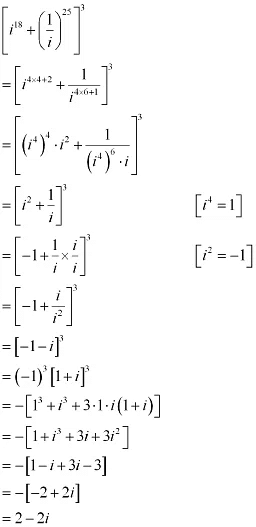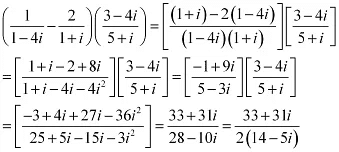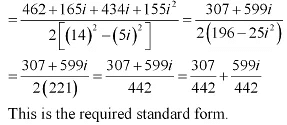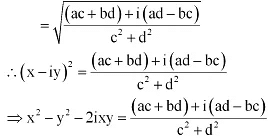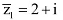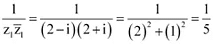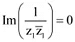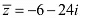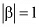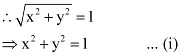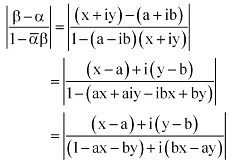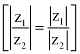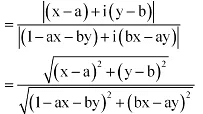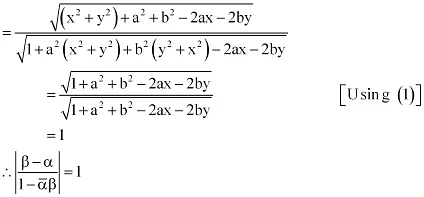NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 4 - Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Exercise 4.1
Que 1: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib : (5i)( -35 i)
Ans:
( -35 i) = -5 x -35 × i × i
= -3i2
= -3 × (-1) [i2 = -1]
= 3
Que 2: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: i9+ i19
Ans:
i9 + i19 = i4×2+1 + i4×4+3
= (i4)2 · i + (i4)4 · i3
= 1 × i + 1 × (−i) [i4 = 1, i3 = −i]
= i + (−i)
= 0
Que 3: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: i–39
Ans:
i−39 = i−4×9−3 = (i4)−9 · i−3
= (1)−9 · i−3 [i4 = 1]
= 1/i3 = 1/−i [i3 = −i]
= −1/i × i/i
= −i/i2 = −i/−1 [i2 = −1]
= i
Que 4: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: 3(7 + i7) + i(7 + i7)
Ans:
3(7 + 7i) + i(7 + 7i) = 21 + 21i + 7i + 7i2
= 21 + 28i + 7 × (−1) [∵ i2 = −1]
= 14 + 28i
Que 5: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: (1 – i) – (–1 + i6)
Ans:
(1 − i) − (1 + i6) = 1 − i + 1 − 6i
= 2 − 7i
Que 6: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: ( 15 + i 25) − ( 4 + i 52 )
Ans:
( 15 + i 25) − ( 4 + i 52 )
= 15 − 4 + i 25 − i 52
= ( 15 − 4) + i( 25 − 52)
= −195 + i −2110
= −195 − i 2110
Que 7: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib:[ 13 + i 73 ] + [ 43 + i 13 ] − ( −43 + i)
Ans:
[ 13 + i 73 ] + [ 43 + i 13 ] − ( −43 + i)
= 13 + i 73 + 43 + i 13 + 43 − i
= ( 13 + 43 + 43) + i( 73 + 13 − 1)
= 173 + i 53
Que 8: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: (1 – i)4
Ans:
(1 − i)4 = [(1 − i)2]2
= [12 + i2 − 2i]2
= [1 − 1 − 2i]2
= (−2i)2
= (−2i) × (−2i)
= 4i2 = −4 [∵ i2 = −1]
Que 9: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: ( 13 + 3i)3
Ans:
( 13 + 3i)3 = 133 + (3i)3 + 3 13(3i)( 13 + 3i)
= 127 + 27i3 + 3i( 13 + 3i)
= 127 + 27(−i) + i + 9i2 [i3 = −i, i2 = −1]
= 127 − 27i + i − 9
= ( 127 − 9) + i(−27 + 1)
