NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Geography - The World Population: Distribution, Density and Growth in Geography
Q1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) India’s population as per 2011 census is :
(a) 1028 million
(b) 3182 million
(c) 3287 million
(d) 1210 million
Ans: (a)
(ii) Which one of the following states has the highest density of population in India?
(a) West Bengal
(b) Kerala
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Punjab
Ans: (a)
(iii) Which one of the following states has the highest proportion of urban population in India according to 2011 Census?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Kerala
(d) Goa
Ans: (b)
(iv) Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
(a) Sino – Tibetan
(b) Indo – Aryan
(c) Austric
(d) Dravidian
Ans: (b)
Q2: Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Very hot and dry and very cold and wet regions of India have low density of population. In this light, explain the role of climate on the distribution of population.
Ans:
- Climate plays a very important role in influencing population. The two elements of climate, rainfall and temperature play the most important role in determining the population of an area.
- When a place has extremes of climate, the density of population is low such as too cold climate of Himalayas, and the too hot and dry climate of the Thar Desert. When a place has moderate climate, it attracts people and has high density of population.
- Rainfall supplies water for agriculture which is the main occupation of Indian people. The amount of rainfall decreases as we move from the Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta in the east towards the Thar Desert in the west.
(ii) Which states have large rural population in India? Give one reason for such large rural population.
Ans: The states like Bihar and Sikkim have very high percentage of rural population. The reason is both states Bihar and Sikkim are highly dependent on agriculture for their livelihood.
(iii) Why do some states of India have higher rates of work participation than others?
Ans: In India, the work participation rate are higher in the areas of lower levels of economic development since number of manual workers are needed to perform the subsistence or near subsistence economic activities.
(iv) ‘The agricultural sector has the largest share of Indian workers.’ – Explain.
Ans: About 54.6 per cent of total working population are cultivators and agricultural labourers, whereas only 3.8% of workers are engaged in household industries and 41.6 % are other workers including nonhousehold industries, trade, commerce, construction and repair and other services.
Q3: Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Discuss the spatial pattern of density of population in India.
Ans: Density of population, is expressed as number of persons per unit area. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population in relation to land. The density of population in India is 382 persons per sq km.
- The spatial variation of population densities in the country ranges from as low as 17 persons per sq km in Arunachal Pradesh to 11,320 persons in the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Among the northern Indian States, Bihar (1102), West Bengal (1029) and and Uttar Pradesh (828) have higher densities, while Kerala (859) and Tamil Nadu (555) have higher densities among the peninsular Indian states.
- States like Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Odisha have moderate densities.
- The hill states of the Himalayan region and North eastern states of India (excluding Assam) have relatively low densities while the Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar islands) have very high densities of population.
(ii) Give an account of the occupational structure of India’s population.
Ans: The occupational structure of a country refers to the division of its work force engaged in different economic activities.
- India have a large proportion of primary sector workers compared to secondary and tertiary sectors.
- About 54.6 percent of total working population are cultivators and agricultural labourers, whereas only 3.8% of workers are engaged in household industries and 41.6 % are other workers including nonhousehold industries, trade, commerce, construction and repair and other services.
- As far as the occupation of country’s male and female population is concerned, male workers outnumber female workers in all the three sectors.
- The number of female workers is relatively high in primary sector, though in recent years there has been some improvement in work participation of women in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- The proportion of workers in agricultural sector in India has shown a decline over the last few decades (58.2% in 2001 to 54.6% in 2011).
- Consequently, the participation rate in secondary and tertiary sector has registered an increase. This indicates a shift of dependence of workers from farmbased occupations to non-farm based ones, indicating a sectoral shift in the economy of the country.
Old NCERT Questions
Q1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) Which one of the following continents has the highest growth of population?
(a) Africa
(b) South America
(c) Asia
(d) North America
Ans: (a)
(ii) Which one of the following is not an area of sparse population?
(a) The Atacama
(b) South-east Asia
(c) Equatorial region
(d) Polar regions
Ans: (b)
(iii) Which one of the following is not a push factor ?
(a) Water shortage
(b) Medical/educational facilities
(c) Unemployment
(d) Epidemics
Ans: (b)
(iv) Which one of the following is not a fact?
(a) Human population increased more than ten times during the past 500 years.
(b) Nearly 80 million people are added to the world population each year.
(c) It took 100 years for the population to rise from 5 billion to 6 billion.
(d) Population growth is high in the first stage of demographic transition?
Ans: (c)
Q2: Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Name three geographical factors that influence the distribution of population.
Ans: Three geographical factors that influence the distribution of population are:
- Availability of water
- Landforms
- Climate
(ii) There are a number of areas with high population density in the world. Why does this happen?
