NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Civics Chapter 3 - Gender, Religion and Caste
Q1. Mention different aspects of life in which women are discriminated or disadvantaged in India.
Ans: The different aspects of life in which women are discriminated or disadvantaged in India are:
- Sex-ratio: In India, sex-selective abortions occur due to a preference for male children, with a sex ratio of 927 girls to 1000 boys, and even lower in some areas.
- Literacy: The literacy rate for women is 54% compared to 76% for men, as many girls drop out of school. Financially weak parents often prioritize sons’ education or save for daughters' dowries instead of their education.
- High-paid Jobs: Women are underrepresented in high-paying jobs due to barriers like early marriage, lack of access to higher education, and financial constraints.
- Safety: Sexual harassment and domestic violence are common, making it difficult for women to pursue their goals, fueled by the belief that women are weaker and lack protection from authorities in a patriarchal society.
Q2. State different forms of communal politics with one example each.
Ans: Different forms of communal politics:
- The expression of communal superiority in everyday beliefs.
Example: Militant religious groups. - The desire to form a majoritarian dominance or a separate state.
Example: Separatist leaders and political parties in Jammu and Kashmir and Central India. - The use of religious symbols and leaders in politics to appeal to the voters.
Example: Hate speeches against particular minorities during elections. - Communal politics can take the form of communal violence and riots.
Example: The riots in Gujarat in 2002.
Q3. State how caste inequalities are still continuing in India.
Ans: Caste inequalities are still continuing in India in the following ways:
- Most people still marry within their own caste or tribe, and inter-caste marriages are often discouraged, especially by upper castes.
- Despite being banned by the Constitution, untouchability persists, particularly in rural areas.
- Groups with historical access to education continue to excel, while those previously excluded still lag behind.
- Caste contributes to economic inequality, as it affects access to resources. Upper castes are best off, Dalits and Adivasis are worst off, with backward classes in between.
- Poverty is more prevalent among lower castes, with higher rates among rural landless laborers. In 1999-2000, poverty rates were 45.8% for STs, 35.9% for SCs, and 27% for OBCs in rural areas.
Q4. State two reasons to say that caste alone cannot determine election results in India.
Ans: Caste alone cannot determine election results in India because:
- No parliamentary constituency has a clear majority of one single caste. Hence, every candidate and party needs to win the candidate of more than one caste/community to win elections.
- No party wins all the votes of a particular caste. When it said that caste is a 'vote bank' of one party, it means that a large proportion of the voters from that caste vote for that party.
Q5. What is the status of women’s representation in India’s legislative bodies?
Ans: The status of women’s representation in India’s legislative bodies is very less as mentioned below:
- In Lok Sabha, the percentage of elected women members has never reached even 10 per cent of its total strength.
- Their share in the state assemblies is less than 5 per cent. India is among the bottom group of nations in the world in this respect.
- Thus the proportion of women in legislative bodies has been very low. Women’s organisations and activists have been demanding reservation of at least one-third of seats in the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies for women.
Q6. Mention any two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state.
Ans: Two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state are:
- The Constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion, or not to follow any.
- The Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
 Secular India
Secular India
Q7. When we speak of gender divisions, we usually refer to:
(a) Biological difference between men and women
(b) Unequal roles assigned by the society to men and women
(c) Unequal child sex ratio
(d) Absence of voting rights for women in democracies
Ans: (b) Unequal roles assigned by the society to men and women
Gender division usually refers to the societal assignment of unequal roles, responsibilities, and expectations to men and women, which often leads to inequality and discrimination.
 Unequal Roles Assigned
Unequal Roles Assigned
Q8. In India, seats are reserved for women in
(a) Lok Sabha
(b) State Legislative Assemblies
(c) Cabinets
(d) Panchayati Raj bodies
Ans: (d) Panchayati Raj bodies
In India, seats are reserved for women in Panchayati Raj bodies, which are the rural local government institutions. This reservation aims to promote women's participation in local governance.
 Panchayati Raj Bodies
Panchayati Raj Bodies
Q9. Consider the following statements on the meaning of communal politics. Communal politics is based on the belief that:
Α. One religion is superior to that of others.
Β. People belonging to different religions can live together happily as equal citizens.
