NCERT Exemplars: The Living World - 1 | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics
(a) Will decrease
(b) Will increase
(c) Remain the same
(d) May increase or decrease
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (a)
- As we go higher from species to the kingdom, the number of common characteristics goes on decreasing.

- The lower the taxa, the more are the characteristics that the members within the taxon share.
- The higher the category, the greater is the difficulty of determining the relationship to other taxa at the same level.
NCERT Reference: Topic “Kingdom” From Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.2. Which of the following ‘suffixes’ used for units of classification in plants indicates a taxonomic category of 'family’?
(a) —ales
(b) —onae
(c) —aceae
(d) —ae
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (c)
(a) —ales —> Order (plant)
(b) —onae —> Class (plant)
(c) —aceae —> Family (plant)
(d) —ae —> Phylum (plant)
- "aceae" is the suffix used in the classification of plants to define the taxonomic division of "family". Families hold fifth place in the taxonomic classification.
- The plant family name is a plural adjective and is formed by adding a suffix-aceae. Some examples are Rosaceae, Linaceae, and Cucurbitaceae.
Q.3. The term ‘systematics’ refers to
(a) Identification and study of organ systems of plants and animals.
(b) Identification and preservation of plants and animals.
(c) Diversity of organisms and their relationship.
(d) Study of habitats of organisms and their classification.
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Human beings were, for long, interested in knowing more about different kinds of organisms and their diversities and the relationships among them. This branch of study was referred to as systematics.
- Systematics takes into account of evolutionary relationships between organisms.
NCERT Reference: Topic Page No. 8 of Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.5. The taxonomic unit ‘Phylum’ in the classification of animals is equivalent to which hierarchical level in the classification of plants?
(a) Class
(b) Order
(c) Division
(d) Family
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Classes comprising animals like fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals constitute the next higher category called Phylum. All these classes are included in the phylum Chordata.
- In plants' case, classes with a few similar characters are assigned to a higher category called Division.
NCERT Reference: Topic “Phylum” from Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.6. Botanical gardens and zoological parks have
(a) Collection of endemic living species only
(b) Collection of exotic living species only
(c) Collection of endemic and exotic living species
(d) Collection of only local plants and animals
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Botanical gardens and zoological parks are specialised places where living plants are grown and living animals are kept (where they can reproduce too) respectively.
- Both, endemic (local), as well as exotic (foreign to that place) species, are kept in these places.
- They can be used for scientific studies.
- Botanical garden at Kew, England and Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah (India) examples.

NCERT Reference: Topic “Botanical Garden” from Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.7. The taxonomic key is one of the taxonomic tools in the identification and classification of plants and animals. It is used in the preparation of:
(a) Monographs
(b) Flora
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (c)
A taxonomic key is a simple tool that is used to identify a living organism. The keys are used in the preparation of both monographs and flora.
(i) Flora contains the actual account of habitat and distribution of plants of a given area. These provide the index to the plant species found in a particular area.
(ii) Manuals are useful in providing information to identify names of species found in an area. Monographs contain information on any one taxon, i.e. any one genus or family at a particular time. They also help with incorrect identification.
NCERT Reference: Page No. 14 of Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.8. All living organisms are linked to one another because
(a) They have the common genetic material of the same type.
(b) They share common genetic material but to varying degrees.
(c) All have a common cellular organization.
(d) All of the above
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (b)
They share common genetic material but to varying degrees. In fact, the whole theory of evolution is based on the similarity of genetic materials which indicates common ancestry for living organisms. Variations in the similarity of genetic material give biodiversity which we see all around us.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 5- last Paragraph from Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.10. Match the following and choose the correct option.
(a) D—(i), C—(ii), E—(iii), B—(iv), A-(v)
(b) E—(i), D—(ii), B—(iii), A—(iv), C-(v)
(c) D—(C), E—(ii), B—(iii), A—(iv), C-(v)
(d) E—(i), C—(ii), B—(iii), A—(iv), D-(v)
Ans: Correct Answer is Option (a)
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Linnaeus is considered the Father of Taxonomy. Name two other botanists known for their contribution to the field of plant taxonomy?
