NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Identify the suitable reagent for the following conversion (NEET 2025)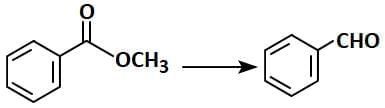 (a) (i) NaBH₄, (ii) H⁺/H₂O
(a) (i) NaBH₄, (ii) H⁺/H₂O
(b) (i) H₂/Pd-BaSO₄
(c) (i) LiAlH₄, (ii) H⁺/H₂O
(d) (i) AlH(iBu)₂, (ii) H₂O
Ans: (d)
- For the given reaction:
R-C=O-OR' + DIBAL-H → R-C=O-H + ROH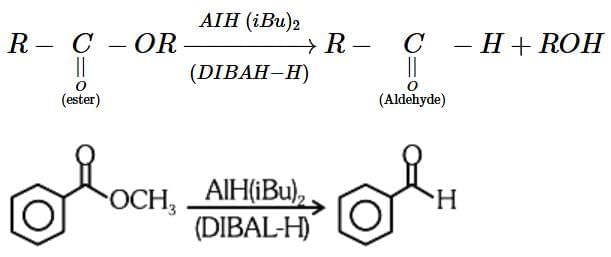
- In this case, DIBAL-H selectively reduces the ester (R-C=O-OR') to an aldehyde (R-C=O-H) and the alcohol group (ROH) is released.
- The correct reagent for the conversion is Option 2 (AlH(iBu)2, H2O). DIBAL-H reduces the ester to the aldehyde, and water (H2O) is used to hydrolyze the intermediate to the final aldehyde product.
Why not the other options:
- Option 1: LiAlH4 (Lithium aluminium hydride) followed by H2O: LiAlH4 is a strong reducing agent that reduces esters to alcohols rather than aldehydes. It would not stop at the aldehyde stage, which makes it unsuitable for this transformation.
- Option 3: NaBH4 (Sodium borohydride) followed by H2O: NaBH4 is a milder reducing agent than LiAlH4 and typically reduces aldehydes and ketones to alcohols, but it is not reactive enough to reduce esters to aldehydes.
- Option 4: H2/Pd-BaSO4 (Hydrogen and palladium on barium sulfate): This is a catalytic hydrogenation method, typically used to reduce alkenes or aromatic compounds. It will reduce aldehydes to alcohols, so it would not be selective enough to stop at the aldehyde stage when reducing esters.
Therefore, the correct answer is AlH(iBu)2, H2O, which reduces the ester to an aldehyde selectively.
Q2: The correct order of decreasing acidity of the following aliphatic acids is: (NEET 2025)
(a) (CH3)3CCOOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > CH3COOH > HCOOH
(b) CH3COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH > HCOOH
(c) HCOOH > CH3COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH
(d) HCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > CH3COOH
Ans: (c)
- HCOOH (formic acid): No alkyl group, highest acidity.
- CH3COOH (acetic acid): One methyl group (-CH3), moderately acidic. (+I)
- (CH3)2CHCOOH (isobutyric acid): Two methyl groups attached to the same carbon, further decreases acidity. ( two +I)
- (CH3)3CCOOH (pivalic acid): Three methyl groups attached to the same carbon, lowest acidity due to strong electron-donating effect. (three +I)
- The correct order of decreasing acidity is:
- HCOOH > CH3COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 3: HCOOH > CH3COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH.
Q3: The major product of the following reaction is: (NEET 2025)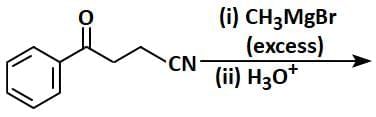 (a)
(a) 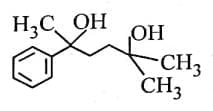
(b) 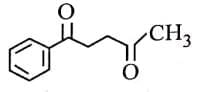
(c) 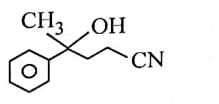
(d) 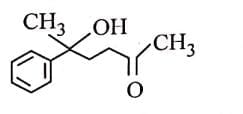
Ans: (d)
2024
Q1: Fehling's solution 'A' is(a) aqueous copper sulphate
(b) alkaline copper sulphate
(c) alkaline solution of sodium potassium tartrate (Rochelle's salt)
(d) aqueous sodium citrate (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
Fehling's solution is a chemical reagent used to differentiate between water-soluble carbohydrates and ketone-functional groups, and as a test for monosaccharides. It is used specially in the Fehling's test for reducing sugars. The test involves two solutions, generally known as Fehling's A and Fehling's B, which are mixed together and added to perform the test.
Fehling's solution 'A' is an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate. Thus, the correct option is:
Option A: aqueous copper sulphate
The function of Fehling's A is to provide copper(II) ions, Cu2+, which act as the oxidizing agent in the reaction with the reducing sugar. When Fehling's Solution A and B are mixed and heated with a reducing sugar, the copper(II) ions are reduced to copper(I) oxide, which precipitates as a red solid, indicating a positive result.
