NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 18 |

|
| Page No. 22 |

|
| Page No. 25 |

|
| Page No. 28 |

|
| Page No. 33 |

|
| Exercises (Page No. 34 & 35) |

|
Page No. 18
Q1. You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water, and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Ans:
(i) Put the red litmus paper in all the test tubes, turn by turn. The solution which turns red litmus to blue will be a basic solution. The blue litmus paper formed here can now be used to test the acidic solution.
(ii) Put the blue litmus paper obtained above in the remaining two test-tubes, turn-by-turn. The solution which turns the blue litmus paper to red will be the acidic solution.
(iii) The solution which has no effect on any litmus paper will be neutral and hence it will be distilled water.
Page No. 22
Q1. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Ans:
Curd and sour substances should not be kept in brass and copper vessels because these and other sour food-stuffs contain acids which can react with the metal of the vessel to form poisonous metal compounds which can cause food poisoning and affect our health adversely.
Q2. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Ans:
Usually, hydrogen gas is liberated when an acid reacts with a metal. For example, let us take the reaction between zinc and sulphuric acid.
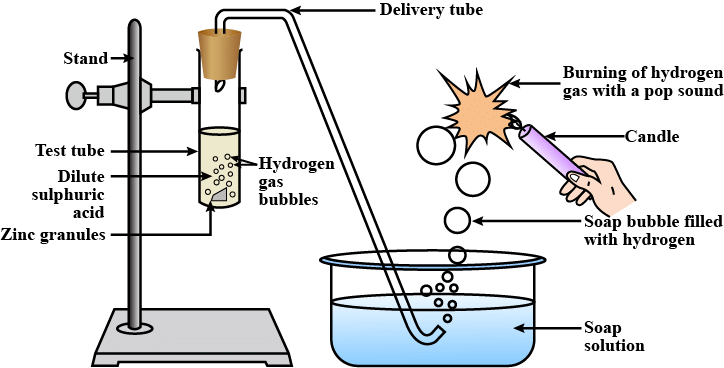
The reaction of zinc granules with dil. H2SO4 to liberate hydrogen gas which burns with a ‘pop’ sound
(i) Take 5 g of zinc granules in a test tube.
(ii) Set the apparatus, as shown in the diagram.
(iii) Add 20 mL of dil. H2SO4 with the help of a thistle funnel.
(iv) Collect the gas evolved in a gas jar, as shown in the figure.
(v) Observe the colour and odour of the gas.
(vi) Bring a burning matchstick near the gas jar and record your observations.
Observation: A colourless, odourless gas is evolved. It burns explosively with a ‘pop’ sound when a burning matchstick is brought near it, indicating the presence of hydrogen gas.
The pop sound is because whenever we bring hydrogen in contact with heat it expands , it is so fast that it breaks the sound barrier.
Chemical Reaction: Zn(s) + H2SO4(dil) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Q3. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Ans:
Calcium carbonate (A), when reacts with hydrochloric acid, produces carbon dioxide gas with effervescence. Carbon dioxide gas is used as a fire extinguisher. Therefore, it extinguishes a burning candle. Hence, the metal compound A is calcium carbonate.
Chemical Reaction: CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(s)+ CO2 (g) + H2O(l)
Page No. 25
Q1. Why do HCl, HNO3, etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Ans:
Release of H+ ion in water will make a compound acidic or non-acidic. Acids are substances which, upon dissociating with water, resulting in the production of Hydrogen ions. HCI, HNO3, etc. dissociate into their ions in the presence of water. They form hydrogen ions (H+). These hydrogen ions combine with H2O to form hydronium ions (H3O+).
The reaction can be given as follows:
HCl → H+ + Cl-
H+ + H2O → H3O+
Similarly, HNO3 → H+ + NO3-
H+ + H2O → H3O+
- Due to this property, HCl and HNO3 show acidic character in aqueous solutions. On the other hand, alcohol and glucose cannot dissociate in water to form hydrogen ions. Hence, they do not show acidic character.
Q2. Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Ans:
An aqueous solution of acid conducts electricity because of the presence of charged particles called ions in it. When dissolved in water, acids dissociate to form ions.
Example:
HCl + H2O → Cl- + H3O+
These ions are responsible for conducting electricity.
Q3. Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Ans:
Dry HCl gas do not change the colour of dry litmus paper because:
- We know that H+ ions of acid change the colour of the litmus.
- Dry HCI does not dissociate to give H+ ions.
- Acids dissociate to give ions only in the aqueous medium.
- Since in this case, neither HCI is in the aqueous form nor is the litmus paper wet, so the colour of the litmus paper does not change.
Q4. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Ans:
The process of dissolving an acid in water is highly exothermic. The acid must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring. If water is added to a concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause severe burns. The glass container may also break due to excessive heating.