Ans: The natural system of classification for flowering plants was given by George Bentham and Joseph Dalton Hooker, in a three-volume of Genera Plantarum.
Q.2. What does ICZN stand for?
Ans: ICZN stands for International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.
Q.3. Couplet in taxonomic key means _____
Ans: The keys are based on the contrasting characters generally in a pair called a couplet. It represents the choice made between two opposite options. This results in the acceptance of only one and the rejection of the other.
NCERT Reference: Topic “key” from Chapter 1 from NCERT
Q.4. What is a Monograph?
Ans: Monographs contain information on anyone taxon, i.e. anyone genus or family at a particular time.
NCERT Reference: Topic “Key” from Chapter 1 from NCERT
Q.5. Amoeba multiplies by mitotic cell division. Is this phenomenon growth or reproduction? Explain.
Ans: Amoeba is a unicellular organism. It undergoes division and gives rise to two Amoeba. Therefore, in unicellular organisms, cell division is the same as reproduction. It is a form of asexual reproduction called binary fission.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 4- Reproduction from chapter 1
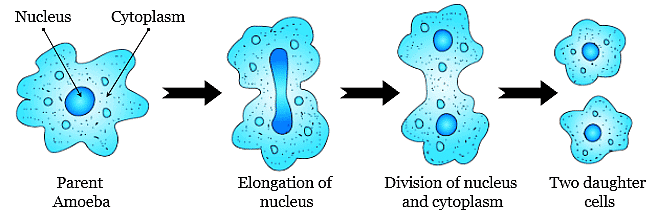 Binary fission in Amoeba
Binary fission in Amoeba
Q.6. Define Metabolism.
Ans: Metabolism refers to a series of chemical reactions that occur in a living organism to sustain life.
NCERT Reference: Page No. 4- Reproduction from Chapter 1 of NCERT
 Process of Metabolism
Process of Metabolism
Q.7. Which is the largest botanical garden in the world? Name a few well known botanical gardens in India.
Ans:
- The largest famous botanical garden globally is Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (London), England.
- India's largest botanical garden is Indian Botanical Garden, Shibpur Howrah, Kolkata, West Bengal. National Botanical Research Institute is situated at Lucknow (India).
NCERT Reference: Topic “Botanical Garden” from Chapter 1 from NCERT
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. A ball of snow when rolled over snow increases in mass, volume, and size. Is this comparable to growth as seen in living organisms? Why?
Ans: No, this is not comparable to growth as seen in living organisms. Non-living objects like snowball also grow if we increase body mass as a criterion for growth. However, this kind of growth exhibited by non-living objects is by accumulating material on the surface (accretion). In living organisms, growth is from the inside because of accumulation of material inside the cells of the organisms i.e. through mitosis & meiosis.
NCERT Reference: Page No. 3- Growth from Chapter 1 of NCERT
Q.2. In a given habitat we have 20 plant species and 20 animal species. Should we call this ‘diversity’ or ‘biodiversity’? Justify your answer.
Ans: In a given habitat we have 20 plant species and 20 animal species. We can call this ‘biodiversity’. Because “bio” refers to living and diversity means “variation or variety”. Each different kind of plant, animal, or organism that we see represents a species. This refers to biodiversity or the number and types of organisms present on earth.
NCERT Reference: Topic “Diversity in The Living World” from Chapter 1 from NCERT
Q.3. International Code of Botanical nomenclature (ICBN) has provided a code for the classification of plants. Give hierarchy of units of classification botanists follow while classifying plants and mention different ‘Suffixes’ used for the units.
Ans:

Q.4. A plant species shows several morphological variations in response to the altitudinal gradient. When grown under similar growth conditions, the morphological variations disappear, and all the variants have common morphology. What are these variants called?
Ans: Ecotypes are plant species that show morphological differences in response to an altitudinal gradient. When plants are exposed to climatic and other biotic & abiotic differences, their populations undergo genetic changes in order to adapt to their new surroundings. When given similar conditions, however, these groups can interbreed and achieve the same morphological features.
Euphorbia hirta, Arabidopsis thaliana, and other plants are examples.

Q.5. How do you prepare your own Herbarium sheets? What are the different tools you carry with you while collecting plants for the preparation of a herbarium? What information should a preserved plant material on the herbarium sheet provide for taxonomic studies?