= −24227 − 26i
Que 10: Express the given complex number in the form a + ib: (−2 − 13 i)3
Ans:
(−2 − 13 i)3 = (−1)3(2 + 13 i)3
= −[ 23 + (13 i)3 + 3(2)( 13 i )(2 + 13 i)]
= −[ 8 + i327 + 2i( 2 + i3)]
= −[ 8 − i27 + 4i + 2i23] [i3 = −i, i2 = −1]
= −[ 8 − i27 + 4i − 23]
= −[ 223 + i( 10727)]
= 223 − 10727 i
Que 11: Find the multiplicative inverse of the complex number: 4 – 3i
Ans:
Let z = 4 − 3i
Then, z̅ = 4 + 3i and |z|2 = 42 + (−3)2 = 16 + 9 = 25
Therefore, the multiplicative inverse of 4 − 3i is given by:
z−1 = z̅|z|2 = 4 + 3i25
= 425 + 325 i
Que 12: Find the multiplicative inverse of the complex number :√5 + 3i
Ans:
Let z = √5 + 3i
Then, z̅ = √5 − 3i and |z|2 = (√5)2 + 32 = 5 + 9 = 14
Therefore, the multiplicative inverse of √5 + 3i is given by:
z−1 = z̅|z|2 = √5 − 3i14
= √514 − 314i
Que 13: Find the multiplicative inverse of the complex number: –i
Ans:
Let z = −i
Then, z̅ = i and |z|2 = |i|2 = 12 = 1
Therefore, the multiplicative inverse of −i is given by:
z−1 = z̅|z|2 = i1 = i
Que 14: Express the following expression in the form of a + ib.
(3 + i√5)(3 − i√5)(√3 + i√2) − (√3 − i√2)
Ans:
(3 + i√5)(3 − i√5)(√3 + i√2) − (√3 − i√2)
= (3)2 − (i√5)2√3 + i√2 − √3 + i√2 [(a + b)(a − b) = a2 − b2]
= 9 − 5i22i√2
= 9 − 5(−1)2i√2 [i2 = −1]
= 9 + 52i√2 = 14i2√2i
= 142(−1) = −7√2 − 7i2
Miscellaneous Exercise
Que 1: Evaluate: 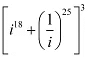
Ans:
Que 2: For any two complex numbers z1 and z2, prove that
Re (z1z2) = Re z1 Re z2 – Im z1 Im z2
Ans:
Let z1 = x1 + iy1 and z2 = x2 + iy2
.∴ z1z2 = (x1 + iy1) (x2 + iy2)
= x1(x2 + iy2) + iy1(x2 + iy2)
= x1x2 + i(x1y2 + x2y1) + i2y1y2
= (x1x2 − y1y2) + i(x1y2 + x2y1)
.∴ Re(z1z2) = x1x2 − y1y2
.∴ Re(z1z2) = Re(z1) Re(z2) − Im(z1) Im(z2)
Hence, proved.
Que 3: Reduce 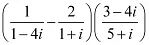 to the standard form.
to the standard form.
Ans:
[ On Multiplying numerator and denomunator by (14 + 5i)]
Que 4: If x – iy = 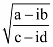 prove that
prove that 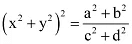 .
.
Ans:
[ On Multiplying numerator and denomunator by (c + id)]
(x2 + y2)2 = (x2 − y2)2 + 4x2y2
= (ac + bd)(c2 + d2) + (ad − bc)(c2 + d2)
= a2c2 + b2d2 + 2acbd + a2d2 + b2c2 − 2adbc(c2 + d2)2
= a2c2 + b2d2 + a2d2 + b2c2 + 2acbd(c2 + d2)2
= a2(c2 + d2) + b2(c2 + d2)(c2 + d2)2
= (c2 + d2)(a2 + b2)
= (a2 + b2)(c2 + d2)
Hence, proved.
