NCERT Summary: Sustainable Development | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Environment |

|
| Functions of Environment |

|
| Carrying capacity of the environment |

|
| State of India’s Environment |

|
| Sustainable Development |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Environment
The environment comprises all living and non-living components, including plants, animals, air, water, soil, and minerals, that form the surroundings of an ecosystem and influence our existence and well-being.
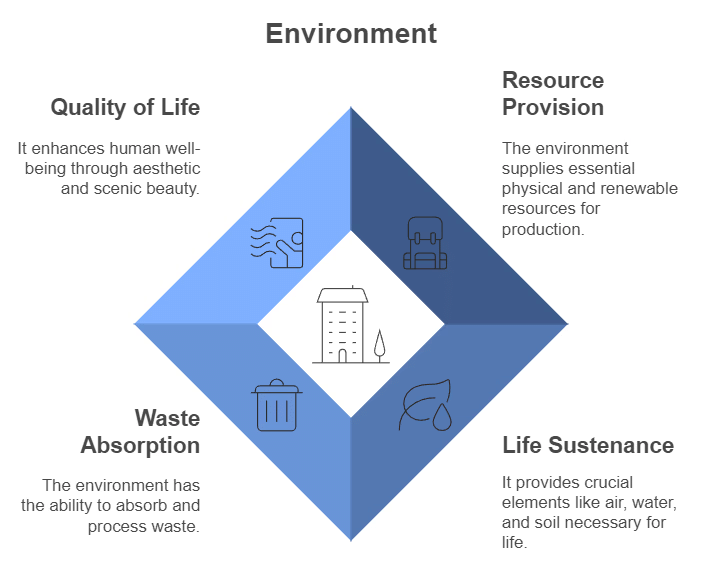
Functions of Environment
- The environment provides resources that are used for production, including physical resources such as minerals, wood, water, and soil. There are two types of resources: renewable resources like air and sunlight, which can be used indefinitely, and non-renewable resources like coal and fossil fuels, which can deplete over time.
- The environment is necessary for sustaining life, as it provides resources like sun, soil, water, and air that are essential for human existence. Without these elements, life would not be possible.
- The environment has the capacity to absorb waste generated by production and consumption activities.
- The environment contributes to the quality of life by providing aesthetic and scenic beauty that enhances human well-being.
Carrying capacity of the environment
- Sustainable development is achieved when the utilization of resources is balanced with their regeneration, and when the waste generated is within the capacity of the environment to absorb, preventing pollution.
- Environmental crises arise when the capacity of the environment to carry a load is exceeded due to excessive exploitation of natural resources or the generation of waste.
State of India’s Environment
- India possesses abundant natural resources and a diverse range of flora and fauna. However, due to development activities, the exploitation of these resources has escalated, resulting in increased strain on the limited natural resources.
- The major environment-related issues are
1. Land Degradation
2. Air Pollution
3. Biodiversity Loss
4. Management of Freshwater
5. Solid Waste Management.
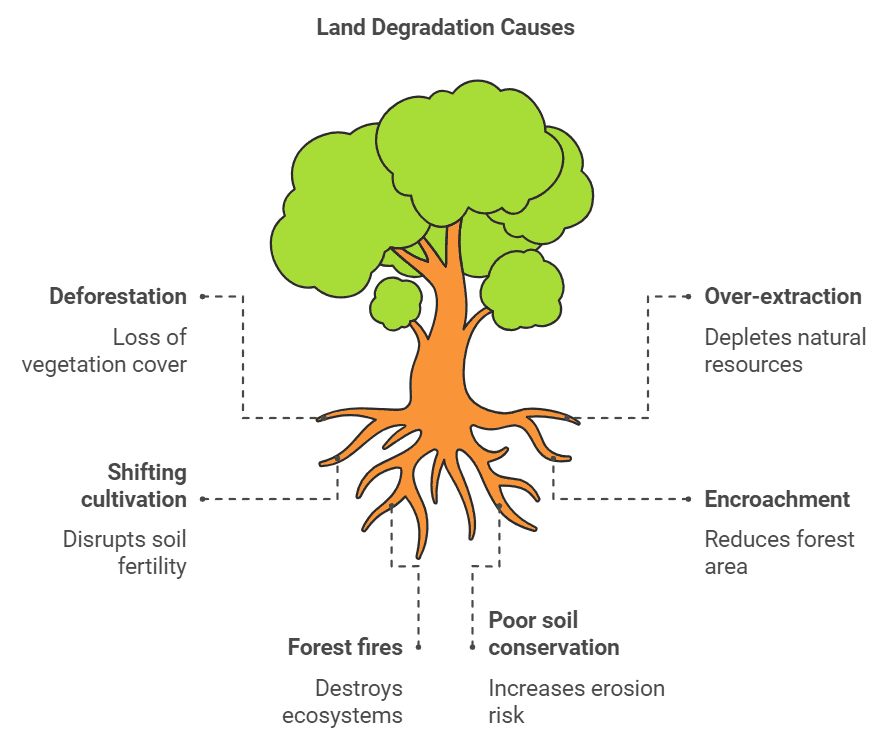
1. Land Degradation
Land degradation is the decline in the fertility of the soil caused by various factors, including but not limited to:
- Deforestation leads to the loss of vegetation.