Fehling's Solution B, on the other hand, contains alkaline sodium potassium tartrate, which helps to maintain the solution in an alkaline condition and keeps the copper(II) ions in solution.
Thus, in summary, Fehling's A consists of aqueous copper sulfate, which directly matches with Option A.
Q2: Match List I with List II.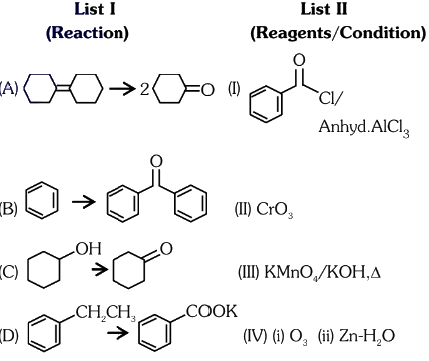
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
(b) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III (NEET 2024)
Ans: (c)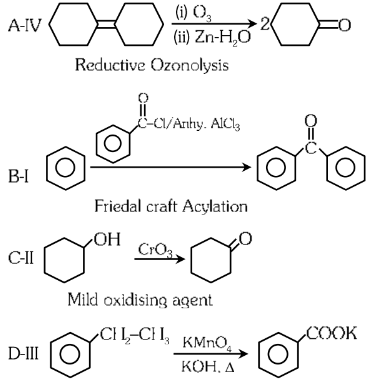
Answer: (c) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV.
Explanation: The reconstructed reactions align with the reagents’ typical behavior in organic chemistry for aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. PCC selectively oxidizes to aldehydes, CrO₃ and KMnO₄ oxidize primary alcohols to carboxylic acids, and K₂Cr₂O₇ oxidizes secondary alcohols to ketones.
Q3: For the given reaction: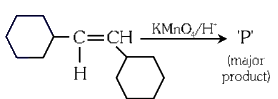
'P' is
(a) 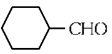
(b) 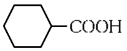
(c) 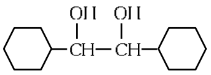
(d) 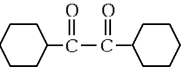 (NEET 2024)
(NEET 2024)
Ans: (b)
Q4: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Benzoic acid produces effervescence on treatment with aq. NaHCO₃.
Statement II: The effervescence is due to the release of hydrogen gas.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Ans: (c)
Statement I: Benzoic acid produces effervescence on treatment with aqueous NaHCO₃.
This statement is correct. Benzoic acid (C₆H₅COOH) is a carboxylic acid. When it reacts with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), it undergoes a neutralization reaction, releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, which causes effervescence. The reaction is:
C₆H₅COOH + NaHCO₃ → C₆H₅COONa + CO₂ + H₂O
Statement II: The effervescence is due to the release of hydrogen gas.
This statement is incorrect. The effervescence observed during the reaction of benzoic acid with sodium bicarbonate is due to the release of carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, not hydrogen gas. The reaction between an acid and a bicarbonate typically releases carbon dioxide, not hydrogen gas.
Correct Answer: (c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
Q5: The product that cannot be formed in the following reaction is: (NEET 2024)
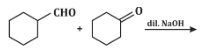
(a) 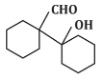
(b) 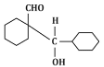
(c) 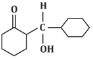
(d) 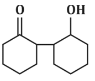
Ans: (d)
The reaction shown in the image involves the condensation of an aldehyde (probably an aldehyde group attached to a cyclohexane ring) with a carbonyl compound under the influence of dilute sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This type of reaction is indicative of the aldol condensation process.
Analyzing the options:
Option (a): This is a typical aldol addition product, where two molecules of aldehyde combine to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde.
Option (b): This is also a plausible aldol addition product, where the structure shows a β-hydroxy aldehyde as expected from an aldol reaction.
Option (c): This shows a similar aldol addition product with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the β-position.
Option (d): This structure does not align with the typical aldol addition product. It shows a product where the structure is inconsistent with the expected reaction pathway, possibly due to ring formation that doesn’t follow the usual mechanism.
Correct Answer: (d) This product cannot be formed from the reaction because it does not align with the typical aldol addition or condensation mechanism.