Que 5: If z1 = 2 − i, z2 = 1 + i, find z1 + z2 + 1z1 − z2 + i
Ans:
z1 = 2 − i, z2 = 1 + i
.∴ z1 + z2 + 1z1 − z2 + i = (2 − i) + (1 + i) + 1(2 − i) − (1 + i) + i= 42(−i) = 2−i × 1 + i1 + i = 2(1 + i)1 − i2 [i2 = −1]
= 2(1 + i)2 = 1 + i
|1 + i| = √(12 + 12) = √2
Thus, the value of z1 + z2 + 1z1 − z2 + i is √2.
Que 6: If a + ib = (x + i)22x2 + 1, prove that a2 + b2 = (x2 + 1)2(2x2 + 1)
Ans:
a + ib = (x + i)22x2 + 1
= x2 + i2 + 2xi2x2 + 1
= x2 − 1 + i2x2x2 + 1
= x2 − 12x2 + 1 + i 2x2x2 + 1
On comparing real and imaginary parts, we obtain
a = x2 − 12x2 + 1, b = 2x2x2 + 1∴ a2 + b2 = (x2 − 1)2(2x2 + 1)2 + (2x)2(2x2 + 1)2
= x4 − 2x2 + 1 + 4x2(2x2 + 1)2
= x4 + 2x2 + 1(2x2 + 1)2
= (x2 + 1)2(2x2 + 1)2
∴ a2 + b2 = (x2 + 1)2(2x2 + 1)2
Hence, proved.
Que 7: Let z1 = 2 − i, z2 = −2 + i. Find:
(i) Re z1z2z1
(ii) Im 1z1z1
Ans:
z1 = 2 − i, z2 = −2 + i
(i)
z1z2 = (2 − i)(−2 + i) = −4 + 2i + 2i − i2 = −4 + 4i − (−1) = −3 + 4i
∴ z1z2z1 = -3 + 4i2 + i
(ii)
On multiplying numerator and denominator by (2 − i), we obtain:z1z2z1 = (−3 + 4i)(2 − i)(2 + i)(2 − i)
= −6 + 3i + 8i − 4i222 + 12
= −6 + 11i − 4(-1)22 + 12
= −2 + 11i5
= = −25 + 11i5
On comparing real parts, we obtain
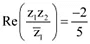
(ii)
On comparing imaginary parts, we obtain
Que 8: Find the real numbers x and y if (x – iy) (3+5i) is the conjugate of –6 – 24i.
Ans:
Let z = (x − iy)(3 + 5i)z = 3x + 5xi − 3yi − 5yi2 = 3x + 5xi − 3yi + 5y
= (3x + 5y) + i(5x − 3y)
∴ z = (3x + 5y) − i(5x − 3y)
It is given that,
∴ (3x + 5y) − i(5x − 3y) = −6 − 24i
Equating real and imaginary parts, we obtain:
3x + 5y = −6 ... (i)
5x − 3y = 24 ... (ii)Multiplying equation (i) by 3 and equation (ii) by 5, and then adding them, we obtain:
9x + 15y = −18 ... (from i × 3)
25x − 15y = 120 ... (from ii × 5)Adding: 34x = 102
∴ x = 10234 = 3
Putting the value of x in equation (i), we obtain
3(3) + 5y = -6
⇒ 5y = -6 - 9 = -15
⇒ y = -3Thus, the values of x and y are 3 and –3 respectively.
Que 9: Find the modulus of 1 + i1 − i − 1 − i1 + i.
Ans:
1 + i1 − i − 1 − i1 + i = (1 + i)2 − (1 − i)2(1 − i)(1 + i)
= 1 + i2 + 2i − 1 − i2 − 2i12 + 12 = 4i2 = 2i
∴ 1 + i1 − i − 1 − i1 + i = |2i| = √22 = 2
Que 10: If (x + iy)3 = u + iv, then show that ux + vy = 4(x2 − y2).
Ans:
(x + iy)3 = u + iv
⇒ x3 + (iy)3 + 3·x·iy(x + iy) = u + iv
⇒ x3 + i y3 + 3x2yi + 3xy2i2 = u + iv
⇒ x3 − 3xy2 + i(3x2y − y3) = u + iv
∴ u = x3 − 3xy2, v = 3x2y − y3
On equating real and imaginary parts, we obtain:
∴ ux + vy = x3 − 3xy2x + 3x2y − y3y
= x(x2 − 3y2)x + y(3x2 − y3)y
= x2 − 3y2 + 3x2 − y2
= 4x2 − 4y2
= 4(x2 − y2)
∴ ux + vy = 4(x2 − y2)
Hence, proved.
