NCERT Summary: Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution- 2 | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Right to Freedom of Religion
- According to our , everyone enjoys the right to follow the religion of his or her choice. This freedom is considered as a hallmark of democracy.
- Historically, there were rulers and emperors in different parts of the world who did not allow residents of their countries to enjoy the right to freedom of religion. Persons following a religion different from that of the ruler were either persecuted or forced to convert to the official religion of the rulers. Therefore, democracy has always ‘incorporated the freedom to follow the religion of one’s choice as one of its basic principle’.
1. Freedom of Faith and Worship
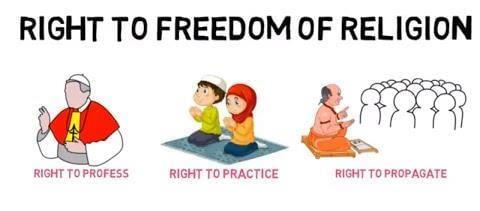
- In India, everyone is free to choose a religion and practice that religion. Freedom of religion also includes freedom of conscience. This means that a person may choose any religion or may choose not to follow any religion. Freedom of religion includes the freedom to profess, follow and propagate any religion.
- Freedom of religion is subject to certain limitations. The government can impose restrictions on the practice of freedom of religion in order to protect public order, morality and health. This means that the freedom of religion is not an unlimited right. The government can interfere in religious matters for rooting out certain social evils.
Example: In the past, the government has taken steps banning practices like sati, bigamy or human sacrifice. Such restrictions cannot be opposed in the name of interference in right to freedom of religion. - The limitations on the right to freedom of religion always produce tensions between followers of various religions and the government. When the government seeks to restrict some activities of any religious group, people of that religion feel that this is interference in their religion.
- Freedom of religion becomes a matter of political controversy for yet another reason. The Constitution has guaranteed the right to propagate one’s religion. This includes persuading people to convert from one religion to another.
- However, some people recent conversions on the ground that these are based on intimidation or inducement. The Constitution does not allow forcible conversions. It only gives us the right to spread information about our religion and thus attract others to it.
2. Equality of All Religions
- Being a country which is home to several religions, it is necessary that the government must extend equal treatment to different religions. Negatively, it means that government will not favour any particular religion. India does not have any official religion. We don’t have to belong to any particular religion in order to be a prime minister or president or judge or any other public official.
- We have also seen that under the right to equality, there is a guarantee that government will not discriminate on the basis of religion in giving employment. The institutions run by the state will not preach any religion or give religious education nor will they favour persons of any religion. The objective of these provisions is to sustain and nurture the principle of secularism.
Cultural and Educational Rights
- When we talk of Indian society, the image of diversity comes before our minds. India is not made up of a monolithic society. We are a society that has vast diversity. In such a society that is full of diversity, there would be social sections which are small in numbers compared to some other groups.
- Our Constitution believes that diversity is our strength. Therefore, one of the fundamental rights is the right of minorities to maintain their culture. This minority status is not dependent only upon religion. Linguistic and cultural minorities are also included in this provision.
- Minorities are groups that have common language or religion and in a particular part of the country or in the country as a whole, they are outnumbered by some other social section. Such communities have a culture, language and a script of their own, and have the right to conserve and develop these.
- All minorities, religious or linguistic, can set up their own educational institutions. By doing so, they can preserve and develop their own culture. The government will not, while granting aid to educational institutions, discriminate against any educational institution on the basis that it is under the management of minority community.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
One would agree that our Constitution contains a very impressive list of Fundamental Rights. But merely writing down a list of rights is not enough. There has to be a way through which they could be realised in practice and defended against any attack on these rights.
➢ Fundamental Duties of Citizens
- In 1976, the 42nd amendment to the Constitution was passed. Among other things, this amendment inserted a list of Fundamental Duties of Citizens. In all, ten duties were enumerated. However, the Constitution does not say anything about enforcing these duties.
- As citizens, we must abide by the Constitution, defend our country, promote harmony among all citizens, protect the environment.
- However, it must be noted that our Constitution does not make the enjoyment of rights dependent or conditional upon fulfillment of duties. In this sense, the inclusion of fundamental duties has not changed the status of our fundamental rights.
Right to constitutional remedies is the means through which this is to be achieved. Dr. Ambedkar considered the right to constitutional remedies as ‘heart and soul of the constitution’, It is so because this right gives a citizen the right to approach a High Court or the Supreme Court to get any of the fundamental rights restored in case of their violation. The Supreme Court and the High Courts can issue orders and give directions to the government for the enforcement of rights.
➢ The Courts Can Issue Various Special Orders Known As Writs
(a) Habeas Corpus: A writ of habeas corpus means that the court orders that the arrested person should be presented before it. It can also order to set free an arrested person if the manner or grounds of arrest are not lawful or satisfactory.
(b) Mandamus: This writ is issued when the court finds that a particular officeholder is not doing legal duty and thereby is infringing on the right of an individual.
(c) Prohibition: This writ is issued by a higher court (High Court or Supreme Court) when a lower court has considered a case going beyond its jurisdiction.
(d) Quo Warranto: If the court finds that a person is holding office but is not entitled to hold that office, it issues the writ of quo warranto and restricts that person from acting as an officeholder.
(e) Certiorari: Under this write, the court orders a lower court or another authority to transfer a matter pending before it to the higher authority or court. Apart from the judiciary, many other mechanisms have been created in later years for the protection of rights. You may have heard about the National Commission on Minorities, the National Commission on Women, the National Commission on Scheduled Castes, etc. These institutions protect the rights of women, minorities, and Dalits. Besides, the National Human Rights Commission has also been established by law to protect the fundamental and other kinds of rights.
Directive Principles of State Policy
- The makers of our Constitution knew that independent India was going to face many challenges. Foremost among these was the challenge to bring about equality and well being of all citizens.
- They also thought that certain policy direction was required for handling these problems. At the same time, the Constitution did not want future governments to be bound by certain policy decisions. Therefore, some guidelines were incorporated in the Constitution but they were not made legally enforceable: this means that if a government did not implement a particular guideline, we cannot go to the court asking the court to instruct the government to implement that policy.
- Thus, these guidelines are ‘non-justiciable’ in parts of the Constitution that cannot be enforced by the judiciary. Those who framed our Constitution thought that the moral force behind these guidelines would ensure that the government would take them seriously. Besides, they expected that the people would also hold the government responsible for implementing these directives. So, a separate list of policy guidelines is included in the Constitution. The list of these guidelines is called the Directive Principles of State Policy.
➢ Directive Principles
1. Goals
- The welfare of the people: Social, economic, and political justice.
- Raising the standard of living: Equitable distribution of resources.
- Promotion of international peace.
2. Policies
- Uniform civil code, Prohibition of consumption of alcoholic liquor.
- Promotion of cottage industries.
- Prevention of slaughter of useful cattle.
- Promotion of village panchayats.
3. Non-Justiciable Rights
- Adequate livelihood equal pay for equal work (for men and women)
- Right against economic exploitation, Right to work.
- Right of children to free and compulsory education.
4. What do the Directive Principles Contain?
- The chapter on Directive Principles lists mainly three things:
(i) The goals and objectives that we as a society should adopt.
(ii) Certain rights that individuals should enjoy apart from the Fundamental Rights.
(iii) Certain policies that the government should adopt.
