NCERT Exemplars: Chemical Coordination & Integration | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Select the right match of the endocrine gland and their hormone among the options given below:
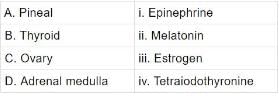
Options:
(a) A-iv, B-ii, C-iii, D-i
(b) A-ii, B-iv, C-i, D-iii
(c) A-iv, B-ii, C-i, D-iii
(d) A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
Ans. (d)
Solution:
Q.2. Which of the following hormones is not secreted by anterior pituitary.
(a) Growth hormone
(b) Follicle-stimulating hormone
(c) Oxytocin
(d) Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Ans. (c)
Solution:
The anterior pituitaryproduces six hormones:
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Prolactin (PRL)
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Oxytocin and Vasopressin is not produced by the anterior pituitary; it is made in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary.
Q.3. Mary is about to face an interview. But during the first five minutes before the interview she experiences sweating, increased rate of heartbeat, respiration, etc. Which hormone is responsible for her restlessness?
(a) Estrogen and Progesterone
(b) Oxytocin and Vasopressin
(c) Adrenaline and Noradrenaline
(d) Insulin and Glucagon
Ans. (c)
Solution: Adrenaline and noradrenaline trigger the body's 'fight or flight' response.These hormones are released during stressful situations.They cause symptoms such as:
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Sweating
Q.4. The steroid responsible for balance of water and electrolytes in our body is
(a) Insulin
(b) Melatonin
(c) Testosterone
(d) Aldosterone
Ans. (d)
Solution: Aldosterone is the hormone responsible for regulating the balance of water and electrolytes in the body.It primarily acts on the kidneys to:(I) Reabsorb sodium and water (II) Excrete potassium and phosphate ions
This regulation helps maintain: Fluid balance, Blood pressure, Osmotic pressure.
Q.5. Thymosin is responsible for
(a) Raising the blood sugar level
(b) Raising the blood calcium level
(c) Differentiation of T lymphocytes
(d) Decrease in blood RBC
Ans. (c)
Solution: Thymosin plays a vital role in the immune system by:
- Promoting the differentiation of T-lymphocytes.
- Supporting the body's cell-mediated immunity.
- Encouraging the production of antibodies for humoral immunity.
As we age, the thymus gland shrinks, leading to reduced thymosin production and weaker immune responses.
Q.6. In the mechanism of action of a protein hormone, one of the second messengers is
(a) Cyclic AMP
(b) Insulin
(c) T3
(d) Gastrin
Ans. (a)
Solution: Hormones which interact with membrane-bound receptors normally do not enter the target cell, but generate secondary messengers (e.g., cyclic AMP, cGMP, DAG, IP3, Ca++ etc.) which in turn regulate cellular metabolism.
Q.7. Leydig cells produce a group of hormones called
(a) Androgens
(b) Estrogens
(c) Aldosterone
(d) Gonadotropins
Ans. (a)
Solution: Leydig cells mainly produce androgens, particularly testosterone. These hormones are essential for:
- Development and function of male reproductive organs.
- Regulating secondary sexual characteristics, such as facial hair and deeper voice.
- Stimulating muscle growth and influencing sexual behaviour.
- Supporting the process of spermatogenesis, which is the formation of sperm.
Q.8. Corpus luteum secretes a
(a) Prolactin
(b) Progesterone
(c) Aldosterone
(d) Testosterone
Ans. (b)
Solution: In the luteal phase, corpus luteum is formed by the remaining tissue of the ruptured Graafian follicle after ovulation. Corpus luteum secretes a large amount of progesterone for the proliferation and maintenance of the endometrium for the implantation of the fertilized ovum.
Q.9. Cortisol is secreted from gland called
(a) Pancreas
(b) Thyroid
(c) Adrenal
(d) Thymus
Ans. (c)
Solution: Adrenal or suprarenal glands are paired structures located on the top of the kidneys. The cells of Zona fasciculata of adrenal cortex secretes mainly glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids include three main hormones: cortisol(= hydrocortisone), corticosterone and cortisone. They affect carbohydrate metabolism, however, they also affect the metabolism of proteins and fats.
Q.10. A hormone responsible for normal sleep-wake cycle is
(a) Epinephrine
(b) Gastrin
(c) Melatonin
(d) Insulin
Ans. (c)
Solution: A hormone responsible for normal sleep-wake cycle is melatonin.