Que 11: If α and β are different complex numbers with 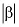 = 1, then find
= 1, then find 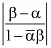 .
.
Ans:
Let α = a + ib and β = x + iy
It is given that,
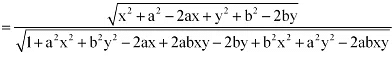
Que 12: Find the number of non-zero integral solutions of the equation 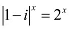 .
.
Ans:
|1 − i|x = 2x⇒ √(12 + (−1)2)x = 2x
⇒ (√2)x = 2x
⇒ 2x/2 = 2x
⇒ x 2 = x
⇒ x = 2x
⇒ 2x − x = 0
⇒ x = 0
Thus, 0 is the only integral solution of the given equation. Therefore, the number of non-zero integral solutions of the given equation is 0.
Que 13: If (a + ib) (c + id) (e + if) (g + ih) = A + iB, then show that
(a2 + b2) (c2+ d2) (e2 + f2) (g2 + h2) = A2 +B2.
Ans:
(a + ib)(c + id)(e + if)(g + ih) = A + iB
∴ |(a + ib)(c + id)(e + if)(g + ih)| = |A + iB|
⇒ |(a + ib)| × |(c + id)| × |(e + if)| × |(g + ih)| = |A + iB|
⇒ √(a2 + b2) × √(c2 + d2) × √(e2 + f2) × √(g2 + h2) = √(A2 + B2)
On squaring both sides, we obtain:
(a2 + b2)(c2 + d2)(e2 + f2)(g2 + h2) = A2 + B2
Hence, proved.
Que 14: If (1 + i)(1 − i)m = 1, then find the least positive integral value of m.
Ans:
(1 + i)(1 − i)m = 1
⇒ (1 + i)(1 − i) × (1 + i)(1 + i)m = 1
⇒ (1 + i)2(12 + 12)m = 1
⇒ (12 + i2 + 2i)2m = 1
⇒ (−1 + 2i)2m = 1
⇒ (2i)2m = 1
⇒ im = 1
∴ m = 4k, where k is some integer.
Therefore, the least positive integer is 1.
Thus, the least positive integral value of m is 4 (= 4 × 1).
Que 15: Convert the following in the polar form (Out of NCERT)
(i) 1 + 7i(2 − i)2,
(ii) 1 + 3i(1 − 2i)
Ans:
(i) Here, z = 1 + 7i(2 − i)2
= 1 + 7i(2 − i)2 = 1 + 7i4 + i2 − 4i = 1 + 7i4 − 1 − 4i
= 1 + 7i3 − 4i × 3 + 4i3 + 4i = 3 + 4i + 21i + 28i232 + 42
= 3 + 4i + 21i − 2832 + 42 = −25 + 25i25
= −1 + iLet r cos θ = –1 and r sin θ = 1
On squaring and adding, we obtain
r2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = 1+ 1
⇒ r2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = 2
⇒ r2 = 2 [cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1]
⇒ r = √2 [Conventionally, r > 0].∴ √2 cos θ = −1 and √2 sin θ = 1
⇒ cos θ = −1√2, sin θ = 1√2.∴ θ = π − π4 = 3π4 [As θ lies in II quadrant]
.∴ z = r cos θ + i r sin θ
= √2 cos 3π4 + i √2 sin 3π4= √2 ( cos 3π4 + i sin 3π4 )This is the required polar form.
(ii) Here, z = 1 + 3i(1 − 2i)
= 1 + 3i1 − 2i × 1 + 2i1 + 2i
= 1 + 2i + 3i − 61 + 4
= −5 + 5i5 = −1 + i
Let r cos θ = –1 and r sin θ = 1
On squaring and adding, we obtain
r2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = 1+ 1
⇒r2 (cos2 θ +sin2 θ) = 2⇒ r2 = 2 [cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1]
⇒ r = √2 [Conventionally, r > 0]
.∴ √2 cos θ = −1 and √2 sin θ = 1
⇒ cos θ = −1√2, sin θ = 1√2.∴ θ = π − π4 = 3π4 [As θ lies in II quadrant]
.∴ z = r cos θ + i r sin θ
= √2 cos 3π4 + i √2 sin 3π4= √2 ( cos 3π4 + i sin 3π4 )This is the required polar form.