You may get some idea of the vision of makers of our Constitution by looking at some of the Directive Principles shown below:
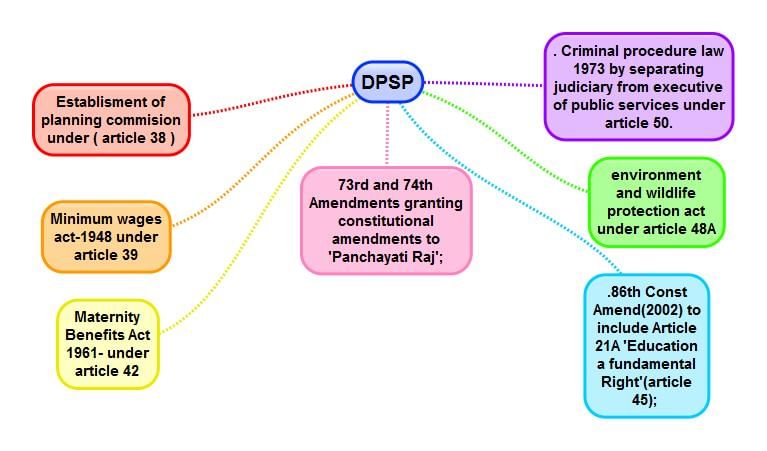
The governments from time to time tried to give effect to some Directive Principles of State Policy. They passed several zamindari abolition bills, nationalised banks, enacted numerous factory laws, fixed minimum wages, cottage and small industries were promoted and provisions for reservation for the uplift of the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes were made. Such efforts to give effect to the Directive Principles include the right to education, formation of panchayati raj institutions all over the country, partial right to work under employment guarantee programme and the mid-day meal scheme etc.
Relationship Between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles
- It is possible to see both Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles as complementary to each other. Fundamental Rights restrain the government from doing certain things while Directive Principles exhort the government to do certain things. Fundamental Rights mainly protect the rights of individuals while directive principles ensure the well being of the entire society.
- However, at times, when the government intends to implement the Directive Principles of State Policy, it can come in conflict with the Fundamental Rights of the citizen.
- However, keeping in mind the societal needs that are greater than the individual interests, the government amended the Constitution to give effect to the Directive Principles of State Policy. This led to a long legal battle.
- The executive and the judiciary took different positions. The government claimed that rights can be abridged for giving effect to Directive Principles. This argument assumed that rights were a hindrance to the welfare of the people.
- On the other hand, the court held the view that Fundamental Rights were so important and sacred that they cannot be limited even for purposes of implementing Directive Principles.
➢
Right to Property
- Behind the controversy about the relationship between rights and directive principles, there was one important reason: In the Constitution, originally, there was a fundamental right to ‘acquire, possess and maintain’ property. But the Constitution made it clear that property could be taken away by the government for public welfare. Since 1950, the government made many laws that limited this right to property. This right was at the centre of the long debate over the relationship between rights and directive principles.
- Finally, in 1973, the Supreme Court gave a decision that the right to property was not part of the basic structure of the Constitution and therefore, parliament had the power to abridge this right by an amendment. In 1978, the 44th amendment to the Constitution removed the right to property from the list of Fundamental Rights and converted it into a simple legal right under article 300 A.
- This generated another complicated debate. This related to the amendment of the Constitution. The government was saying that Parliament can amend any part of the Constitution. The court was saying that Parliament cannot make an amendment that violated Fundamental Rights. This controversy was settled by an important decision of the Supreme Court in the Kesavananda Bharati case. In this case, the court said that there are certain basic features of the Constitution and these cannot be changed by Parliament.
➢
Conclusion
- In the writings of Jyotirao Phule (1827-1890), a radical social reformer from Maharashtra, we find one of the earliest expressions of the view that rights include both freedom and equality. During the national movement, this idea of rights was further sharpened and expanded to constitutional rights. Our Constitution reflected this long tradition and listed the fundamental rights.
- Since 1950, the judiciary has functioned as an important protector of rights. Judicial interpretations have expanded the scope of rights in many respects. The government and administration of our country function within this overall framework. Rights enforce limitations on the functioning of the government and ensure the democratic governance of the country.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution- 2 - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of the Right to Freedom of Religion in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. How do Cultural and Educational Rights protect the interests of minorities in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Right to Constitutional Remedies in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. How do Directive Principles of State Policy guide the government in policymaking? |  |
| 5. Explain the relationship between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles in the Indian Constitution. |  |






