Q6: Match the reagents in List-I with the corresponding reactions in List-II: (NEET 2024)
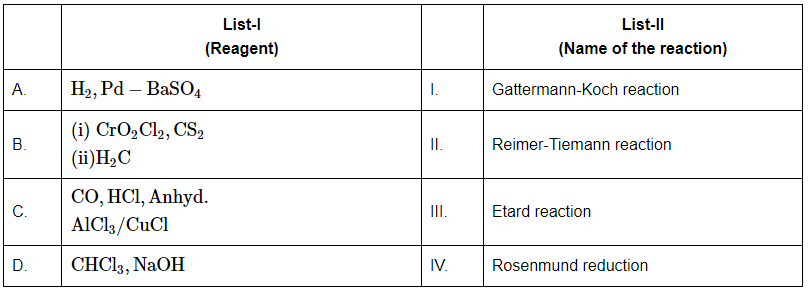
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(c) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(d) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
Ans: (b)
A: H₂, Pd – BaSO₄
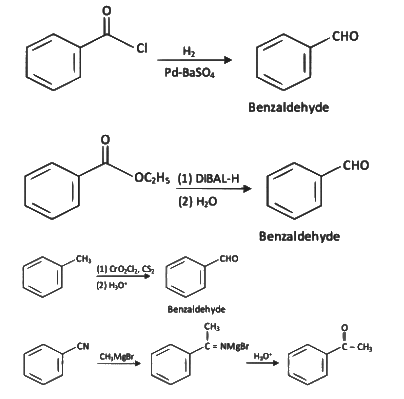
This corresponds to Rosenmund reduction (IV), where acyl chlorides are reduced to aldehydes using hydrogen gas and palladium on barium sulfate (Pd/BaSO₄).
B: (i) CrO₂Cl₂, CS₂ (ii) H₂C
This is associated with the Etard reaction (III), which is used to oxidize toluene to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride and carbon disulfide.
C: CO, HCl, Anhyd. AlCl₃/CuCl
This corresponds to the Gattermann-Koch reaction (I), which is a method to introduce a formyl group (–CHO) to an aromatic compound using carbon monoxide, hydrochloric acid, and a Lewis acid catalyst.
D: CHCl₃, NaOH
This also refers to the Reimer-Tiemann reaction (II), where phenol reacts with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide to produce salicylaldehyde.
Correct Answer: (b) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Q7: Identify [X] and [Y] in the given reaction: (NEET 2024)
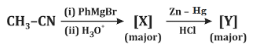
(a) 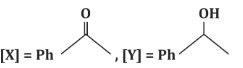
(b) 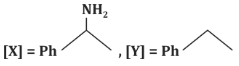
(c) 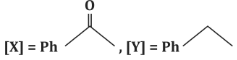
(d) 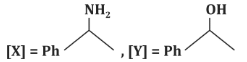
Ans: (c)
Step 1: Formation of [X]
- CH₃CN (acetonitrile) reacts with PhMgBr (phenylmagnesium bromide), a Grignard reagent, followed by hydrolysis with H₂O.
- Grignard reagents are strong nucleophiles and typically add to the carbon of the nitrile group (C≡N).
- The reaction of CH₃CN with PhMgBr involves the addition of the phenyl group (Ph) to the carbon of the nitrile, forming an intermediate imine salt. After the first step, the intermediate is protonated and hydrolyzed to form a ketone.
- The product [X] is thus PhC(=O)CH₃ (acetophenone), where the phenyl group (Ph) is attached to the carbonyl carbon, and the methyl group (CH₃) remains from the original acetonitrile.
Step 2: Formation of [Y]
- PhC(=O)CH₃ is then subjected to Zn - Hg, HCl, which is a Clemmensen reduction.
- The Clemmensen reduction converts a carbonyl group (C=O) in ketones or aldehydes to a methylene group (CH₂).
- Therefore, PhC(=O)CH₃ is reduced to PhCH₂CH₃ (ethylbenzene).
Matching with Options:
- (a)[X] = PhC(=O)H, [Y] = PhOH: Incorrect, as [X] is a ketone, not an aldehyde, and [Y] is not a phenol.
- (b)[X] = PhC(=O)N H₂, [Y] = PhNH₂: Incorrect, as the reaction does not form an amide or amine.
- (c)[X] = PhC(=O)CH₃, [Y] = PhCH₂CH₃: Correct, as the reaction proceeds as described.
- (d)[X] = PhC(=O)CH₃, [Y] = PhC₂H₅: Incorrect, as it does not match the expected reduction product.
Correct Answer: (c) [X] = PhC(=O)CH₃, [Y] = PhCH₂CH₃.
Q8: Select the incorrect reaction among the following: (NEET 2024)
(a) 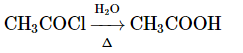
(b) 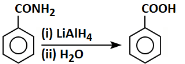
(c) 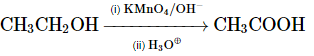
(d)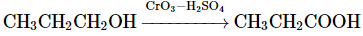
Ans: (b)
Option 1: CH₃COOC₂H₅ → CH₃COOH (ester hydrolysis to acetic acid) is correct under acidic or basic conditions.
Option 2: The reaction shows a cyclic compound with -CONH₂ being converted to -COOH using LiAlH₄ and H₂O. LiAlH₄ is a reducing agent that typically reduces amides to amines, not to carboxylic acids. This makes the reaction incorrect.
Option 3: CH₃CH₂OH → CH₃COOH (oxidation of ethanol to acetic acid) using KMnO₄/OH⁻ and heat is correct.
Option 4: CH₃CH₂CH₂OH → CH₃CH₂COOH (oxidation of propanol to propanoic acid) using CrO₃-H₂SO₄ is correct.