Melatonin is a hormone secreted by pineal gland. Immediately above the optic chiasma(in the brain) in a nucleus, are present melatonin receptors that react to this hormone and synchronise the nucleus to the 24hrs day/night rhythm, thus informing the brain when it is day and when it is night.
Q.11. Hormones are called chemical signals that stimulate specific target tissues. Which is the correct location of these receptors in case of protein hormones?
(a) Extracellular matrix
(b) Blood
(c) Plasma membrane
(d) Nucleus
Ans. (c)
Solution:
- Protein hormones attach to receptors on the plasma membrane of target cells.
- This binding creates a hormone-receptor complex.
- These receptors are crucial for the hormone's action on the target tissue.
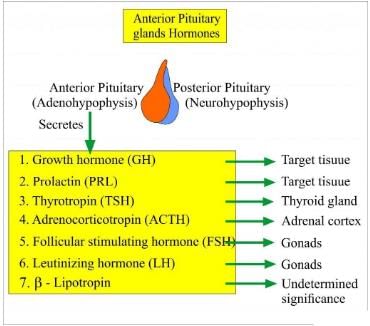
Q.12. Choose the correct option among the following:
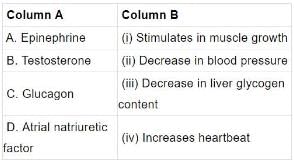
Options:
(a) A—(ii), B—(i), C—(iii), D—(iv)
(b) A—(iv), B—(i), C—(iii), D—(ii)
(c) A—(i), B—(ii), C—(iii), D—(iv)
(d) A—(i), B—(iv), C—(ii), D—(iii)
Ans. (b)
Solution:
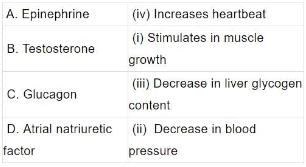
A. Role of epinephrine and non- epinephrine: They whip up metabolism for preparing the animal to face special conditions created by physical stress such as fall in BP or blood sugar, anger, fear etc. All these conditions require more energy which is provided by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, sugar level of blood.
B. Testosterone: It stimulates the development of male accessory sex characters such as hair on the face, growth and distribution of hair on the body, stronger bones and muscles.
C. Glucagon: It is secreted by alpha cells of the islands of Langerhans in response to a fall in the blood glucose level. It brings about change of liver glycogen to blood glucose( glycogenolysis).
D. Atrial natriuretic factor: The cells, called cardiocytes, of the atria, secrete a peptide, ANF in response to an increased return of the venous blood. This hormone regulates the blood volume through increased excretion of ions and water.
Q.13. Which of the following does not play any role in calcium balance in the human body?
(a) Vitamin D
(b) Parathyroid hormone
(c) Thyrocalcitonin
(d) Thymosin
Ans. (d)
Solution: Thymosin is a hormone released by the thymus. It has a major role in the maturation of the T lymphocytes. It has no role in maintaining the calcium balance in the body.
Q.14. Which of the following organs in mammals does not consist of a central medullary region surrounded by a cortical region?
(a) Ovary
(b) Adrenal
(c) Liver
(d) Kidney
Ans. (c)
- The ovaries are solid organs and are composed of connective tissue, the stroma. The stroma consists of an outer ovarian cortex and central ovarian medulla.
- Adrenal: The adrenals are conical, yellowish bodies. Each has two distinct regions are called adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla.
- Kidney: The two regions of the kidney are outer region is called renal cortex and inner region is termed renal medulla.
So, the correct answer is 'Liver'.
Q.15. Which of the following conditions is not linked to deficiency of thyroid hormones?
(a) Cretinism
(b) Goitre
(c) Myxedema
(d) Exophthalmia
Ans. (d)
Solution:
- Exophthalmos happen due to hyperthyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism is a disorder caused due to deficiency of thyroid hormone. It may lead to cretinism, myxoedema, simple goitre, Hashimoto's disease.
- Exophthalmic goitre is thyroid enlargement in which thyroid secretes excessive amount of thyroid hormone. It is caused due to hypersecretion of thyroid hormone.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. There are many endocrine glands in human body. Name the glands which is absent in male and the one absent in female.
Ans. Ovary is absent in male and testis is absent in female.
Q.2. Which of the two adrenocortical layers, zona glomerulosa and zona reticularis lies outside enveloping the other?
Ans. Zona glomerulosa is the outermost layer and zona reticularis is the innermost layer of the adrenal gland.