Q5. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Ans:
- When a given amount of acid is added to water, there is a fixed number of hydronium ions per unit volume of the solution.
- On dilution number of hydronium ions per unit volume decreases and the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) decreases and becomes weak.
Q6. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH−) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Ans:
- The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) increases when the excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide.
- The concentration of (OH−) Hydroxide ions increases when the excessive base is added to the solution of Sodium Hydroxide as the base itself dissociates to give out OH− ions which increase their concentration per unit volume.
Page No. 28
Q1. You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6, and the pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of these is acidic, and which one is basic?
Ans:
Solution A has more H+ ion concentration. A pH value of less than 7 indicates the acidic nature, while greater than 7 indicates the basic nature of a solution. So, solution A is acidic, and solution B is basic.
Q2. What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Ans:
The concentration of H+(aq) can have a varied effect on the nature of the solution. With an increase in H+ ion concentration, the solution becomes more acidic, while a decrease in H+ ion causes an increase in the basicity of the solution.
Q3. Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Ans:
Yes, the basic solution also has H+(aq) ions. However, their concentration is less as compared to the concentration of OH- ions that makes the solution basic.
Q4. Under what soil conditions do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Ans:
If the farmer finds his soil to be more acidic, then to increase the basicity of the soil, he should treat the soil of his field with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate).
Page No. 33
Q1. What is the common name of the compound Ca(OCl)2?
Ans:
Bleaching Powder
Explanation: The compound Ca(OCl)2 is commonly known as bleaching powder. The reason for this common name is due to the compound's primary use. It is often used as a disinfecting agent and to bleach cotton and linen in the textile industry. The chemical name for this compound is calcium hypochlorite, but it is more widely recognized and referred to as bleaching powder.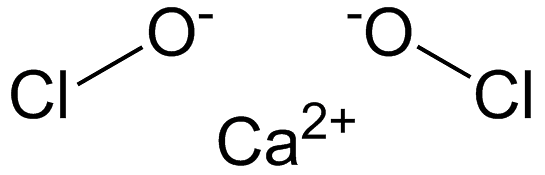 Bleaching powder structural formula
Bleaching powder structural formula
Q2. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder?
Ans:
Dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2].
Explanation: Bleaching powder, also known as Calcium hypochlorite [Ca(OCl)2], is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2]. This reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 → Ca(OCl)2 + CaCl2 + 2H2O
In this reaction, chlorine (Cl2) is added to dry slaked lime (Ca(OH)2) to produce bleaching powder (Ca(OCl)2), calcium chloride (CaCl2), and water (H2O). The chlorine oxidizes the calcium hydroxide to produce the calcium hypochlorite, which is the main component of bleaching powder. The calcium chloride is a byproduct of this reaction.
So, the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder is dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2].
Q3. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Ans:
Washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O)
Explanation: Hard water contains minerals like calcium and magnesium that can cause a buildup in plumbing and appliances, and make it difficult for soap to lather. Sodium carbonate, also known as washing soda or soda ash, is used to soften hard water. When added to water, it reacts with the calcium and magnesium ions, forming insoluble precipitates that can be removed from the water. This reduces the mineral content of the water, effectively "softening" it. The formula Na2CO3.10H2O represents washing soda, which means it is a hydrated salt with 10 molecules of water of crystallization.
Q4. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydro carbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Ans:
When sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated, then sodium carbonate and water are formed along with carbon dioxide gas evolution.
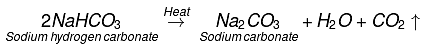
Q5. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Ans:
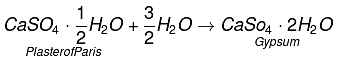
Exercises (Page No. 34 & 35)
Q1. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Ans: (d)
Solution: pH = 10, bases turn red litmus blue, and their pH is more than 7.
Q2. A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KCl
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Eggshells are made up of CaCO3 which reacts with HCl to form CO2, and this CO2 turns lime water milky.
Example:
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(dil)→ CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Q3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 ml of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 ml of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL
Ans: (d)
Solution:
∴ 10 mL of NaOH will neutralise
= 8 mL of HCI.
= 20 mL of NaOH will neutralise
= 8/10 x 20 = 16 mL.
Q4. Which one of the following types of medicines are used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic
Ans: (c)
Solution:
- Antacids are used to neutralise hyperacidity in the stomach due to excess of HCI which causes indigestion.
- Antibiotics are used to fight infections.
- Analgesics are pain killer while antiseptics prevent the growth of bacteria and other micro-organisms on wounds.
Q5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when:
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Ans:
(a)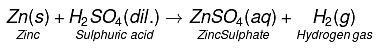
(b)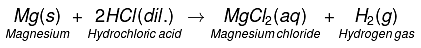
(c)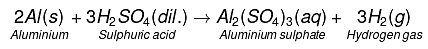
(d)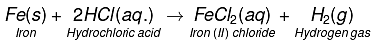
Q6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorized as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Ans:
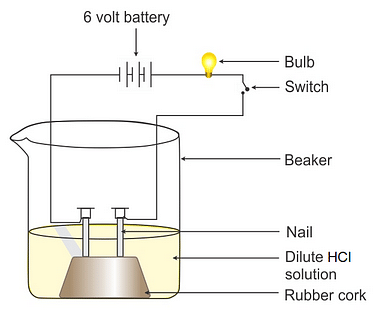
- Fix two iron nails on a cork and place this cork in a beaker.
- Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6-volt battery through a switch and a bulb, as shown in the figure.