- Over-extraction of fuelwood and fodder.
- Shifting cultivation practices.
- Encroachment of forest land.
- Forest fires and overgrazing.
- Inadequate implementation of soil conservation measures.
- Improper crop rotation or lack thereof.
- Overuse of agrochemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers.
- Inefficient planning and management of irrigation systems.
- Excessive extraction of groundwater.
2. Air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the air that can cause health problems. These harmful substances come from various sources such as:
- Industries that use coal as an energy source and emit smoke into the air.
- Chemical treatment of materials that release poisonous gases.
- Motor vehicles that emit gases have increased significantly due to the exponential rise in the number of vehicles.
3. Biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss refers to the reduction or disappearance of the various living species in the world. This can be caused by factors such as climate change, pollution, and over-exploitation of natural resources.
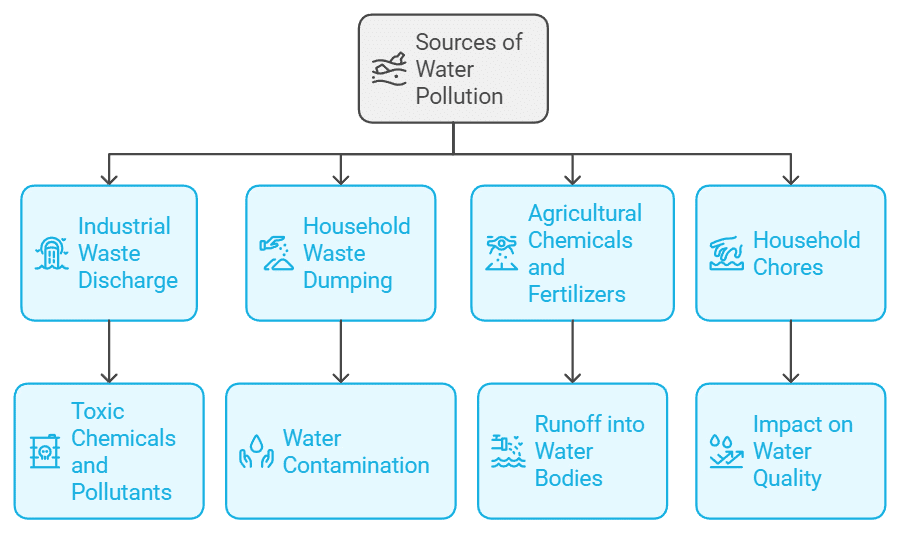
4. Management of Freshwater
The environment is also facing issues related to water resources such as improper management or water pollution. Water pollution is caused by the following factors:
- Discharge of industrial waste in water bodies that contaminates water with toxic chemicals and pollutants.
- Dumping of household waste in water bodies.
- Use of chemicals and fertilizers by farmers, which get mixed up with rainwater and flow into rivers and other water bodies.
- Household chores like washing clothes and bathing also impact water quality.
5. Solid Waste Management
The accumulation of large amounts of waste in both rural and urban areas poses various health risks and diseases. Improper disposal of household waste and littering on the streets are significant environmental threats, emphasizing the urgent need for solid waste management.
