Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Human Resources
Human Resources Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 5
Introduction
- People are the most valuable asset of a nation. The resources found in nature are only important when people can use them. It is the needs and skills of people that transform these resources into something valuable. Therefore, human resources are considered the most important resource. Healthy, educated, and motivated individuals create resources according to their needs.
- Human resources, like other resources, are not evenly distributed around the globe. They vary in terms of education, age, and gender, and their numbers and characteristics are constantly changing.
Distribution of Population
- The way people are spread out across the Earth's surface is called the pattern of population distribution.
- This distribution is very uneven worldwide.
- Over 90% of the world’s population resides in only about 30% of the land area.
- Some regions are very crowded, while others have few inhabitants.
- Crowded regions include South and Southeast Asia, Europe, and northeastern North America.
- Nearly three-quarters of the global population lives in two continents: Asia and Africa.
- Sixty percent of the world’s population is concentrated in just ten countries: China, India, USA, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nigeria, Russian Federation, and Japan.
- Very few people live in high-latitude regions, tropical deserts, high mountains, and areas with equatorial forests.
Density of Population
- Population density refers to how many people live in a specific area of the earth's surface, typically measured in people per square kilometre.
- The global average population density is 51 individuals per square kilometre, with South Central Asia having the highest density, followed by East and South East Asia.
- In India, the average population density is 382 persons per square kilometre.
Factors affecting distribution of Population
Geographical Factors
- Topography: People always prefer to live on plains rather than mountains and plateaus because these areas are suitable for farming, manufacturing and service activities.
- Example: The Ganga plains are the most densely populated areas of the world while mountains like Andes, Alps and Himalayas are sparsely populated.
- Climate: People usually avoid extreme climates that are very hot or very cold.
- Example: Sahara desert is very hot and polar regions of Russia, Canada and Antarctica are cold are sparsely populated.
- Soil: Fertile soils provide suitable land for agriculture.
- Example: Fertile plains such as Ganga and Brahmaputra in India, Hwang-He, Chang Jiang in China and the Nile in Egypt are densely populated.
- Water: People prefer to live in the areas where fresh water is easily available.
- Example: The river valleys of the world are densely populated while deserts have spare population.
- Minerals: Areas with mineral deposits are more populated.
- Example: Diamond mines of South Africa and discovery of oil in the Middle east lead to settling of people in these areas.
Social, Cultural and Economic Factors
- Social: Areas of better housing, education and health facilities are more densely populated. Example: Pune.
- Cultural: Places with religion or cultural significance attract people. Example: Varanasi, Jerusalem and Vatican city.
- Economic: Industrial areas attract large number of people as it provide employment opportunities. → Example: Osaka in Japan and Mumbai in India.
Population Change
- Population change refers to change in the number of people during a specific time.
- The change happens due to changes in the number of births and deaths.
- Until the 1800s, the world’s population grew steadily but slowly
- Large numbers of babies were born, but they died early too as there were no proper health facilities.
- Also, Sufficient food was not available for all the people.
- In 1804, the world’s population reached one billion.
- In 1959, the world’s population reached 3 billion which is often called population explosion.
- In 1999, 40 years later, the population doubled to 6 billion.
- The main reason for this growth was that with better food supplies and medicine, deaths were reducing, while the number of births still remained fairly high.
Natural Growth Rate
- Birth rate: The number of live births per 1,000 individuals.
- Death rate: The number of deaths per 1,000 individuals.
- Migration refers to the movement of people into and out of a specific area.
- The natural growth rate of a country is the difference between the birth rate and the death rate.
- The global population increase is largely due to a swift rise in the natural growth rate.
Migration
- Migration is another way by which population size changes.
- Emigrants are people who leave a country.
- Countries like the United States of America and Australia have gained in-numbers by in-migration or immigration.
- Immigrants are those who arrive in a country.
- Sudan is an example of a country that has experienced a loss in population numbers due to out-migration or emigration.
Patterns of Population Change
- Rates of population growth vary across the world.
- Countries like Kenya have high population growth rates as they had both high birth rates and death rates.
- Countries like United Kingdom, population growth is slowing because of both low death and low birth rates.
Population Composition
- Population composition refers to the structure of the population.
- It tells about age, sex, literacy level, health condition, occupation and income level of population.
- It tells about age, sex, literacy level, health condition, occupation and income level of population.
- Population pyramid, also called an age-sex pyramid is a way to study the population composition of a country.
