NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 - Triangles (Exercise 6.6)
Q.1. In Figure, PS is the bisector of ∠ QPR of ∆ PQR. Prove that QS/PQ = SR/PR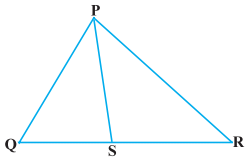 Sol.
Sol.
Let us draw a line segment RT parallel to SP which intersects extended line segment QP at point T.
Given, PS is the angle bisector of ∠QPR. Therefore,
∠QPS = ∠SPR……….(i)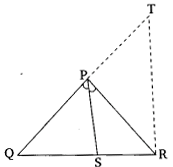 As per the constructed figure,
As per the constructed figure,
∠SPR=∠PRT(Since, PS||TR)……………(ii)
∠QPS = ∠QRT(Since, PS||TR) …………..(iii)
From the above equations, we get,
∠PRT=∠QTR
Therefore,
PT=PR
In △QTR, by basic proportionality theorem,
QS/SR = QP/PT
Since, PT=TR
Therefore,
QS/SR = PQ/PR
Hence, proved.
Q.2. In the figure, D is a point on hypotenuse AC of ΔABC, such that BD ⊥ AC, DM ⊥ BC and DN ⊥ AB.
Prove that:
(i) DM2 = DN.MC
(ii) DN2 = DM.AN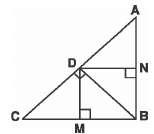 Sol.
Sol.
(i) Let us join Point D and B.
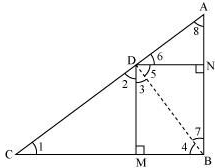
Given,
BD ⊥AC, DM ⊥ BC and DN ⊥ AB
Now from the figure we have,
DN || CB, DM || AB and ∠B = 90 °
Therefore, DMBN is a rectangle.
So, DN = MB and DM = NB
The given condition which we have to prove, is when D is the foot of the perpendicular drawn from B to AC.
∴ ∠CDB = 90° ⇒ ∠2 + ∠3 = 90° …… (i)
In ∆CDM, ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠DMC = 180°
⇒ ∠1 + ∠2 = 90° …………….. (ii)
In ∆DMB, ∠3 + ∠DMB + ∠4 = 180°
⇒ ∠3 + ∠4 = 90° …………….. (iii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
∠1 = ∠3
From equation (i) and (iii), we get
∠2 = ∠4
In ∆DCM and ∆BDM,
∠1 = ∠3 (Already Proved)
∠2 = ∠4 (Already Proved)
∴ ∆DCM ∼ ∆BDM (AA similarity criterion)
BM/DM = DM/MC
DN/DM = DM/MC (BM = DN)
⇒ DM2 = DN × MC
Hence, proved.
(ii) In right triangle DBN,
∠5 + ∠7 = 90° ………….. (iv)
In right triangle DAN,
∠6 + ∠8 = 90° ………… (v)
D is the point in triangle, which is foot of the perpendicular drawn from B to AC.
∴ ∠ADB = 90° ⇒ ∠5 + ∠6 = 90° ………….. (vi)
From equation (iv) and (vi), we get,
∠6 = ∠7
From equation (v) and (vi), we get,
∠8 = ∠5
In ∆DNA and ∆BND,
∠6 = ∠7 (Already proved)
∠8 = ∠5 (Already proved)
∴ ∆DNA ∼ ∆BND (AA similarity criterion)
AN/DN = DN/NB
⇒ DN2 = AN × NB
⇒ DN2 = AN × DM (Since, NB = DM)
Hence, proved.
Q.3. In the figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠ABC >90° and AD ⊥ CB produced. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2 BC.BD.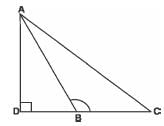 Sol. Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔADB, we obtain
Sol. Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔADB, we obtain
AB2 = AD2 + DB2 … (1)
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔACD, we obtain
AC2 = AD2 + DC2
AC2 = AD2 + (DB + BC)2
AC2 = AD2 + DB2 + BC2 + 2DB × BC
From equation (i), we can write,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2DB × BC
Hence, proved
Q.4. In the figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠ABC < 90° and AD ⊥ BC. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 - 2 BC.BD.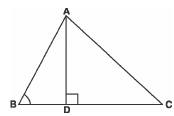 Sol. By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆ADB, we get
Sol. By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆ADB, we get
AD2 + DB2 = AB2
We can write it as;
⇒ AD2 = AB2 − DB2 … (1)
By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆ADC, we get,
AD2 + DC2 = AC2
From equation (i),
AB2 − BD2 + DC2 = AC2
AB2 − BD2 + (BC − BD)2 = AC2
AC2 = AB2 − BD2 + BC2 + BD2 − 2BC × BD
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 − 2BC × BD
Q.5. In the figure, AD is a median of a triangle ABC and AM ⊥ BC. Prove that:
(i) AC2 = AD2 + BC.DM + 2 (BC/2)2
(ii) AB2 = AD2 – BC.DM + 2 (BC/2)2
(iii) AC2 + AB2 = 2AD2 + ½ BC2
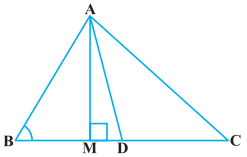 Sol.