Ans: Following are the various steps of preparing a herbarium:
 Herbarium Sheet
Herbarium Sheet
(ii) Pressing: This step involves spreading the specimen and pressing it between two sheets of paper to preserve most parts.
(iii) Drying: This step usually involves drying under the sun.
(iv) Poisoning: Sometimes, antifungal treatment needs to be given to the specimen to preserve it for a longer duration.
(v) Mounting: This step involves mounting the specimen over a herbarium sheet.
(vi) Labelling: This step involves writing full information and classification of the specimen.
- Different tools that need to be carried while collecting plants for the preparation of a herbarium are; digger and pruning knife, sickle, vasculum, polythene bags, old newspaper or magazine, blotting paper, plant press, field notebooks, herbarium sheets, glue, labels, etc.
- The preserved material should have thorough information and classification. This should include the names of division, order, family, genus, and species.
Q.6. What is the difference between flora, fauna, and vegetation? Eichhornia crassipes is called an exotic species while Rauwolfia serpentina is an endemic species in India. What do these terms exotic and endemic refer to?
Ans: The sum of plant species in a given geographical area is called the flora of that area. The sum of animal species in a given geographical area is called the fauna of that area. The term ‘vegetation’ has a wider scope than the term ‘flora’. Vegetation is often used for a much wider geographical area than a particular ecosystem. In many cases, the term ‘vegetation’ is used for all the plants globally.
- Endemic Species: A species found only in a particular geographical area is called the endemic species.
Example: Rauwolfia serpentina is found only in India. So, it is an endemic species in India. Rauwolfia serpentina
Rauwolfia serpentina - Exotic Species: A species that is not naturally found in a particular area but maybe living because of careful selection and breeding or because of being imported is called an exotic species.
Example: Eichhornia crassipes is native to another country, but it was introduced in India. So, it is an exotic species in India. Eichhornia crassipes
Eichhornia crassipes
Q.7. A plant may have different names in different regions of the country or world. How do botanists solve this problem?
Ans:
- There are many languages and even more, dialects being spoken in different parts of the world. This means a plant may have different names in different regions of the country or world. This compounds the problem for anybody because nobody can remember all those names.
- To solve this problem, botanists have devised a binomial nomenclature system so that a particular species can have a unique name for scientific study.
- A botanical name is usually composed of two terms, viz. genus name and species name. Care is taken to make a unique name for a particular species.
NCERT Reference: Topic “Diversity in The Living World” from Chapter 1 from NCERT
Q.8. Brinjal and potato belong to the same genus Solanum, but to two different species. What defines them as separate species?
Ans: “Species is a group of potentially interbreeding groups that are reproductively isolated from other such groups”. Brinjal and potato belong to the same genus Solanum, but to two different species as they have distinct morphological differences and are reproductively isolated.
Brinjal → Solanum melongena
Potato → Solanum tuberosum
Q.9. Properties of cell organelles are not always found in the molecular constituents of cell organelles. Justify.
Ans: Properties of cellular organelles are not present in the molecular constituents of the organelle but arise as a result of interactions among the molecular components comprising the organelle. For example, Ribosome is a non-membrane bound cell organelle, which is a site for protein synthesis. It is made of proteins and rRNA. If these components are separated, individually, they cannot perform the process of protein synthesis. So, the given statement is true.
Q.10. The number and kinds of an organism are not constant. How do you explain this statement?
Ans:
- The number and types of creatures that exist at any particular time are determined by the environmental factors that exist at the time.
- With period, these conditions will change, resulting in the extinction of certain species and the evolution and adaptation of others to the formation of new species.
For example, Reptiles dominated the Mesozoic era, with dinosaurs abundant and diverse, whereas flowering plants had only recently emerged.
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplars: The Living World - 1 - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the importance of biodiversity in the living world? |  |
| 2. How does deforestation impact the living world? |  |
| 3. What are the major threats to biodiversity in the living world? |  |
| 4. How can individuals contribute to conserving biodiversity in the living world? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of conservation strategies used to protect the living world's biodiversity? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|






















