NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - The Making of Regional Cultures
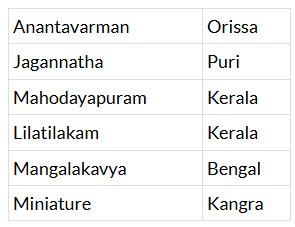
Q1. Match the following:
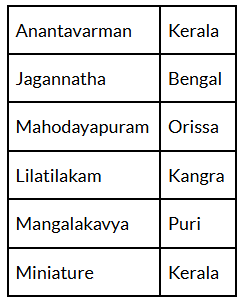
Ans:
Q2. What is Manipravalam? Name a book written in that language.
Ans: Manipravalam means “diamonds and corals” referring to the two languages, Sanskrit and the regional language. A book written in Manipravalam is Lilatilakam which deals with grammar and poetics.
Q3. Who were the major patrons of Kathak?
Ans: Major patrons of Kathak were the Mughal emperors and the Nawabs of Lucknow, especially Wajid Ali Shah.
 KathakQ4. What are the important architectural features of the temples of Bengal?
KathakQ4. What are the important architectural features of the temples of Bengal?
Ans: Important architectural features of the temples of Bengal are:
- Temples began to copy the double-roofed or four-roofed structure of the thatched huts.
- In the comparatively more complex four-roofed structure, four triangular roofs placed on the four walls move up to converge on a curved line or a point.
- Temples were usually built on a square platform.
- The interior was relatively plain but the outer walls of many temples were decorated with paintings, ornamental tiles or terracotta tablets.

Q5. Why did minstrels proclaim the achievements of heroes?
Ans: Minstrels used to recite poems and songs which depicted the stories of the ” Rajputs’ heroic deeds. By reciting such poems and songs these minstrels inspired others to follow the examples of Rajputs. Ordinary people were also attracted by these stories.
Q6. Why do we know much more about the cultural practices of rulers than about those of ordinary people?
Ans: The cultural practices of rulers were carefully preserved in palaces for centuries. Hence we know much more about them. Ordinary men and women also painted on pots, walls, floors, cloth. But they did not survive for long.
Q7. Why did conquerors try to control the temple of Jagannatha at Puri?
Ans: Conquerors sought control over the Jagannatha temple at Puri for several reasons:
- It was a significant pilgrimage site for local people.
- Control over the temple would enhance their legitimacy among the populace.
- The temple served as a centre of social and political authority.
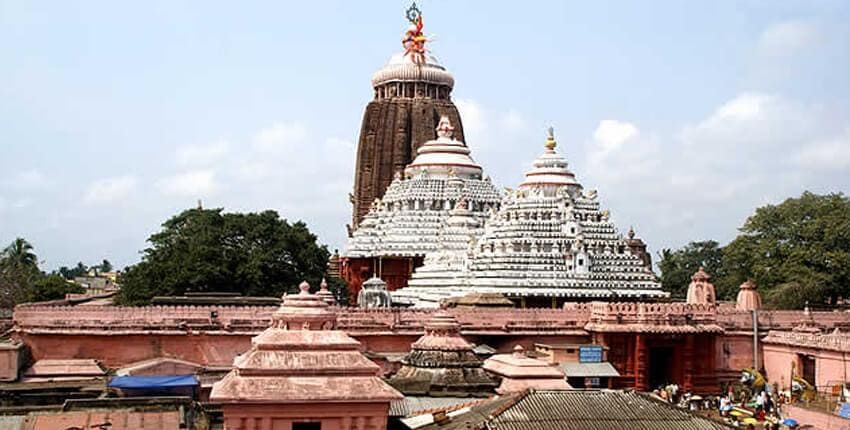 Jagannatha TempleMajor patrons of Kathak were the Mughal emperors and the Nawabs of Lucknow.
Jagannatha TempleMajor patrons of Kathak were the Mughal emperors and the Nawabs of Lucknow.
- The Mughal emperors played a significant role in promoting Kathak.
- The Nawabs of Lucknow, particularly Wajid Ali Shah, were key supporters of this dance form.
Q8. Why were temples built in Bengal?
Ans: The arrival of European trading companies brought new economic opportunities to Bengal, which led to the construction of temples. Key points include:
- Many temples were built with support from lower social groups, such as the Kolu (oil pressers) and the Kansari (bell metal workers).
- Local deities, previously worshipped in thatched huts, gained recognition from the Brahmanas, leading to their images being housed in temples.
- The architectural style evolved from the traditional thatched huts, adopting features like the double-roofed and four-roofed structures.
- Temples were often built on square platforms with plain interiors, while the outer walls showcased intricate decorations
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - The Making of Regional Cultures
| 1. What are regional cultures? |  |
| 2. How did regional cultures evolve in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of regional cultures? |  |
| 4. How did the British colonial rule impact regional cultures in India? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of studying regional cultures? |  |






