Sol.
(i) By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆AMD, we get,
AM2 + MD2 = AD2 … (1)
Again, by applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆AMC, we get,
AM2 + MC2 = AC2
AM2 + (MD + DC)2 = AC2
(AM2 + MD2) + DC2 + 2MD.DC = AC2
From equation(i), we get,
AD2 + DC2 + 2MD.DC = AC2
Since, DC=BC/2, thus, we get,
AD2 + (BC/2)2 + 2MD.(BC/2)2 = AC2
AD2 + (BC/2)2 + 2MD × BC = AC2
Hence, proved.
(ii) By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆ABM, we get;
AB2 = AM2 + MB2
= (AD2 − DM2) + MB2
= (AD2 − DM2) + (BD − MD)2
= AD2 − DM2 + BD2 + MD2 − 2BD × MD
= AD2 + BD2 − 2BD × MD
= AD2 + (BC/2)2 – 2(BC/2) MD
= AD2 + (BC/2)2 – BC MD
Hence, proved.
(iii) By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆ABM, we get,
AM2 + MB2 = AB2 … (1)
By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆AMC, we get,
AM2 + MC2 = AC2 … (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2), we obtain
2AM2 + MB2 + MC2 = AB2 + AC2
2AM2 + (BD − DM)2 + (MD + DC)2 = AB2 + AC2
2AM2 +BD2 + DM2 − 2BD.DM + MD2 + DC2 + 2MD.DC = AB2 + AC2
2AM2 + 2MD2 + BD2 + DC2 + 2MD (− BD + DC) = AB2 + AC2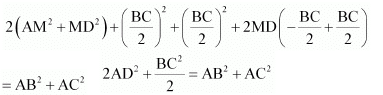
Q.6. Prove that the sum of the squares of the diagonals of parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of its sides.
Sol.
Let us consider, ABCD be a parallelogram. Now, draw perpendicular DE on extended side of AB, and draw a perpendicular AF meeting DC at point F.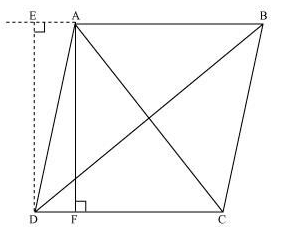 By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆DEA, we get,
By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆DEA, we get,
DE2 + EA2 = DA2 … (i)
By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆DEB, we get,
DE2 + EB2 = DB2
DE2 + (EA + AB)2 = DB2
(DE2 + EA2) + AB2 + 2EA × AB = DB2
DA2 + AB2 + 2EA × AB = DB2 … (ii)
By applying Pythagoras Theorem in ∆ADF, we get,
AD2 = AF2 + FD2
Again, applying Pythagoras theorem in ∆AFC, we get,
AC2 = AF2 + FC2
= AF2 + (DC − FD) 2
= AF2 + DC2 + FD2 − 2DC × FD
= (AF2 + FD2) + DC2 − 2DC × FD
AC2 = AD2 + DC2 − 2DC × FD … (iii)
Since ABCD is a parallelogram,
AB = CD … (iv)
And, BC = AD … (v)
In ΔDEA and ΔADF,
∠DEA = ∠AFD (Both 90°)
∠EAD = ∠ADF (EA || DF)
AD = AD (Common)
∴ ΔEAD ≅ ΔFDA (AAS congruence criterion)
⇒ EA = DF … (vi)
Adding equations (i) and (iii), we obtain
DA2 + AB2 + 2EA × AB + AD2 + DC2 − 2DC × FD = DB2 + AC2
DA2 + AB. + AD2 + DC2 + 2EA × AB − 2DC × FD = DB2 + AC2
From equation (iv) and (vi),
BC2 + AB2 + AD2 + DC2 + 2EA × AB − 2AB × EA = DB2 + AC2
AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2 = AC2 + BD2
Q7. In the figure, two chords AB and CD intersect each other at the point P. Prove that:
(i) Δ APC ~ Δ DPB
(ii) AP·PB = CP·DP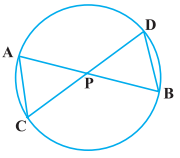 Sol.
Sol.
Firstly, let us join CB, in the given figure.
(i) In ∆APC and ∆DPB,
∠APC = ∠DPB (Vertically opposite angles)
∠CAP = ∠BDP (Angles in the same segment for chord CB)
Therefore,
∆APC ∼ ∆DPB (AA similarity criterion)
(ii) In the above, we have proved that ∆APC ∼ ∆DPB
We know that the corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional.
