction half cell.
Reason (R) : In the representation 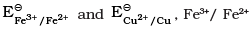 and Cu2+/Cu are redox couples.
and Cu2+/Cu are redox couples.
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(3) A is true but R is false.
(4) Both A and R are false.
Ans. (2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation.
A redox couple is defined as pair of compounds or elements having together the oxidised and reduced forms of it and taking part in an oxidation or reduction half reaction.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.33. Explain redox reactions on the basis of electron transfer. Give suitable examples.
Ans. 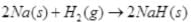 is a redox change.
is a redox change.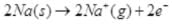 and the other half reaction is:
and the other half reaction is: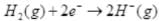
This splitting of the reaction into two half reactions automatically reveals here that sodium is oxidised and hydrogen is reduced. Any sustance which loses electron is oxidised and gains electron is reduced hence is the case of sodium and hydrogen atoms respectively. Therefore, the complete reaction is a redox change.
Q.34. On the basis of standard electrode potential values, suggest which of the following reactions would take place? (Consult the book for Eθ value).
(1) Cu + Zn2+ → Cu2+ + Zn
(2) Mg + Fe2+ → Mg2+ + Fe
(3) Br2 + 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2Br–
(4) Fe + Cd2+ → Cd + Fe2+
Ans. On the basis of standard reduction potential suggested in the reactivity series (ii) reaction can take place as Mg has more negative value of E° cell. Thus, Mg will be oxidized by losing electron and iron will be reduced by gaining electron.
Q.35. Why does fluorine not show disporportionation reaction?
Ans. Flourine shows disproportionation reaction because fluorine is most electronegative element of its period as well as group. It shows only -1 oxidation state and is smallest in size of all the halogens.
Q.36. Write redox couples involved in the reactions (i) to (iv) given in question 34.
Ans.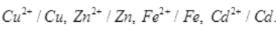
Q.37. Find out the oxidation number of chlorine in the following compounds and arrange them in increasing order of oxidation number of chlorine.
NaClO4, NaClO3, NaClO, KClO2, Cl2O7, ClO3, Cl2O, NaCl, Cl2, ClO2.
Which oxidation state is not present in any of the above compounds?
Ans.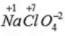 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +7
Oxidation no. of chlorine = +7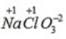 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +5
Oxidation no. of chlorine = +5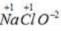 Oxidation no. of chlorine= +1
Oxidation no. of chlorine= +1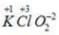 Oxidation no. of chlorine =+3
Oxidation no. of chlorine =+3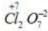 Oxidation no. of chlorine =+7
Oxidation no. of chlorine =+7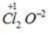 Oxidation no. of chlorine =+6
Oxidation no. of chlorine =+6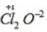 Oxidation no. of chlorine = + l
Oxidation no. of chlorine = + l
NaCl Oxidation no. of chlorine = - l
Cl2 Oxidation no. of chlorine =0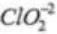 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +4
Oxidation no. of chlorine = +4
NaCl, Cl2, Cl2O, NaClO, KClO2, ClO2, NaClO3, ClO3, NaClO4
Q.38. Which method can be used to find out strength of reductant/oxidant in a solution? Explain with an example.
Ans. In redox systems, the titration method can be adopted to determine the strength of a reductant/oxidant using a redox sensitive indicator. The usage of indicators in redox titration is illustrated below: (i) In one situation, the reagent itself is intensely coloured, e.g.. permanganate ion, MnO-4. Here, MnO4- acts as the self indicator. The visible end point in this case is achieved after the last of the reductant (Fe2+ or C2O2-4) is oxidised and the first lasting tinge of pink colour appears at MnO4- concentration as low as 10-6 mol (10-6 mol L-1). This ensures a minimal ‘overshoot’ in colour beyond the equivalence point, the point where the reductant and the oxidant are equal in terms of their mole stoichiometry.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Redox Reactions - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are redox reactions? |  |
| 2. How can we identify redox reactions? |  |
| 3. What is a reducing agent in a redox reaction? |  |
| 4. How do redox reactions occur in everyday life? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of oxidation and reduction in redox reactions? |  |




