Thus, the incorrect reaction is option B.
2023
Q1: Complete the following reaction: (NEET 2023)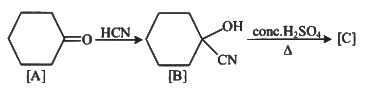
[C] is _______.
(a) 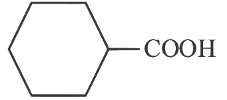
(b) 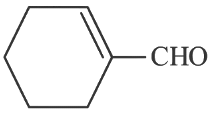
(c) 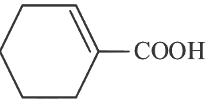
(d) 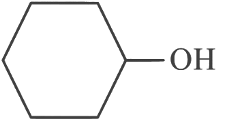
Ans: (c)
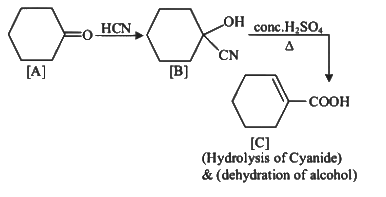
Q2: Identify the major product obtained in the following reaction: (NEET 2023)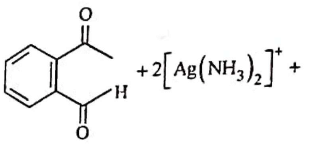 3 – OH
3 – OH 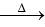 major product
major product
(a) 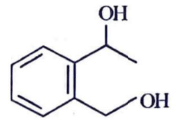
(b) 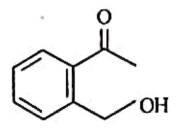
(c) 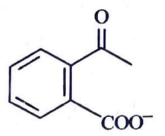
(d) 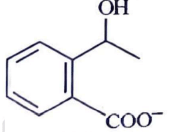
Ans: (c)
Ammoniacal silver nitrate solution is Tollens’ reagent. Tollens’ reagent can be used to distinguish aldehyde & ketone as aldehyde upon warming with Tollens’ reagent produces a silver mirror due to formation of silver metal in alkaline medium. Aldehyde is oxidised to corresponding carboxylate anion.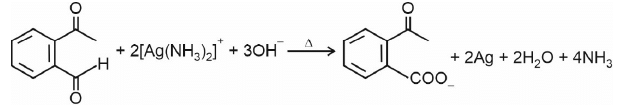
Q3: Identify the final product [D] obtained in the following sequence of reactions. (NEET 2023)
(a) 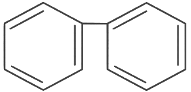
(b) C3H10
(c) 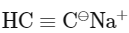
(d) 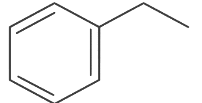
Ans: (d)
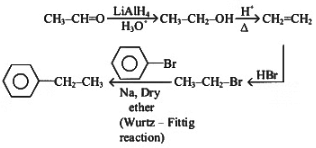
Q4: The weight (g) of two moles of the organic compound, which is obtained by heating sodium ethanoate with sodium hydroxide in the presence of calcium oxide, is: (NEET 2023)
(a) 18
(b) 16
(c) 32
(d) 30
Ans: (c)
The organic compound obtained by heating sodium ethanoate (CH₃COONa) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in the presence of calcium oxide (CaO) is methane (CH₄). This is an example of a decarboxylation reaction, specifically the Kolbe's electrolysis or a related process where sodium ethanoate decomposes to form methane.
Molar mass of CH₄ = 12 (C) + 4 × 1 (H) = 16 g/mol.
Weight of 2 moles of CH₄ = 2 × 16 = 32 g.
The correct answer is (c) 32.
Q5: Identify the product (A) in the following reaction: (NEET 2023)
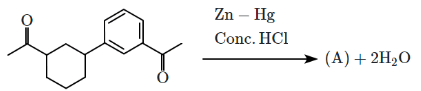
(a) 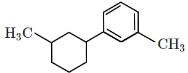
(b) 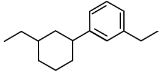
(c) 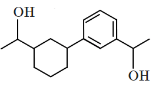
(d) 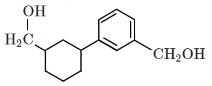
Ans: (b)
In this reaction:
Reagents: Zn – Hg and Conc. HCl
This is a Clemmensen reduction, which reduces a carbonyl group (–C=O) in ketones or aldehydes to a methylene group (–CH₂–), removing the oxygen.
The given reactant is acetophenone (C₆H₅–CO–CH₃), which is a ketone.
The Clemmensen reduction converts acetophenone into ethylbenzene (C₆H₅–CH₂–CH₃), where the carbonyl group (–C=O) in acetophenone is reduced to a methylene group (–CH₂–), producing ethylbenzene.
Checking the options:
(a): This is ethylbenzene (C₆H₅–CH₂–CH₃), which is the correct product.
(b): This is cyclohexene, which is also the product of the Clemmensen reduction if the starting ketone is cyclohexanone.
