UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > NCERT Summary: Motions of the Earth
NCERT Summary: Motions of the Earth | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
MOTIONS OF THE EARTH
- The earth has two types of motion, namely rotation, and revolution.
- Rotation is the movement of the earth on its axis. An axis is an invisible line around which an object rotates or spins.
- The ancient Indian astronomer Aryabhata had stated that the earth is round and rotates on its own axis.
- The earth takes about 24 hours to complete one rotation around its axis.
- The axis of the earth is not 90 degrees, it is tilted (23.5 degrees) and the angle of the earth’s axis is 66.5 degrees.

What caused the tilt?
- When Earth was young, it is thought that something big hit Earth and knocked it off-kilter. So instead of rotating with its axis straight up and down, it leans over a bit.
- By the way, that big thing that hit Earth is called Theia. It also blasted a big hole in the surface. That big hit sent a huge amount of dust and rubble into orbit. Most scientists think that that rubble, in time, became our Moon.
 DAY and Night
DAY and Night
- The earth receives light from the sun. Due to the spherical shape of the earth, only half of it gets light from the sun at a time. The portion facing the sun experiences day while the other half away from the sun experiences night.

Day and Night
- The movement of the earth around the sun in a fixed path or orbit is called Revolution.
- Earth takes 365 ¼ days to revolve around the sun in its orbital plane.
- The orbital plane of a planet is the geometric plane in which it revolves around the sun.

Orbital plane
- We consider a year as having 365 days. Six hours saved every year are added to make one extra day every four years (leap year).
- The orbit of the earth around the sun is not in a perfect circle. Earth is going around the sun in an elliptical orbit.
- When an object moves around another object in an oval shaped path, it is known to be revolving in an elliptical orbit. All planets move in elliptical orbits around the sun. The Moon also moves around the earth in an elliptical orbit.
Question for NCERT Summary: Motions of the EarthTry yourself:Which of the following causes day and night on the Earth?
View Solution
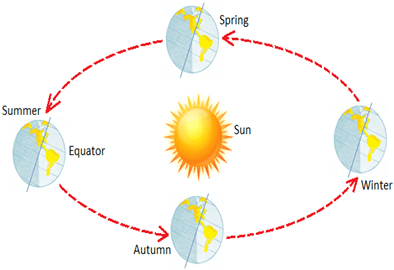
➢ Seasons
- A year is usually divided into summer, winter, spring, and autumn seasons.
➢ What Causes the Seasons?
- Earth's tilted axis and its revolution around the sun causes the seasons.
- As Earth orbits the sun, its tilted axis always points in the same direction.

- Throughout the year, different parts of Earth receive the Sun's most direct rays. So, when the North Pole tilts toward the Sun, it's summer in the Northern Hemisphere. And when the South Pole tilts toward the Sun, its winter in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Sometimes it is the North Pole tilted toward the sun and sometimes it is the South Pole tilted toward the sun.
- It is summer in June in the Northern Hemisphere because the sun's rays hit that part of Earth more directly than at any other time of the year. It is summer in December in the Southern Hemisphere because that is when it is the South Pole turn to be tilted toward the sun.
➢ Solstices and Equinoxes 
Revolution of the earth and seasons
➢ Summer Solstice
- On 21st June, the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun. The rays of the sun fall directly on the tropic of cancer. As a result, these areas receive more heat. The longest day and shortest night in the North Hemisphere occur on June 21st. At this time, in the southern hemisphere, all these conditions are reversed. The nights are longer than the days. This position of the earth is called the Summer Solstice.
➢ Winter Solstice
- On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn receives direct rays of the sun as the South Pole tilts towards the sun. As a result, these areas receive more heat. The longest day and shortest night Southern Hemisphere occur on December 22nd. The reverse happens in the Northern Hemisphere. This position of the earth is called Winter Solstice.
- When it is summer in Northern Hemisphere, places beyond Arctic Circle (66½° N) experience continuous daylight for about six months and, places beyond the Antarctica circle (66½° S) in the Southern Hemisphere experiences continuous light for six months and vice versa.
➢ Equinoxes
- On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun. So the whole earth experiences an equal length of days and nights. This is called Equinox.
Question for NCERT Summary: Motions of the EarthTry yourself:On which of the following date, occurs the longest day and shortest night in the Northern hemisphere of the Earth?
View Solution
The document NCERT Summary: Motions of the Earth | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
180 videos|475 docs|198 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Motions of the Earth - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the different motions of the Earth? |  |
Ans. The Earth has three main motions: rotation, revolution, and precession. Rotation refers to the spinning of the Earth on its axis, causing day and night. Revolution is the Earth's movement around the Sun, resulting in the change of seasons. Precession is a slow change in the direction of the Earth's axis, which takes around 26,000 years to complete.
| 2. How does the rotation of the Earth affect day and night? |  |
Ans. The rotation of the Earth causes the alternation between day and night. As the Earth spins on its axis, different parts of it face towards or away from the Sun, creating daylight and darkness. The side facing the Sun experiences daytime, while the opposite side experiences nighttime.
| 3. What is the impact of the Earth's revolution on the change of seasons? |  |
Ans. The Earth's revolution around the Sun is responsible for the change of seasons. The tilt of the Earth's axis causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year. When a particular hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it experiences summer, while the opposite hemisphere experiences winter. As the Earth continues its revolution, the tilt changes, leading to the onset of spring and autumn.
| 4. How long does it take for the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun? |  |
Ans. It takes approximately 365.25 days for the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun. This extra quarter-day is accounted for in the form of a leap year, which occurs every four years, adding an extra day to the calendar.
| 5. What is the significance of the Earth's precession? |  |
Ans. The Earth's precession has several significant effects. It causes a slow change in the position of the Earth's axis over a period of thousands of years. This results in a shift in the positions of the North and South Poles relative to the stars. Additionally, precession influences the length and intensity of the seasons, as it affects the Earth's axial tilt.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches