NCERT Summary: The Earth in the Solar System | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Celestial Bodies
By definition, a celestial body is any natural body outside of the Earth’s atmosphere. Easy examples are the Moon, Sun, and the other planets of our solar system. Any asteroid in space is a celestial body.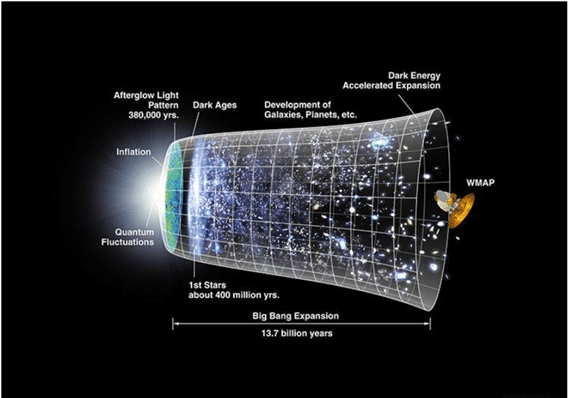 Big Bang theory
Big Bang theory
Stars
Stars are celestial objects that can produce their own light. They are extremely hot and extremely large. They are made up of gases. The Sun is a star. Sun
Sun
Constellation
A group of stars forming a recognizable pattern that is traditionally named after its apparent form or identified with a mythological figure.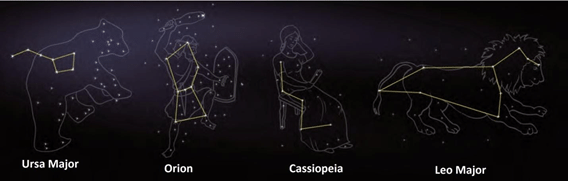 Constellations
Constellations
Pole Star
It also called (Northern Hemisphere) North Star, It is a bright star that can be seen in the sky in northern parts of the world when one looks directly toward the north.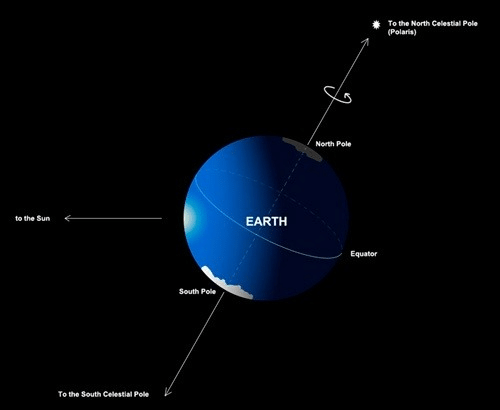 Polaris - Pole Star
Polaris - Pole Star
Planet
A celestial body that does not has its own heat and light. It is lit by the light of the stars. Such a body is called a planet.
IAU Definition: A Planet is a celestial body that orbits around the sun, has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and also has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit.
The Solar System
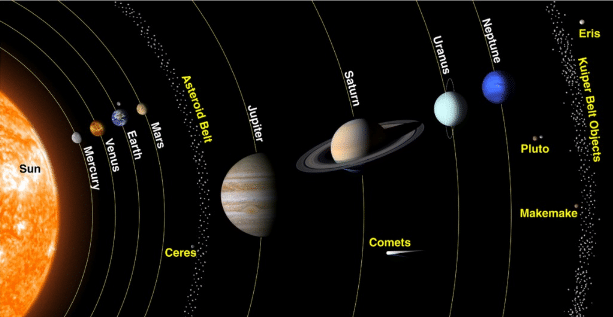 The Solar System
The Solar SystemThe solar system consists of our star, the Sun, and everything bound to it by gravity viz., the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, dwarf planets such as Pluto, dozens of moons, and millions of asteroids, comets and meteoroids.
The Sun
The sun is in the center of the solar system. It is huge and made up of extremely hot gases. It provides the pulling force that binds the solar system. The Sun is the ultimate source of heat and light for the solar system.
The sun is about 150 million km away from earth. The Sun
The Sun
Planets
There are eight planets in our solar system. In order of their distance from the sun, they are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and one draft planet Pluto.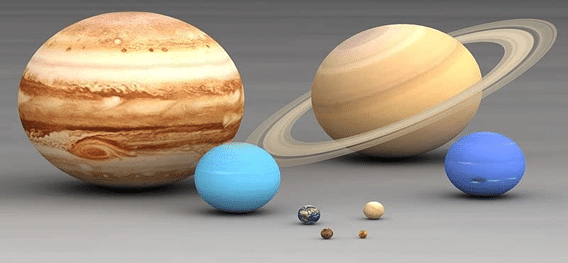 Planets of our Solar System
Planets of our Solar System
- An easy way to memorize the name of the planets in order of their distance from the sun is: My Very Efficient Mother Just Served Us Noodles.
(Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) - All the eight planets of the solar system move around the sun in fixed paths.
- These paths are elongated and called orbits.
- Mercury is nearest to the sun and takes only about 88 days to complete one round along its orbit.
- Neptune is supposed to be farthest till now and takes about 165 Earth years to complete one round around the Sun.
- Venus is considered as ‘Earth-Twin’ because its size and shape are very much similar to that of the Earth.
- Before 2006 Pluto was 9th Planet of the solar system. It was invented in the 1930s but after 1992 it was questioned and in 2006 the International Astronomical Union classified it as Dwarf Planet.
The Earth
- The Earth is the third nearest planet to the Sun. In size, it is the fifth-largest planet.
- Takes about 365 days (1 year) to orbit around the Sun.
- The surface of Earth is 70% water and plate tectonics.
- Earth has one Moon.
- It is slightly flattened at the poles. That is why its shape is described as a Geoid (It means an earth-like shape).
- Conditions favourable to support life are probably found only on the Earth.
- The earth is neither too hot nor too cold.
- It has water and air, which are very essential for life on Earth.
- The air has life-supporting gases like oxygen which put the earth in a unique position in the solar system.
- From outer space, the Earth appears blue because two-third of its surface is covered by water. (Therefore, called a blue planet).
The Moon
- The Earth has only one satellite, that is, the moon. Its diameter is only one quarter that of the earth.
- There are many moons in the solar system and rotates around the planet as moon around the earth. The moon appears very big to us because it is very nearer to the earth around 384,400 km.
- The moon moves around the earth in 27 days. It takes the exact same time to complete one spin. As a result, only one side of the moon is visible to us on the earth. This characteristic of the moon is responsible for the phenomena of the full moon (Poornima) and New moon night (Amavasya).
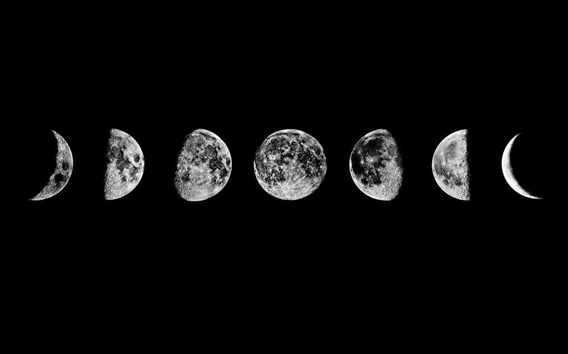 Moon Phases
Moon Phases - The moon does not have conditions favourable for life. It has neither water nor air. It has mountains.
Asteroids
Asteroids are numerous tiny bodies that also move around the Sun apart from the stars, planets, and satellites. They are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Scientist assumes that asteroids are part of a planet which may be exploded many years back.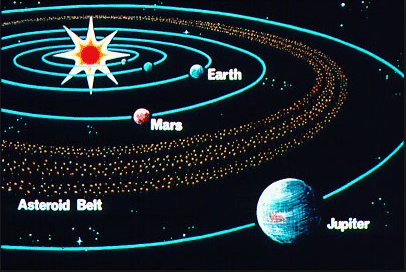 Asteroid Belt
Asteroid Belt
Meteors
- Meteors, also known as shooting stars, are pieces of dust and debris from space that burn up in Earth's atmosphere, where they can create bright streaks across the night sky.
- When Earth passes through the dusty trail of a comet or asteroid's orbit, the many streaks of light in the sky are known as a meteor shower.
Meteorites
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon.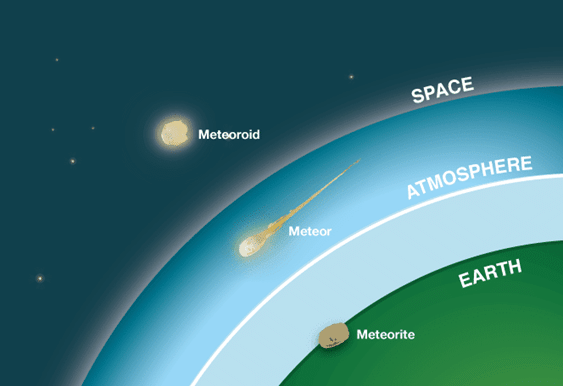 Meteorite
Meteorite
Earth Cosmic Address


|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: The Earth in the Solar System - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is a celestial body? |  |
| 2. How many celestial bodies are there in the solar system? |  |
| 3. What is the Earth's position in the solar system? |  |
| 4. What are some characteristics of celestial bodies? |  |
| 5. How do celestial bodies interact with each other? |  |

















