Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Some Natural Phenomena
Some Natural Phenomena Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 12
Introduction
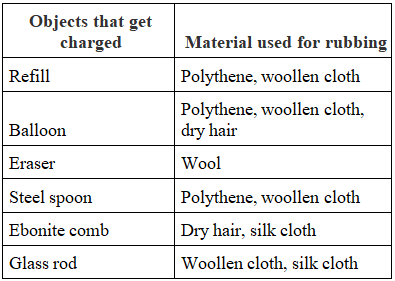
Objects get charged when rubbed with another material.
Charges
- Charges are of two types:
(i) Positive charge
(ii) Negative charge - Similar charges push each other away.
- Opposite charges pull towards each other.
- The electrical charges created by rubbing are static, which means they do not move on their own.
Electroscope
- An electroscope is a tool used to find out if an object is charged.
- This device can check if an object has a charge.
- Two common types of electroscopes are the pith-ball electroscope and the gold-leaf electroscope.
- When the strips have the same charges, they repel each other and spread apart.
Transfer of electric charges
- Electric charge can be transferred from a charged object to another through a conductor.
- Earthing is a process of transferring charge from a charged object to the earth.
Discharging
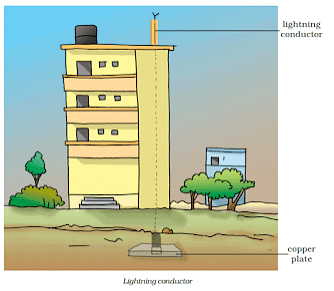
- Removing charge from a charged body is known as discharging.
- Buildings are provided with earthing so that in case of leakage of an electrical charge, people inside the building are not affected, and the charge is transferred to the ground safely.
Discharge of charge
- The static charge in the clouds is the cause of lightning.
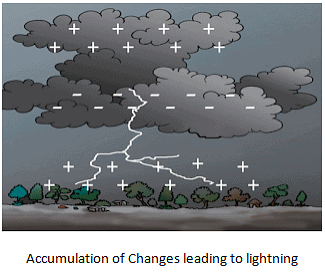
- Positive charges gather near the top of the clouds, while negative charges build up near the bottom.
- Positive charges also accumulate near the ground.
- When these charges become very large, the air, which usually does not conduct electricity well, can no longer hold them back.
- Lightning can occur between two clouds or between a cloud and the Earth.
- This event is known as an electric discharge.
- A lightning strike can cause severe damage to life and property.
Earthquake

- It is the sudden shaking or trembling of the earth’s surface because of disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
- It cannot be predicted.
Causes of Earthquake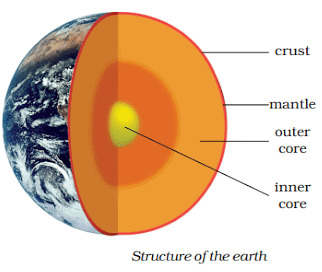
- The uppermost layer of the earth is called crust. Crust is fragmented and each fragment is called plate.
- Movements of earth’s plates (there may be collision or a brushing pass between two plates along their boundary).
- Plate boundaries are called seismic zones or fault zones.
- Earthquake may occur because of volcanic eruption.
- Kashmir, Western and central Himalayas, North-East India, Rann of Kutch, Gangetic plains, and some parts of South India are earthquake prone.
Impact of Earthquakes
- Earthquakes happen frequently across the globe.
- Minor earthquakes occur often, while major ones are less common but can cause significant damage to buildings, bridges, and human life.
- Severe earthquakes can lead to floods, landslides, and tsunamis.
- A notable tsunami occurred in the Indian Ocean on December 26, 2004, following a large earthquake.
The document Some Natural Phenomena Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 12 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
90 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Some Natural Phenomena Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 12
| 1. What are some common natural phenomena discussed in the NCERT chapter "Some Natural Phenomena"? |  |
Ans. The NCERT chapter "Some Natural Phenomena" discusses various natural events such as earthquakes, lightning, and the formation of rainbows. It explains the causes and effects of these phenomena, as well as their significance in nature.
| 2. How do earthquakes occur according to the NCERT summary? |  |
Ans. According to the NCERT summary, earthquakes occur due to the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, which creates seismic waves. This release of energy is often caused by the movement of tectonic plates along faults.
| 3. What is the process of lightning formation as explained in the chapter? |  |
Ans. The chapter explains that lightning is formed due to the buildup of electric charges in clouds during thunderstorms. When the charge becomes strong enough, it results in a discharge of electricity, which we see as lightning.
| 4. How does a rainbow form, based on the information provided in the article? |  |
Ans. A rainbow forms when sunlight is refracted, reflected, and dispersed in water droplets in the atmosphere. The light is bent at different angles, resulting in the spectrum of colors that we see as a rainbow.
| 5. What safety measures should be taken during a thunderstorm, as per the NCERT guidelines? |  |
Ans. The NCERT guidelines suggest that during a thunderstorm, individuals should stay indoors, avoid using electrical appliances, and stay away from tall trees or open fields to reduce the risk of lightning strikes and other hazards.
Related Searches
