Sustainable Development
The United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) defines sustainable development as the type of development that fulfils the requirements of the present generation while ensuring that future generations can fulfil their own needs without any compromise.
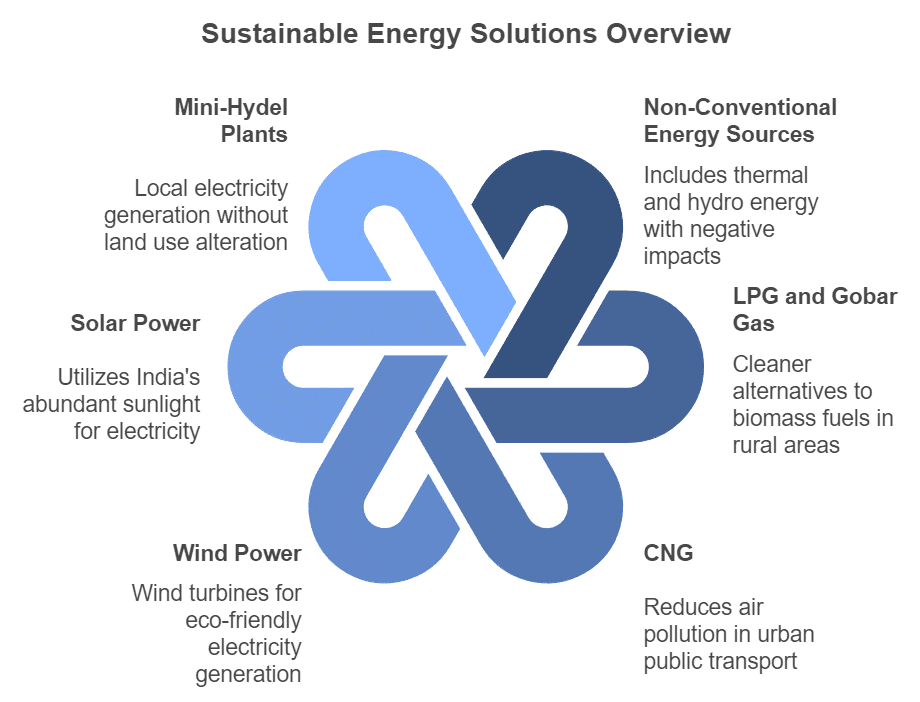
Strategies for Sustainable Development
- Non-Conventional Energy Sources: The use of thermal and hydro energy sources has negative effects on the environment, including carbon dioxide emissions and water pollution. Wind power and solar energy are cleaner alternatives.
- LPG and Gobar Gas in Rural Areas: Biomass fuels like wood and cow dung lead to deforestation, reduced green cover, and air pollution. The use of gobar gas and LPG is recommended as cleaner fuels, with cattle dung used to produce gobar gas and LPG reducing household pollution.
- CNG in Urban Areas: Using Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) in public transport has reduced air pollution in cities.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines can be installed in high-wind areas to generate electricity without causing environmental harm. Though initial setup costs may be high, long-term benefits outweigh the costs.
- Solar Power through Photovoltaic Cells: India has abundant sunlight which can be converted into electricity through solar energy. This is an effective solution for economic growth and sustainable development.
- Mini-Hydel Plants: Mini-hydel plants can be installed in streams to generate electricity for local use. They are eco-friendly and do not alter land use patterns.
Conclusion
- The goal of economic development to fulfil the needs of a growing population by increasing the production of goods and services, results in greater strain on the environment.
- Initially, during the early stages of development, the demand for environmental resources was lower than their supply.
- However, the world is currently dealing with an elevated demand for environmental resources, while their supply is limited due to overuse and misuse.
- The objective of sustainable development is to promote a type of development that minimizes environmental problems and fulfils the present generation's requirements, without compromising the future generation's ability to meet their own needs.
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Sustainable Development - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main functions of the environment? |  |
| 2. What is the carrying capacity of the environment? |  |
| 3. What is the current state of India’s environment? |  |
| 4. How does sustainable development relate to environmental conservation? |  |
| 5. Why is sustainable development important for India? |  |