- Now add some dilute hydrochloric acid in the beaker and switch on the current. Take the observation.
- Repeat the experiment separately with alcohol and glucose solution.
Observation: You will observe that in the case of dilute hydrochloric acid bulb glows, but when glucose or alcohol solution is taken in the beaker, the bulb does not glow.
Conclusion: The aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid conducts electricity due to the presence of types of charged particles: Hydrogen ions and chloride ions. Unlike acids glucose and ethanol do not ionise in an aqueous solution, i.e. they do not give H+ ions; therefore, they cannot conduct electricity. Thus, glucose and ethanol are not categorized as acids.
Q7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Ans:
- Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it does not contain any ionic compound (like acids, bases or salts) dissolved in it.
- Rainwater, while falling to the earth through the atmosphere, dissolves an acidic gas carbon dioxide from the air and forms carbonic acid (H2CO3).
- Carbonic acid provides hydrogen ions, H+ (aq) and carbonate ions, CO(aq)32to rainwater.
- Hence, due to the presence of carbonic acid which provides ions to rainwater, the rainwater conducts electricity.
Q8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Ans:
It is because acids do not dissociate into ions in the absence of water. But when an acid is dissolved in water, it forms hydrogen ions and hence, shows acidic behaviour.
Q9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) Neutral?
(b) Strongly alkaline?
(c) Strongly acidic?
(d) Weakly acidic?
(e) Weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
Ans: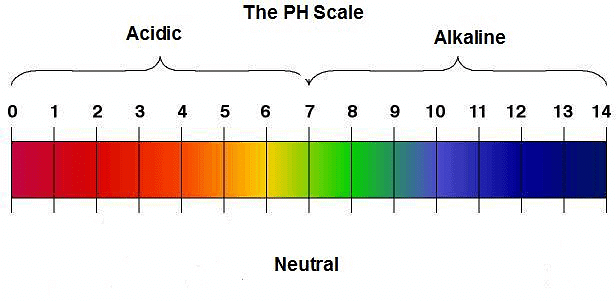 pH level from acidic to basic
pH level from acidic to basic
(b) Strongly alkaline → Solution C with pH 11
(c) Strongly acidic → Solution B with pH 1
(d) Weakly acidic → Solution A with pH 4
(e) Weakly alkaline → Solution E with pH 9
- The pH can be arranged in the increasing order of the concentration of hydrogen ions as: 11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1.
Ans:
Fizzing will occur more vigorously in test tube A. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a strong acid whereas acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid. Being strong acid, the hydrochloric acid solution contains a much greater amount of hydrogen ions in it due to which the fizzing will occur more vigorously in test tube A (containing hydrochloric acid). The fizzing is due to the evolution of hydrogen gas which is formed by the action of acid on the magnesium metal of magnesium ribbon.
Q11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Ans:
Milk contains carbohydrate lactose. When milk sets into curd, lactose gets converted into an acid called lactic acid. Due to the formation of lactic acid, the pH of milk falls below 6.
Q12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Ans:
(a) The milkman shifts the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline because, in alkaline conditions, milk does not set as curd easily.
(b) Since this milk is slightly basic than usual milk, acids produced to set the curd are neutralized by the base. Therefore, it takes a longer time for the curd to set.
Q13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Ans:
It will absorb water to form gypsum which sets into a hard solid mass. This will make Plaster of Paris useless after some time.
Example:
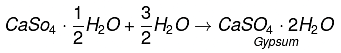
Q14. What is a neutralization reaction? Give two examples.
Ans:
A reaction in which an acid and base react with each other to give salt and water is termed as neutralization reaction.
Example:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) +H2O(l)
H2SO4(aq) + 2NH4OH(aq) → (NH4)2SO4(aq) + 2H2O
Q15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Ans:
 Uses of Washing Soda
Uses of Washing Soda
(i) It is used in the manufacture of glass, soap, paper, and other sodium compounds like borax, etc.
(ii) It is used in softening hard water.
Uses of Baking Soda
(i) It is used as an antacid to neutralise the excess of acidity (hyper-acidity) in the stomach.
(ii) It is an ingredient of baking powder that contains NaHCO3 and tartaric acid.
(iii) It is used in making soda acid fire extinguishers.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts
| 1. What are acids and bases? |  |
| 2. How do acids and bases neutralize each other? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of acids and bases? |  |
| 4. How do acids and bases affect indicators? |  |
| 5. How are acids and bases used in everyday life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|