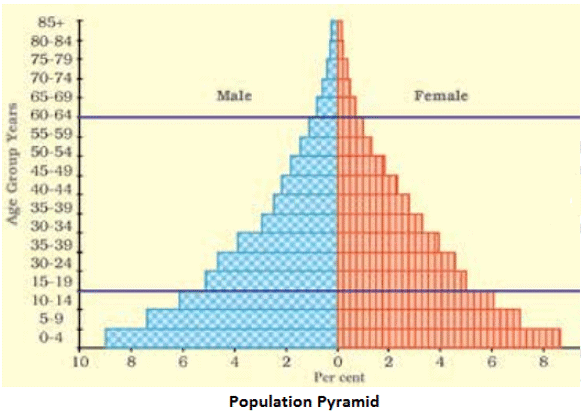
- A population pyramid shows:
- The total population divided into various age groups, example: 5 to 9 years, 10 to 14 years.
- The percentage of the total population, subdivided into males and females, in each of those groups.
- The total population divided into various age groups, example: 5 to 9 years, 10 to 14 years.
- The percentage of the total population, subdivided into males and females, in each of those groups.
- There are two groups of dependents:
- Young dependents (aged below 15 years)
- Elderly dependents (aged over 65 years)
- Young dependents (aged below 15 years)
- Elderly dependents (aged over 65 years)
- Those between the age of 15 years and 65 years are working age and are the economically active.
- The population pyramid tells us how many dependents there are in a country.
- The population pyramid of a country in which birth and death rates both are high is broad at the base and rapidly narrows towards the top because although, many children are born, a large percentage of them die in their infancy, relatively few become adults and there are very few old people.
- Example: Kenya.
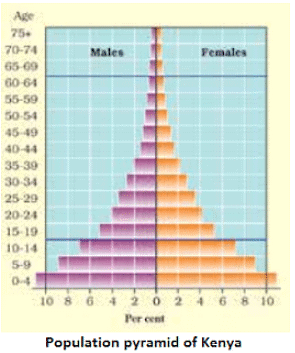
- Example: Kenya.
- The countries where death rates (especially amongst the very young) are decreasing, the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, because more infants survive to adulthood.
- These countries contain a relatively large number of young people and which means a strong and expanding labour force.
- Example: India.
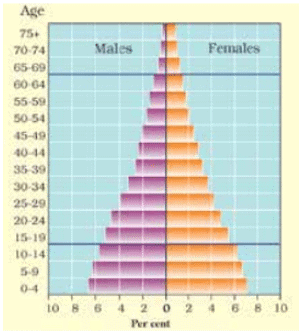
- Example: India.
- The countries where death rates are decreasing allow numbers of people to reach old age.
- Example: Japan.
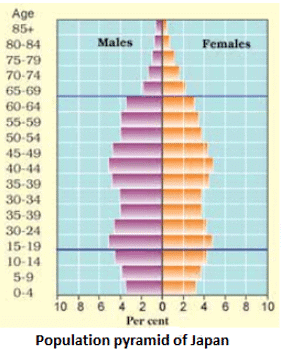
The document Human Resources Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 5 is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
87 videos|558 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Human Resources Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 5
| 1. What are human resources and why are they important in an organization? |  |
Ans.Human resources refer to the personnel or workforce of an organization. They are crucial because they contribute to the overall productivity and success of the organization. Effective management of human resources can lead to better employee performance, higher job satisfaction, and the achievement of organizational goals.
| 2. What are the key functions of human resource management? |  |
Ans.The key functions of human resource management include recruitment and selection, training and development, performance appraisal, compensation management, and employee relations. These functions help ensure that an organization has the right people in the right roles, equipped with the necessary skills and motivation to perform effectively.
| 3. How does the concept of human resources evolve over time? |  |
Ans.The concept of human resources has evolved from viewing employees as mere tools for production to recognizing them as valuable assets. This shift emphasizes the importance of employee engagement, professional development, and a positive work culture, acknowledging that a satisfied workforce is vital for organizational success.
| 4. What role does training and development play in human resources? |  |
Ans.Training and development are essential components of human resources as they help enhance employees' skills and knowledge. This not only improves individual performance but also contributes to the overall effectiveness of the organization. Continuous development ensures that employees can adapt to changing job requirements and stay competitive.
| 5. How can organizations effectively manage their human resources? |  |
Ans.Organizations can effectively manage their human resources by implementing strategic HR practices, such as clear communication, employee engagement initiatives, regular performance evaluations, and opportunities for professional growth. Creating a supportive work environment and fostering a culture of inclusivity also play significant roles in effective HR management.
Related Searches





