Q.3. What is erythropoiesis? Which hormone stimulates it?
Ans. Formation of RBCs from the bone marrow is called erythropoiesis. The hormone erythropoietin stimulates it.
Q.4. Name the only hormone secreted by pars intermedia of the pituitary gland.
Ans. Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH)
Q.5. Name the endocrine gland that produces calcitonin and mention the role played by this hormone.
Ans. Calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin is secreted by thyroid gland. Calcitonin regulates blood calcium level.
Q.6. Name the hormone that helps in cell-mediated immunity.
Ans. Thymosin
Q.7. What is the role of second messenger in the mechanism of protein hormone action?
Ans. Second messenger regulates cell metabolism. Hormones which interact with membrane-bound receptors normally do not enter the cell. Instead, they generate second messengers and thus affect the functioning of the target cells.
Q.8. State whether true or false:
(a) Gastrointestinal tract, kidney and heart also produce hormones.
Ans. True
(b) Pars distalis produces six trophic hormones.
Ans. True
(c) B-lymphocytes provide cell-mediated immunity.
Ans. False
(d) Insulin resistance results in a disease called diabetes mellitus.
Ans. True
Q.9. A patient complains of constant thirst, excessive passing of urine and low blood pressure. When the doctor checked the patient's blood glucose and blood insulin level, the level were normal or slightly low. The doctor diagnosed the condition as diabetes insipidus. But he decided to measure one more hormone in patients blood. Which hormone does the doctor intend to measure?
Ans. Vasopressin or Anti-Diuretic Hormone because low level of this hormone can result in excessive passing of urine and low blood pressure.
Q.10. Correct the following statements by replacing the term underlined.
(a) Insulin is a steroid hormone.
Ans. (a) Insulin is a peptide hormone.
(b) TSH is secreted from the corpus luteum.
Ans. TSH is secreted from anterior pituitary gland.
(c) Tetraiodothyronine is an emergency hormone.
Ans. Tetraiodothyronine is a maintenance hormone.
(d) The pineal gland is located on the anterior part of the kidney.
Ans. The adrenal gland is located on the anterior part of the kidney.
Q.11. Rearrange the following hormones in Column I so as to match with their chemical nature in Column II.
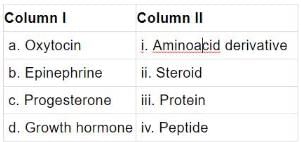
Ans. (a) → (iii), (b) → (i), (c) → (ii), (d) → (iv)
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. What is the role-played by luteinizing hormones in males and females respectively?
Ans. Luteinizing hormones play following roles:
In Males: It stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone.
In Females: It stimulates ovulation.
Q.2. What is the role of second messenger in hormone action?
Ans. Extracellular substances such as some hormones which do not cross the plasma membrane are called first messenger. In such cases, second messengers are released to enter the cell. Second messengers trigger various physiological changes in a cell. Thus, second messengers play the role of relaying the signals from first messengers.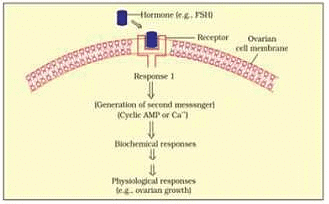 Q.3. On an educational trip to Uttaranchal, Ketki and her friends observe that many local people were having swollen necks. Please help Ketki and her friends to find out the solutions to the following questions.
Q.3. On an educational trip to Uttaranchal, Ketki and her friends observe that many local people were having swollen necks. Please help Ketki and her friends to find out the solutions to the following questions.
(a) Which probable disease are these people suffering from?
(b) How is it caused?
(c) What effect does this condition have on pregnancy?
Ans. (a) These people are suffering from goitre.
(b) Goitre is caused by dietary iodine deficiency.
(c) If a woman is suffering from goitre (which is associated with hypothyroidism); it can have deleterious effects on the foetus. It causes defective development and maturation of the growing baby leading to stunted growth (cretinism), mental retardation, abnormal skin, deaf-mutism, etc.
Q.4. George comes on a vacation to India from US. The long journey disturbs his biological system and he suffers from jet lag. What is the cause of his discomfort?
Ans. The body's biological clock operates on a 24-hour cycle known as the circadian rhythm. When someone travels across multiple time zones, this rhythm is disrupted, leading to jet lag. This condition can cause:
- Sleep disturbances
- Changes in bowel habits
- Loss of appetite
These symptoms result from the misalignment of the body's internal clock with the new local time.
