NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology - What is Psychology
Q1: What is behaviour? Give examples of overt and covert behaviour.
Ans: Behaviour is a response or a reaction of an individual or an activity in which the individual is engaged in. It is the result of a stimulus in the environment or an internal change. Behaviours may be simple or complex and overt or covert.
Examples of overt behaviour
(i) Blinking of eyes when a stone is hurled at a person
(ii) Withdrawing the hand immediately after touching a hot pan
Examples of covert behaviour
(i) The twitching of hand muscles while playing a game of chess.
(ii) Pounding of heart during an interview.
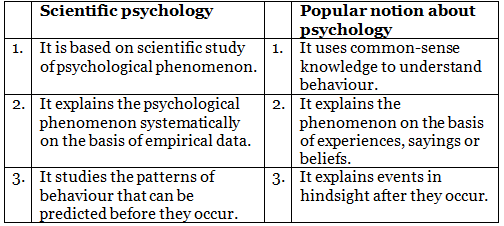
Q2: How can you distinguish scientific psychology from the popular notions about the discipline of psychology?
Ans: Scientific psychology can be distinguished from the popular notions about the discipline of psychology on the basis of the following characteristics:
Q3: Give a brief account of the evolution of psychology.
Ans: The evolution of psychology was an outcome of ancient philosophy. It later varied with the development of different approaches of psychological study. The formal beginning of modern psychology took place in 1879 with the establishment of an experimental laboratory in Leipzig by Wilhelm Wundt.
- The initial approach to study psychology was based on introspection or structuralism in which the individuals were asked to describe their experiences.
- It was followed by functionalism that studied the working of the mind and the impact of behaviour upon people's interaction with their environment.
- Gestalt psychology emerged as a reaction to structuralism in the early 20th century and focused on the organisation of the perceptual experiences.
- Another reaction was the development of behaviourism that studied behaviour or responses in a measurable and objective form.
- This was followed by psychoanalysis of Sigmund Freud that viewed human behaviour as a dynamic manifestation of unconscious desires, conflicts and their gratification.
- In contrast, the humanistic perspective emphasised the free will of human beings and their natural striving to grow and unfold their inner potential.
- Further, Cognitive perspective was a combination of Gestalt approach and structuralismand focused on how anindividual perceived the world.
- Later, Constructivism viewed human beings as activelyconstructing their minds through the exploration of physical and the social world.
- It was followed by Vygotsky's view that human mind develops through social and cultural processes in which the mind is perceived as culturally constructed by joint interaction between children and adults.
Therefore, the evolution of psychology passed through various stages and levels. Starting from the roots of philosophy, it took a new direction and included numerous theories of structuralism, functionalism, behaviourism, constructivism, etc. However, in contemporary era the discipline of psychology has grown into a scientific discipline, which deals with various processes underlying human experiences and behaviours.
Q4: What are the problems for which collaboration of psychologists with other disciplines can be fruitful? Take any two problems to explain.
Ans: The problems for which collaboration of psychologists with other disciplines can be fruitful are as follows:
- While dealing with a criminal case, it is important for a lawyer or a criminologist to understand the psychology of a witness or the criminal. It is also necessary to decide the degree of punishment valid for a crime. Thus, it is important for a lawyer or a criminologist to have the knowledge of psychology in order to regulate the legal system of a country.
- It is important for an architect or an engineer to satisfy his/her customers by providing with mental and physical space in a building. Further, an engineer should also consider the human habits while construction. Thus, they need to have a psychological knowledge in order to understand the needs and demands of their customers.
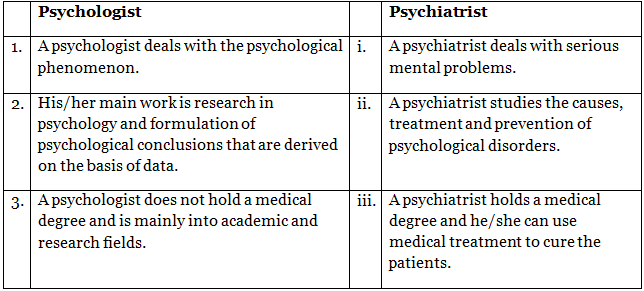
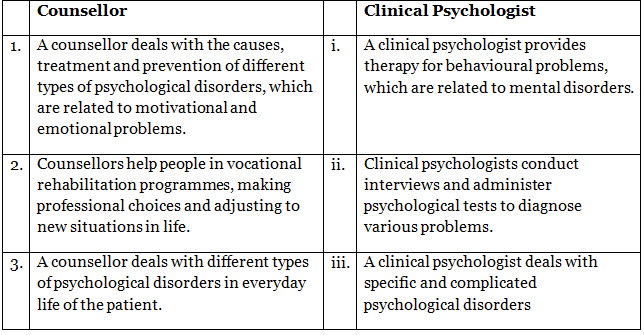
Q5: Differentiate between
(a) a psychologist and a psychiatrist
(b) a counsellor and a clinical psychologist.
Ans:
(a) The difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist are mentioned below:
 (b) The difference between a counsellor and clinical psychologist are mentioned below:
(b) The difference between a counsellor and clinical psychologist are mentioned below:
Q6: Describe some of the areas of everyday life where understanding of psychology can be put to practice.
Ans: Some of the areas of everyday life where understanding of psychology can be put into practice are as follows:
- Psychology helps to understand various personal problems like family, marriage and work sphere. It also helps to deal with larger problems related to community and society.
- Psychology enables an individual to understand oneself in a balanced and positive way without being reactionary, in order to deal with everyday challenges and meet with personal expectations.
- Understanding of psychology further helps in analysing the various social, economic and political problems that affect an individual's life and their solution at individual and collective level.
- Psychology helps in understanding the cause of violence and need for cooperation that makes people wise, which improves the societal relationships by avoiding conflict, frustration and aggression.
- Psychological analysis also enables in decision-making for various spheres and cultivating healthy lifestyles.
Therefore, the understanding of psychology enables a person to build stronger relationships at community level and improves the strength at individual level in order to meet daily challenges and obstacles.
Q7: How can knowledge of the field of environmental psychology be used to promote environment-friendly behaviour?
Ans: The knowledge of environmental psychology is helpful to promote environment friendly behaviour because:
- It studies the interaction of physical factors such as temperature, humidity, pollution and natural disaster on human behaviour.
- It analyses the influence of physical arrangements at work place on the health, emotional state and interpersonal relations of the individual.
- Issues like disposal of waste, population explosion, conservation of energy etc. are related with behaviour of human beings as well as its consequence.
- Thus, an understanding of human behaviour in relation to environment generates awareness and inculcates safe environmental practices.
Q8: In terms of helping solve an important social problem such as crime, which branch of psychology do you think is most suitable? Identify the field and discuss the concerns of the psychologists working in this field.
Ans: The branch of social psychology is most suitable for the purpose of solving social problems like crime.
It explores the thought process of people and their influence upon others and evaluates the impact of social environment upon the actions of an individual.
Social psychologists are concerned with topics like attitudes, conformity and obedience to authority, interpersonal attraction, helpful behaviour, prejudice, aggression, social motivation and inter-group relations.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology - What is Psychology
| 1. What is the scope of psychology? |  |
| 2. How does psychology differ from psychiatry? |  |
| 3. What are the major schools of thought in psychology? |  |
| 4. How is psychology applied in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What are the career opportunities in psychology? |  |

