(c): This is hydroxyacetophenone, which is not the expected product of the Clemmensen reduction.
(d): This is hydroxyethylbenzene, which is also not expected as a product from the Clemmensen reduction.
Correct Answer: (b)
Q6: Consider the given reaction: (NEET 2023)
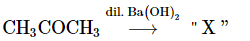
The functional groups present in the compound "X" are:
(a) Ketone and double bond
(b) Double bond and aldehyde
(c) Alcohol and aldehyde
(d) Alcohol and ketone
Ans: (d)
Reactant: CH₃COCH₃ (Acetone)
Reagent: Dilute Ba(OH)₂
The reaction involves acetone (CH₃COCH₃), a ketone. When it reacts with dilute Ba(OH)₂, the reaction is likely a Baeyer-Villiger oxidation.
In the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation, a ketone is converted into an ester. However, when acetone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)₂, the reaction typically results in the formation of acetolactone, which involves the introduction of a double bond (forming a β,β-unsaturated ketone) and possibly a hydroxy group.
Thus, the product "X" will have the following functional groups:
Alcohol group (-OH), which is part of the β-hydroxy ketone structure.
Ketone group (-C=O) as part of the acetone structure.
The correct answer is (d) Alcohol and ketone.
Q7: Mark the name of the reaction associated with the following conversion (NEET 2023)
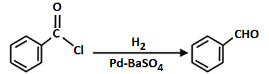
(a) Stephen reaction
(b) Gattermann-Koch reaction
(c) Etard reaction
(d) Rosenmund reaction
Ans: (d)
The given reaction involves the conversion of a benzoyl chloride (C₆H₅COCl) into benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO) using H₂ and Pd-BaSO₄ (palladium on barium sulfate).
This is a Rosenmund reduction, a reaction where acyl chlorides are reduced to aldehydes using hydrogen in the presence of palladium on barium sulfate (Pd-BaSO₄). The reaction is specifically used to reduce the acyl group (–COCl) to an aldehyde group (–CHO).
Correct Answer: (d) Rosenmund reaction.
Q8: Identify the product in the following reaction: (NEET 2023)
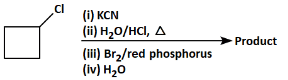
(a) 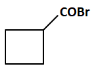
(b) 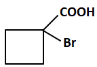
(c) 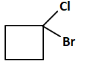
(d) 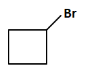
Ans: (b)
Let's analyze the steps and reagents involved in the given reaction:
(i) KCN: Potassium cyanide (KCN) will replace the chlorine atom with a cyano group (–CN) in a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The product after this step will be cyclobutyl cyanide.
(ii) H₂O/HCl, Δ (heat): The reaction of the nitrile (–CN) with water and hydrochloric acid (HCl) under heat leads to the hydrolysis of the nitrile group, converting it to a carboxylic acid (–COOH). The product after this step will be cyclobutyric acid.
(iii) Br₂/red phosphorus: The use of bromine (Br₂) with red phosphorus typically results in a radical halogenation reaction, where a halogen (Br) replaces a hydrogen atom at the β-position (next to the carboxylic acid group).
(iv) H₂O: This step might be used to stabilize the product after the halogenation reaction.
Analyzing the Options:
(a): COBr (This product suggests the presence of a carboxylic acid chloride, which is unlikely from the given steps. So, this is not the correct answer).
(b): COOH and Br (This product corresponds to a halogenated carboxylic acid after the reaction with bromine. This is the correct answer).
(c): Cl (This does not match the reaction pathway because we expect a carboxyl group, not a chlorine atom).
(d): Br (This product shows only the halogen (Br), but there should be a carboxyl group involved too).
Correct Answer: (b) COOH and Br.
2022
Q1: 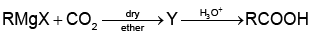
What is Y in the above reaction? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) RCOO-X+
(b) (RCOO)2Mg
(c) RCOO-Mg+X
(d) R3CO-Mg+X
Ans: (c)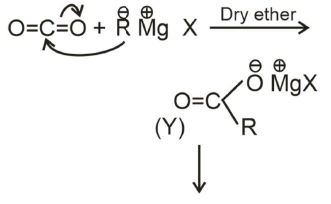
Q2: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses because of weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones due to dipole-dipole interactions.
Statement II: The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than the alcohols of similar molecular masses due to the absence of H-bonding.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
- The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses due to weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of the dipole - dipole interaction.
- Acohols involved intermolecular hydrogen bonding, because of which the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones are lower than the alcohols of similar molecular masses.