Q.5. Inflammatory responses can be controlled by a certain steroid. Name the steroid, its source and also its other important functions.
Ans. Cortisol is the steroid that controls inflammatory responses. It is produced by the adrenal cortex and is one of the main corticoids secreted by the adrenal gland.
- Cortisol stimulates red blood cell (RBC) production.
- It helps the body respond to stress by modulating various physiological changes.
- Cortisol also has anti-inflammatory effects and suppresses the immune response.
Q.6. Old people have weak immune system. What could be the reason?
Ans. The thymus gland is crucial for the immune system, as it produces the hormone thymosin. This hormone helps in the development of T-lymphocytes, which are essential for the body's immune response. As people age:
- The thymus gland gradually degenerates.
- This degeneration leads to a decreased production of thymosin.
- Consequently, the immune response becomes weaker.
Thus, older individuals often experience a weakened immune system.
Q.7. What are the effects of hypothyroidism (observed during pregnancy) on the development and maturation of a growing baby?
Ans. If a woman is suffering from hypothyroidism; it can have deleterious effect on the development and maturation of the foetus. There can be stunted growth (cretinism) of the foetus which may result in an underweight newborn. The effects of hypothyroidism remains even after birth. The child's brain may not develop properly and show mental retardation. The child can also exhibit abnormal skin and deaf-mutism.
Q.8. Mention the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Ans.
| Hypothyroidism | Hyperthyroidism |
| (i) Involves less than normal production of thyroid hormone. | (i) Involves more than normal production of thyroid hormone. |
| (ii) Reduces metabolic rate. | (ii) Increases metabolic rate. |
| (iii) May happen because of iodine deficiency. | (iii) May happen because of development of tumor or nodules in thyroid gland. |
| (iv) Symptoms include fatigue, dry hair, dry skin, muscle cramps, decreased menstrual flow, etc. | (iv) Symptoms include feeling hot, forgetfulness, sweating, increased heart rate, disturbed bowel movement, etc. |
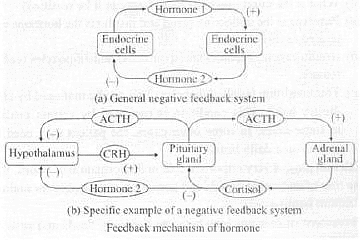
Q.9. You have learnt that a characteristic feature of endocrine system is the presence of feed back loops. By this what is meant if hormone A stimulates gland ‘X’ to secrete hormone B, the production of ‘A’ could be modified when the level of B changes in our blood. An example is the relation between hormones LH and estrogen (E2). An old woman exhibits the following features. High levels of LH in blood but low levels of E2 in the blood. Another woman exhibits high level of LH in blood and also high level of E2 in the blood. Where is the defect in both these women? Provide suitable diagram to support this answer.
Ans. The levels of LH (luteinising hormone) in the blood vary throughout a woman's life, particularly before and after puberty. During the reproductive phase, LH levels fluctuate based on the ovulation cycle. Typically, LH peaks just before ovulation, coinciding with a rise in estrogen (E2) levels, which is a normal physiological response. In older women, however, the situation changes:
- High levels of LH are present in the blood.
- Low levels of E2 indicate the cessation of the reproductive phase.
This condition is often associated with menopause, which marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. After menopause, the ovaries have few or no oocytes left, leading to:
- Increased LH levels due to decreased feedback inhibition.
- Low E2 levels as the ovaries are no longer producing significant amounts of this hormone.
In contrast, if another woman exhibits both high LH and high E2 levels, this may suggest a different hormonal imbalance or condition that requires further investigation.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. A milkman is very upset one morning as his cow refuses to give any milk. The milkman’s wife gets the calf from the shed. On fondling by the calf, the cow gave sufficient milk. Describe the role of endocrine gland and pathway associated with this response?
Ans. Milk secretion in mammals is stimulated by hormone oxytocin which works on positive feedback mechanism.
(a) When the calf sucks the cow's udder; it triggers nerve impulses.
(b) Nerve impulses send signals to the hypothalamus which starts secreting oxytocin.
(c) Oxytocin causes the contraction of smooth muscles around the alveoli (in udder)and milk is released.
