NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - India Climate Vegetation and Wildlife
Exercises
Q.1. Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) Which winds bring rainfall in India? Why is it so important?
Ans: The south-west monsoon winds bring rainfall in India. It is important because agriculture in India is dependent on rainfall. A good amount of rainfall brings a bountiful and adequate crop.
(b) Name the different seasons in India.
Ans: The different seasons in India are:
- Cold weather season (winter)
- Hot weather season (summer)
- South west monsoon season (rainy)
- Season of retreating monsoons (autumn)
(c) What is natural vegetation?
Ans: The grasses, shrubs and trees, which grow on their own without interference or help from human beings are called natural vegetation.
(d) Name the different types of vegetation found in India.
Ans: The different types of vegetation found in India are:
- Tropical rainforests or Evergreen forests
- Tropical deciduous forests
- Thorny bushes
- Mountain vegetation
- Mangrove forests
(e) What is the difference between evergreen forest and deciduous forest?
Ans: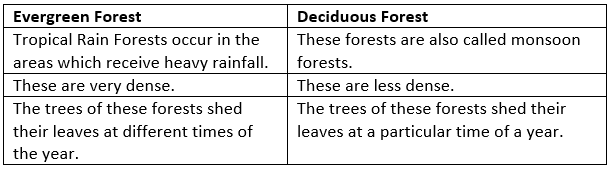
(f) Why is tropical rainforest also called evergreen forest?
Ans: The tropical rainforest is also called evergreen forest because trees in these forests shed their leaves at different times of the year. Therefore, it remains green throughout the year.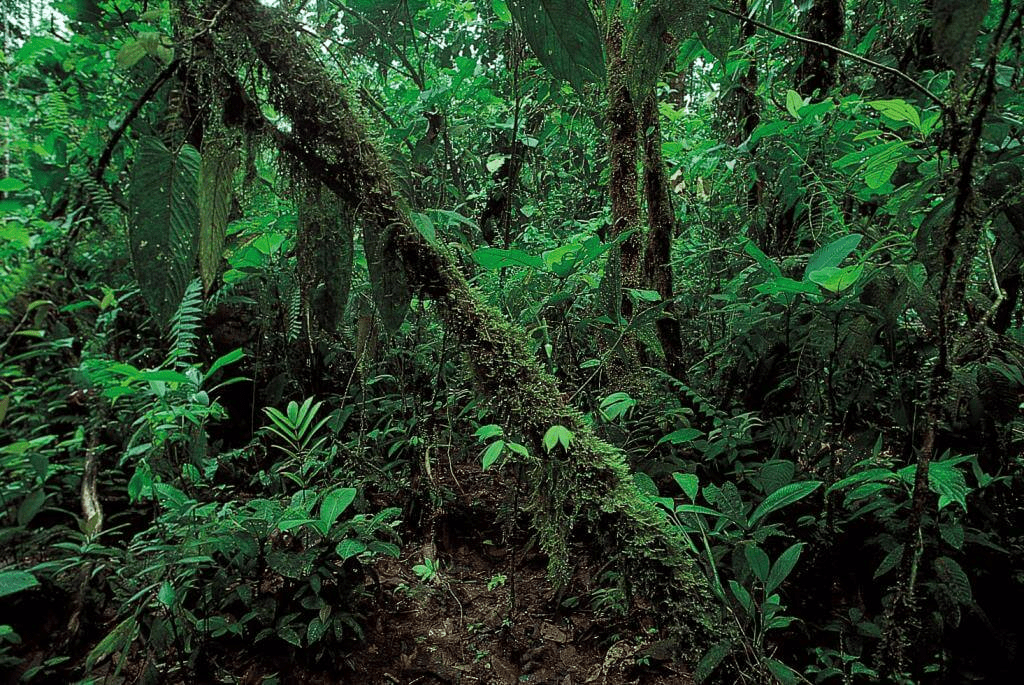
Ques 2. Tick the correct answers.
(a) The world’s highest rainfall occurs in
(i) Mumbai
(ii) Asansol
(iii) Mawsynram
Ans: (iii) Mawsynram
(b) Mangrove forests can thrive in
(i) Saline water
(ii) Fresh water
(iii) Polluted water
Ans: (i) saline water
(c) Mahogany and rosewood trees are found in
(i) Mangrove forests
(ii) Tropical deciduous forests
(iii) Tropical evergreen forests
Ans: (iii) tropical evergreen forests
(d) Wild goats and snow leopards are found in
(i) Himalayan region
(ii) Peninsular region
(iii) Gir forests
Ans: (i) Himalayan region
(e) During the south west monsoon period, the moisture laden winds blow from
(i) Land to sea
(ii) Sea to land
(iii) Plateau to plains
Ans: (ii) sea to land
Ques 3. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Hot and dry winds known as _____ blow during the day in the summers.
Ans: loo
(b) The states of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu receive a great amount of rainfall during the season of_____.
Ans: Retreating monsoons
(c) _____ forest in Gujarat is the home of ______.
Ans: Gir, Asiatic lions
(d) _____ is a well-known species of mangrove forests.
Ans: Sundari
(e) ____ are also called monsoon forests.
Ans: Tropic deciduous forest
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - India Climate Vegetation and Wildlife
| 1. What is the main reason for India's diverse climate and vegetation? |  |
| 2. What are the major types of forests found in India? |  |
| 3. What are the major factors responsible for the depletion of India's wildlife? |  |
| 4. What steps has the government taken to conserve India's wildlife? |  |
| 5. What is the impact of climate change on India's wildlife? |  |



