Q3: Match List-I with List -II. 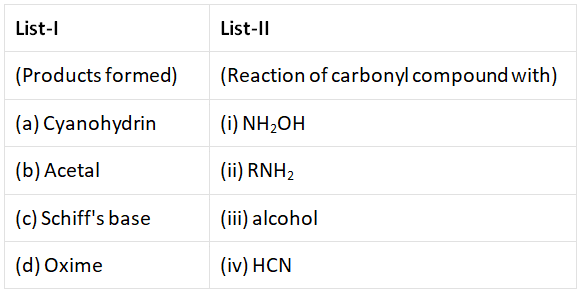 from the options given below correct answer Choose the (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
from the options given below correct answer Choose the (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) (a) – (i), (b) – (iii), (c) – (ii), (d) – (iv)
(b) (a) – (iv), (b) – (iii), (c) – (ii), (d) – (i)
(c) (a) – (iii), (b) – (iv), (c) – (ii), (d) – (i)
(d) (a) – (ii), (b) – (iii), (c) – (iv), (d) – (i)
Ans: (b)
Cyanohydrin → HCN
Acetal → Alcohol
Schiff's base → R–NH2
Oxime → NH2–OH
Q4: Which one of the following is not formed when acetone reacts with 2-pentanone in the presence of dilute NaOH followed by heating? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) 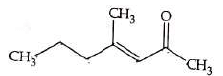
(b) 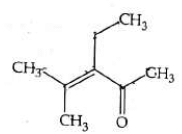
(c) 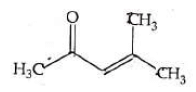
(d) 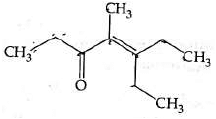
Ans: (d)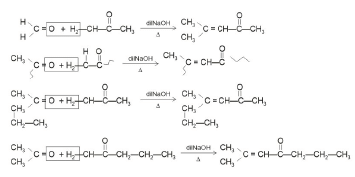
Q5: Compound X on reaction with O3 followed by Zn/H2O gives formaldehyde and 2-methyl propanal as products. The compound X is
(a) 3-Methylbut-1-ene
(b) 2-Methylbut-1-ene
(c) 2-Methylbut-2-ene
(d) Pent-2-ene (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Ans: (a)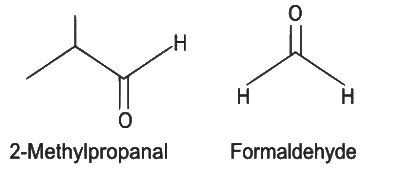
The given reaction is the reductive ozonolysis of an alkene. The alkene will be
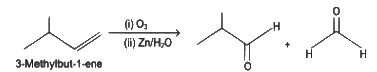
Q6: The incorrect method to synthesize benzaldehyde is (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) 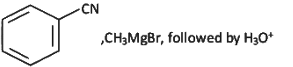
(b) 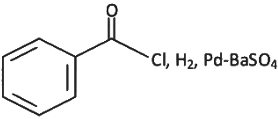
(c) 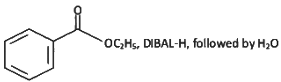
(d) 
Ans: (a)
Q7: Match List-I with List-II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
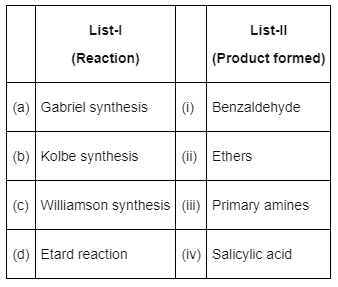
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(b) (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iv)
(c) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iv)
(d) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
Ans: (a)
- Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is used for preparation of aliphatic primary amines.
- Kolbe synthesis with phenol gives salicylic acid
- Williamson synthesis gives ether on reaction of alkyl halide and alcoxide
- Etard reaction gives benzaldehyde from benzene
Q8: The product formed from the following reaction sequence is (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
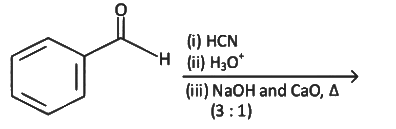
(a) 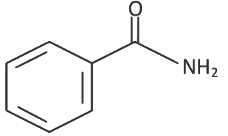
(b) 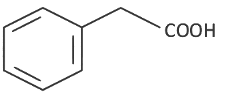
(c) 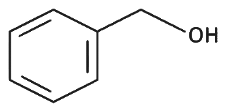
(d) 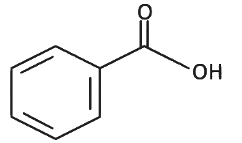
Ans: (c)
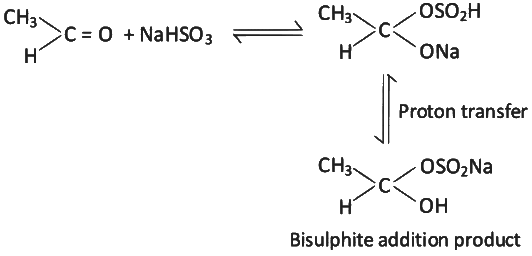
Q9: Which of the following reactions is not an example for nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction?