C. Followers of a particular religion constitute one community.
D. State power cannot be used to establish the domination of one religious group over others.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) A, B, C and D
(b) A, B and D
(c) A and C
(d) B and D
Ans: (c) A and C
Communal politics is based on the belief that one religion is superior to others and followers of a particular religion form one community. Statements Β and D represent principles of secularism and equal citizenship, which are contrary to communal politics.
Q10. Which among the following statements about India’s Constitution is wrong? It
(a) prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion
(b) gives official status to one religion
(c) provides to all individuals freedom to profess any religion
(d) ensures equality of citizens within religious communities
Ans: (b) gives official status to one religion
India’s Constitution does not give official status to any religion; it promotes secularism and prohibits discrimination based on religion.
Q11. Social divisions based on ______________ are peculiar to India.
Ans: Social divisions based on caste are peculiar to India.
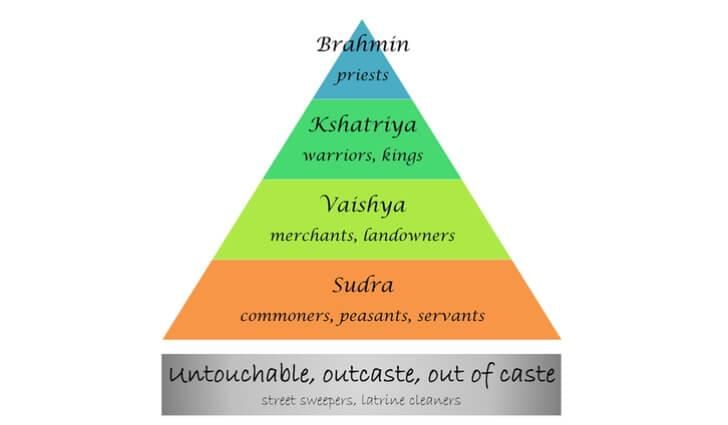 Caste
Caste
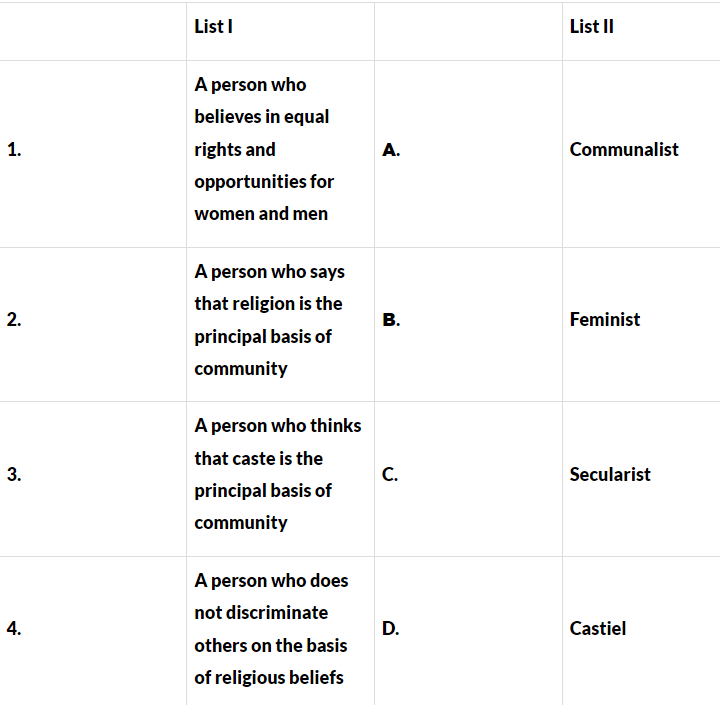
Q12. Match List I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
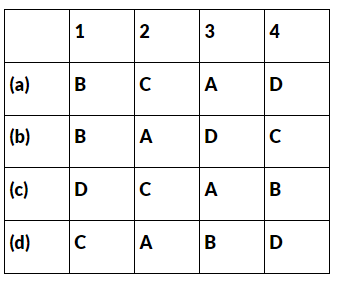
Ans: (b) B, A, D, C is the correct answer.
|
65 videos|517 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Civics Chapter 3 - Gender, Religion and Caste
| 1. Gender, religion, and caste can influence social identity in what ways? |  |
| 2. How does the intersectionality of gender, religion, and caste affect individuals in India? |  |
| 3. What role does education play in addressing issues of gender, religion, and caste in society? |  |
| 4. How can societal attitudes towards caste discrimination be changed? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of caste-based politics in India? |  |