Ans: This happens due to the following factors:
- Geographical factors such as adequate availability of water, plain landforms, comfortable climate and fertile soils attract people.
- Economic factors such as mining and industrial activities generate employment, urbanisation and industrialisation also attract a large number of people.
- Social and Cultural Factors: people tend to move away from places where there is social and political unrest.
(iii) What are the three components of population change?
Ans: Three components of population change are birth rate, death rate and migration.
Q3: Distinguish between:
(i) Birth rate and death rate.
Ans:
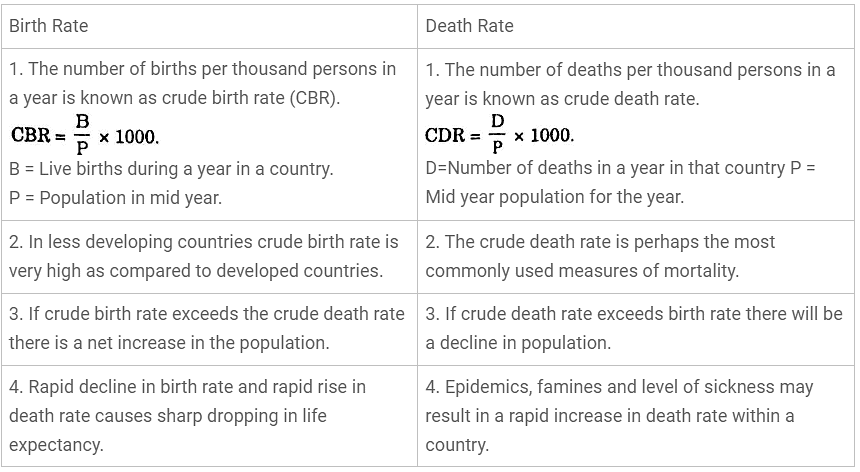
(ii) Push factors and pull factors of migration.
Ans: The distinction:
- The Push factors make the place of origin seem less attractive for reasons like unemployment, poor living conditions, political turmoil, unpleasant climate, natural disasters, epidemics and socio-economic backwardness.
- The Pull factors make the place of destination seem more attractive than the place of origin for reasons like better job opportunities and living conditions, peace and stability, security of life and property and pleasant climate.
Q4: Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Discuss the factors influencing the distribution and density of population in the world.
Ans: The various factors that influence the distribution and density of population in the world are:
Geographical Factors:
- Availability of water: People prefer to live in areas where fresh water is easily available. Water is used for drinking, bathing and cooking – and also for cattle, crops, industries and navigation.
- Landforms: People prefer living on flat plains and gentle slopes because such areas are favourable for the production of crops and to build roads and industries.
- Climate: An extreme climate such as very hot or cold deserts are uncomfortable for human habitation. Areas with a comfortable climate, where there is not much seasonal variation attract more people.
- Soils: Fertile soils are important for agricultural and allied activities. Therefore, areas which have fertile loamy soils have more people living on them.
Economic Factors
- Minerals: Areas with mineral deposits attract industries. Mining and industrial activities generate employment therefore these areas are densly populated.
- Urbanisation: Cities offer better employment opportunities, educational and medical facilities, better means of transport and communication.
- Industrialisation: Industrial belts provide job opportunities and attract large numbers of people.
Social and Cultural Factors: Some places attract more people because they have religious or cultural significance. People tend to move away from places where there is social and political unrest. Many a times governments offer incentives to people to live in sparsely populated areas or move away from overcrowded places.
(ii) Discuss the three stages of demographic transition.
Ans: The three stages of demographic transition are:
- The first stage has high fertility and high mortality because people reproduce more to compensate for the deaths due to epidemics and variable food supply. The population growth is slow and most of the people are engaged in agriculture where large families are an asset. Life expectancy is low, people are mostly illiterate and have low levels of technology.
- Fertility remains high in the beginning of second stage but it declines with time. This is accompanied by reduced mortality rate. Improvements in sanitation and health conditions lead to decline in mortality. Because of this gap the net addition to population is high.
- In the last stage, both fertility and mortality decline considerably. The population is either stable or grows slowly. The population becomes urbanised, literate and has high technical know-how and deliberately controls the family size.
|
50 videos|247 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Geography - The World Population: Distribution, Density and Growth in Geography
| 1. What is population distribution and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How is population density calculated and what does it indicate? |  |
| 3. What factors influence population growth in a region? |  |
| 4. What are the main characteristics of population growth patterns? |  |
| 5. How does urbanization affect population distribution and density? |  |


