(a) CH3CHO + NH3
(b) 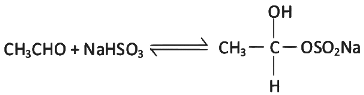
(c) CH3CHO + NH2OH
(d) CH3CHO + C6H5NHNH2
Ans: (b)
It is an example of nucleophilic addition reaction
2021
Q1: 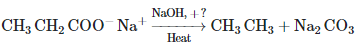
Consider the above reaction and identify the missing reagent/chemical. (NEET 2021)
(a) CaO
(b) DIBAL-H
(c) B2H6
(d) Red Phosphorus
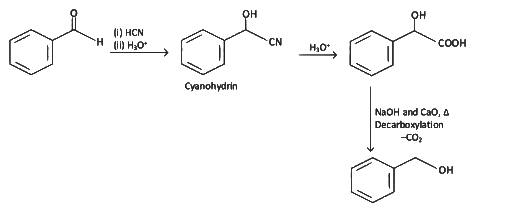
Ans: (a)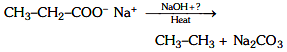 Decarboxylation takes place by soda-lime (NaOH + CaO)
Decarboxylation takes place by soda-lime (NaOH + CaO)
Q2: Match List-I with List-II. (NEET 2021) Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (a)-(i), (b)-(iv), (c)-(iii), (d)-(ii)
(b) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
(c) (a)-(iv), (b)-(i), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iii)
(d) (a)-(iii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(i), (d)-(iv)
Ans: (b)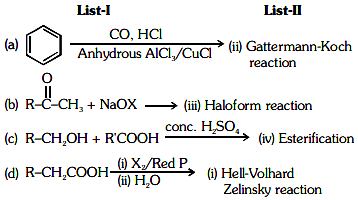
Q3: The product formed in the following chemical reaction is : (NEET 2021)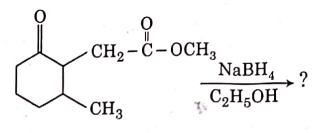
(a) 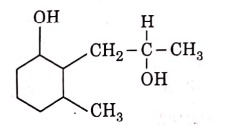
(b) 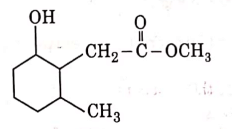
(c) 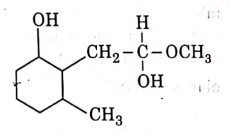
(d) 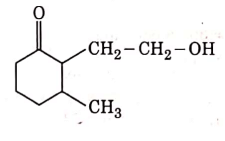
Ans: (b)
NaBH4 is a reducing agent. If reduces carbonyl group into alcohols but does not reduce esters.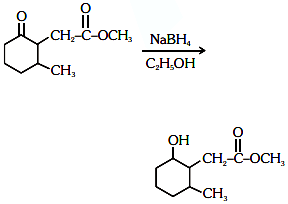
Q4: The intermediate compound 'X' in the following chemical reaction is : (NEET 2021)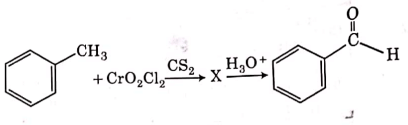
(a)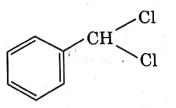
(b)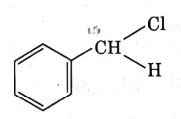
(c)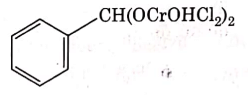
(d)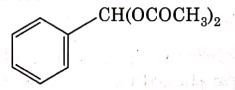
Ans: (c)
This is Etard reaction in which reaction of toluene with chromyl chloride in CCl4 followed by hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde. Toluene reacts with chromyl chloride to form a precipitate called the Etard complex.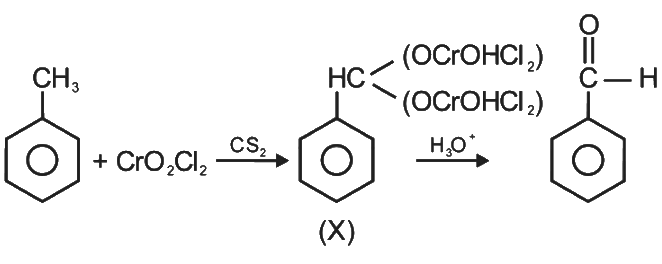
Q5: What is the IUPAC name of the organic compound formed in the following chemical reaction?