Que 16: Solve the equation: 3x2 − 4x + 203 = 0 (Out of NCERT)
Ans:
The given quadratic equation is 3x2 − 4x + 203 = 0
This equation can also be written as 9x2 − 12x + 20 = 0
On comparing this equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we obtain:
a = 9, b = −12, and c = 20Therefore, the discriminant of the given equation is:
D = b2 − 4ac = (−12)2 − 4 × 9 × 20 = 144 − 720 = −576Therefore, the required solutions are:
x = −b ± √D2a
= −(−12) ± √−576
2 × 9
= 12 ± √576 i18 [√−1 = i]= 12 ± 24i18
= 6(2 ± 4i)18
= 2 ± 4i3
= 23 ± 4i3
Que 17: Solve the equation : x2 − 2x + 32 = 0 (Out of NCERT)
Ans:
The given quadratic equation is x2 − 2x + 32 = 0
This equation can also be written as 2x2 − 4x + 3 = 0
On comparing this equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we obtain:
a = 2, b = −4, and c = 3Therefore, the discriminant of the given equation is:
D = b2 − 4ac = (−4)2 − 4 × 2 × 3 = 16 − 24 = −8Therefore, the required solutions are:
x = −b ± √D2a
= −(−4) ± √−82 × 2
= 4 ± 2√2i4 [√−1 = i]= 2 ± √2i2
= 1 ± √2i2
Que 18: Solve the equation: 27x2 – 10x + 1 = 0 (Out of NCERT)
Ans:
The given quadratic equation is 27x2 – 10x + 1 = 0
On comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we obtain
a = 27, b = –10, and c = 1
Therefore, the discriminant of the given equation is
D = b2 – 4ac = (–10)2 – 4 × 27 × 1 = 100 – 108 = –8
Therefore, the required solutions are
x = −b ± √D2a = −(−10) ± √−82 × 27 = 10 ± 2√2i54 [√−1 = i]
= 5 ± √2i27 = 527 ± √2i27
Que 19: Solve the equation: 21x2 – 28x + 10 = 0 (Out of NCERT)
Ans:
The given quadratic equation is 21x2 – 28x + 10 = 0
On comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we obtain
a = 21, b = –28, and c = 10
Therefore, the discriminant of the given equation is
D = b2 – 4ac = (–28)2 – 4 × 21 × 10 = 784 – 840 = –56
Therefore, the required solutions are
= −b ± √D2a = −(−28) ± √−562 × 21 = 28 ± √56 i42
= 28 ± 2√14 i42 = 2842 ± 2√1442 = 23 ± √1421 i
Que 20: Find the modulus and argument of the complex number 1 + 2i1 − 3i. (Out of NCERT)
Ans:
Let z = 1 + 2i1 − 3i, then:
z = (1 + 2i)(1 + 3i)(1 − 3i)(1 + 3i) = 1 + 3i + 2i + 6i212 + 32 = 1 + 5i + 6(−1)1 + 9
= −5 + 5i10 = −510 + 5i10 = −12 + 12i
Let z = r cosθ + i r sinθ
i.e., r cosθ = −12 and r sinθ = 12On squaring and adding, we obtain:
r2(cos2θ + sin2θ) = (−1)222 + (1)222 = 14 + 14 = 12
⇒ r2 = 12, ⇒ r = 1√2 [Conventionally, r > 0]
∴ 1√2 cosθ = −12, and 1√2 sinθ = 12
⇒ cosθ = −1√2, sinθ = 1√2
⇒ θ = π − π4 = 3π4 [As θ lies in the II quadrant]
Therefore, the modulus and argument of the given complex number are 1√2 and 3π4 respectively.
|
172 videos|503 docs|154 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 4 - Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
| 1. What are complex numbers, and how are they defined? |  |
| 2. How do you perform addition and subtraction of complex numbers? |  |
| 3. What is the geometric representation of complex numbers? |  |
| 4. How do you multiply and divide complex numbers? |  |
| 5. What is the conjugate of a complex number and how is it used? |  |