∴ AP/DP = PC/PB = CA/BD
⇒AP/DP = PC/PB
∴ AP. PB = PC. DP
Hence, proved.
Q.8. In the figure, two chords AB and CD of a circle intersect each other at the point P (when produced) outside the circle.
Prove that
(i) Δ PAC ~ Δ PDB
(ii) PA·PB = PC·PD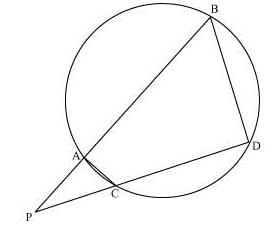 Sol.
Sol.
(i) In ΔPAC and ΔPDB,
∠P = ∠P (Common Angles)
As we know, exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is ∠PCA and ∠PBD is opposite interior angle, which are both equal.
∠PAC = ∠PDB
Thus, ∆PAC ∼ ∆PDB(AA similarity criterion)
(ii) We have already proved above,
∆APC ∼ ∆DPB
We know that the corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional.
Therefore,
AP/DP = PC/PB = CA/BD
AP/DP = PC/PB
∴ AP. PB = PC. DP
Q.9. In the figure, D is a point on side BC of Δ ABC such that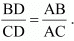 Prove that AD is the bisector of ∠BAC.
Prove that AD is the bisector of ∠BAC.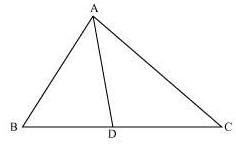 Sol.
Sol.
In the given figure, let us extend BA to P such that;
AP = AC.
Now join PC.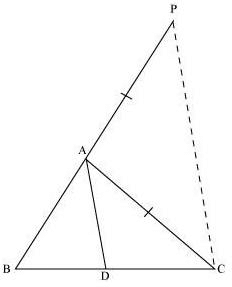 It is given that,
It is given that,
⇒ BD/CD = AP/AC
By using the converse of basic proportionality theorem, we get,
AD || PC
∠BAD = ∠APC (Corresponding angles) ……………….. (i)
And, ∠DAC = ∠ACP (Alternate interior angles) …….… (ii)
By the new figure, we have;
AP = AC
⇒ ∠APC = ∠ACP ……………………. (iii)
On comparing equations (i), (ii), and (iii), we get,
∠BAD = ∠APC
Therefore, AD is the bisector of the angle BAC.
Hence, proved.
Q.10. Nazima is fly fishing in a stream. The tip of her fishing rod is 1.8 m above the surface of the water and the fly at the end of the string rests on the water 3.6 m away and 2.4 m from a point directly under the tip of the rod. Assuming that her string (from the tip of her rod to the fly) is taut, how much string does she have out (see figure)? If she pulls in the string at the rate of 5 cm per second, what will be the horizontal distance of the fly from her after 12 seconds?Sol.
Let us consider, AB is the height of the tip of the fishing rod from the water surface and BC is the horizontal distance of the fly from the tip of the fishing rod. Therefore, AC is now the length of the string.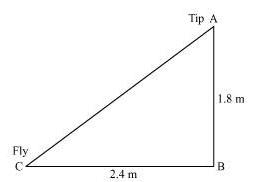 To find AC, we have to use Pythagoras theorem in ∆ABC, is such way;
To find AC, we have to use Pythagoras theorem in ∆ABC, is such way;
AC2 = AB2+ BC2
AB2 = (1.8 m) 2 + (2.4 m) 2
AB2 = (3.24 + 5.76) m2
AB2 = 9.00 m2
⟹ AB = √9 m = 3m
Thus, the length of the string out is 3 m.
As its given, she pulls the string at the rate of 5 cm per second.
Therefore, string pulled in 12 seconds = 12 × 5 = 60 cm = 0.6 m
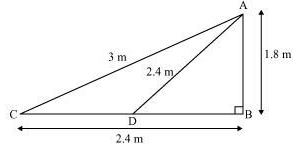 Let us say now, the fly is at point D after 12 seconds.
Let us say now, the fly is at point D after 12 seconds.
Length of string out after 12 seconds is AD.
AD = AC − String pulled by Nazima in 12 seconds
= (3.00 − 0.6) m
= 2.4 m
In ∆ADB, by Pythagoras Theorem,
AB2 + BD2 = AD2
(1.8 m)2 + BD2 = (2.4 m) 2
BD2 = (5.76 − 3.24) m2 = 2.52 m2
BD = 1.587 m
Horizontal distance of fly = BD + 1.2 m
= (1.587 + 1.2) m = 2.787 m
= 2.79 m
|
70 videos|242 docs|187 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 - Triangles (Exercise 6.6)
| 1. What are the different types of triangles? |  |
| 2. How do you determine if three given sides can form a triangle? |  |
| 3. What is the Pythagorean theorem and how is it used in triangles? |  |
| 4. How do you find the area of a triangle? |  |
| 5. How can we determine if two triangles are similar? |  |
