The following figure shows the positive feedback mechanism of oxytocin.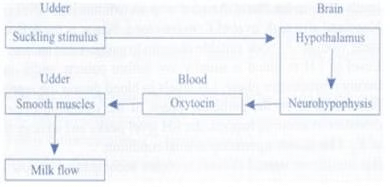 Q.2. A sample of urine was diagnosed to contain high content of glucose and ketone bodies. Based on this observation, answer the following:
Q.2. A sample of urine was diagnosed to contain high content of glucose and ketone bodies. Based on this observation, answer the following:
(a) Which endocrine gland and hormone is related to this condition?
(b) Name the cells on which this hormone acts.
(c) What is the condition called and how can it be rectified?
Ans. (a) Pancreas is the endocrine gland and insulin is the hormone which is related to this condition.
(b) Insulin acts on hepatocytes (liver cells) and adipocytes (cells of fat tissue).
(c) This condition is called diabetes. This can be managed by changing dietary habits, medications etc. In some cases, the patient may need to take insulin on a daily basis.
Q.3. Calcium plays a very important role in the formation of bones. Write on the role of endocrine glands and hormones responsible for maintaining Calcium homeostasis.
Ans. Movement of calcium ions between the body fluids and cells can be termed as calcium homoeostasis. Calcium plays an important role in various metabolic processes and is also an integral part of the bones. Hence, relative levels of calcium in body fluids, cells and bones are highly important. Both thyroid and parathyroid hormones play significant roles in calcium homeostasis.
Role of Thyrocalcitonin (TCT): This hormone is secreted by thyroid gland. It reduces the blood Ca++ level. Thus, it helps in increasing the availability of calcium to the bones.
Role of Parathyroid Hormone: This hormone is secreted by parathyroid gland. It increases the blood Ca++ level. Thus, it ensures the availability of calcium for many other metabolic functions.
It can be said that the roles of TCT and PTH are antagonistic to each other. Thus, they balance the effects of each other.
Q.4. Illustrate the differences between the mechanism of action of a protein and a steroid hormone.
Ans.
| Protein hormones | Steroid hormones |
| (i) They interact with membrane bound receptors. | (i) They interact with intracellular receptors. |
| (ii) They generate second messenger for further action. | (ii) They do not generate second messenger. |
| (iii) Effect of these hormones alters cellular metabolism. | (iii) Effect of these hormones regulates gene expression or chromosome function. |
| (iv) Examples: insulin, glucagon, etc. | (iv) Examples:cortisol,testosterone,etc. |
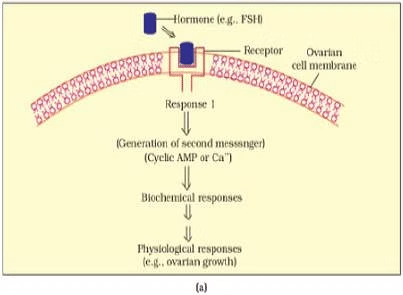
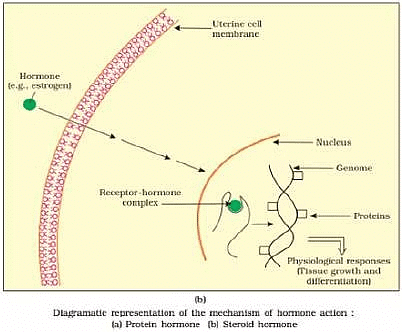 Q.5. Hypothalamus is a super master endocrine gland. Elaborate.
Q.5. Hypothalamus is a super master endocrine gland. Elaborate.
Ans. Hypothalamus contains several groups of neurosecretory cells called nuclei which produces hormones. These hormones regulate the synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormones. It produces two types of hormones, i.e. releasing hormones (that stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones) and inhibiting hormones (that inhibit secretion of pituitary hormones) Pituitary gland secretes the maximum number of hormones. But many hormones secreted from pituitary gland control the function of other endocrine glands. In fact; all the other endocrine glands are controlled by the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. Following are some examples:
• Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) controls the function of thyroid gland.
• Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) controls the function of adrenal gland.
• Luteinizing Hormone (LS) controls the function of gonads.
Hence, pituitary gland is often termed as the ‘Master Gland’. But the hormones secreted by hypothalamus controls the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. Due to this, hypothalamus can be termed as the “Super Master Gland”.
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplars: Chemical Coordination & Integration - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is chemical coordination in living organisms? |  |
| 2. What are the main functions of hormones in the body? |  |
| 3. Which glands are part of the endocrine system? |  |
| 4. How do hormones exert their effects on target cells? |  |
| 5. What is the role of feedback mechanisms in hormone regulation? |  |

