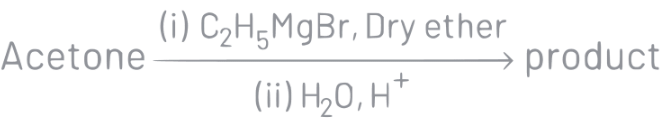 (a) 2-methylbutan-2-ol
(a) 2-methylbutan-2-ol
(b) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(c) pentan-2-ol
(d) pentan-3-ol
Ans: (a)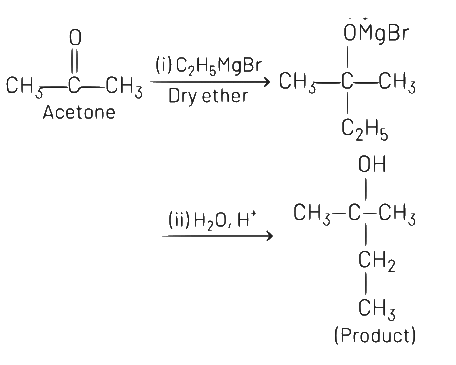
IUPAC name of product is 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
2020
Q1: Identify compound X in the following sequences of reactions : (NEET 2020)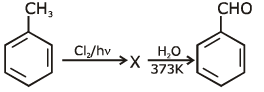
(a)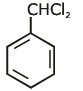
(b)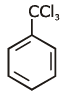
(c)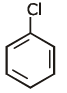
(d)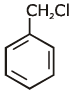
Ans: (a)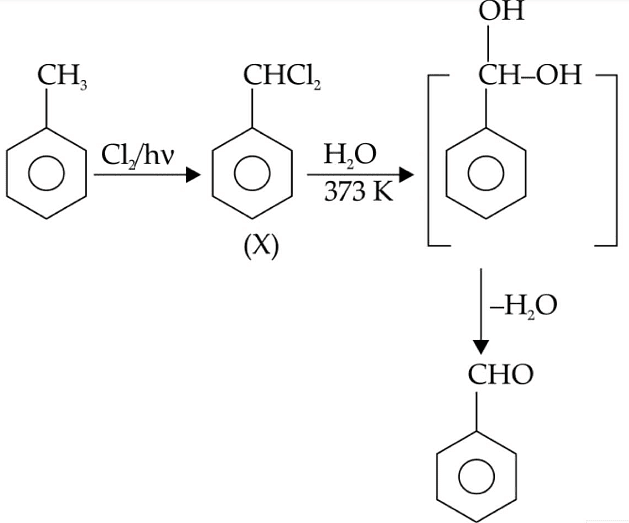
Q2: Reaction between benzaldehyde and acetophenone in presence of dilute NaOH is known as: (NEET 2020)
(a) Cross Cannizzaro’s reaction
(b) Cross Aldol condensation
(c) Aldol condensation
(d) Cannizzaro’s reaction
Ans: (b)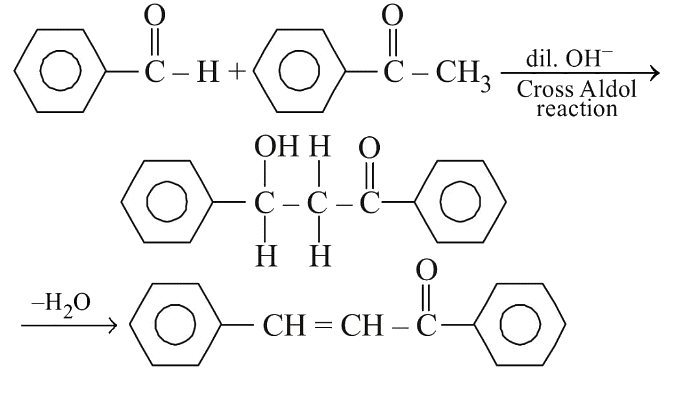 In the presence of dil. OH- , benzaldehyde and acetophenone will react to undergo cross-aldol condensation.
In the presence of dil. OH- , benzaldehyde and acetophenone will react to undergo cross-aldol condensation.
Q3: Reaction between acetone and methylmagnesium chloride followed by hydrolysis will give :
(a) Sec. butyl alcohol
(b) Tert. butyl alcohol
(c) Isobutyl alcohol
(d) Isopropyl alcohol (NEET 2020)
Ans: (b)
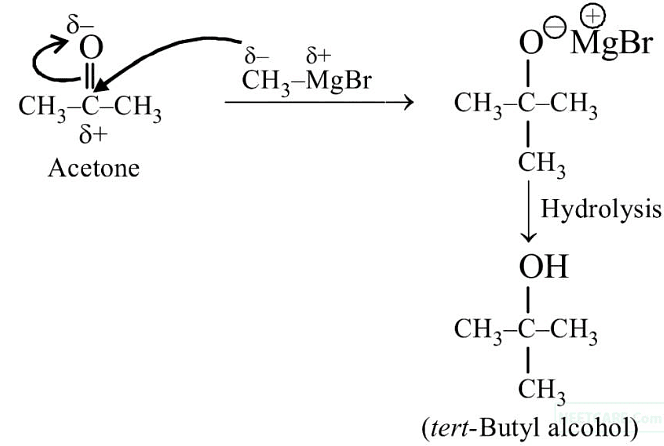
2018
Q1: Carboxylic acid have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their (NEET 2018)
(a) formation of intramolecular H-bonding
(b) formation of carboxylate ion
(c) more extensive association of carboxylic acid via vander Wall force of attraction
(d) formation of intermolecular H-bonding.
Ans: (d)
Due to the formation of intermolecular H-bonding, association occurs in carboxylic acids. So, they have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass.
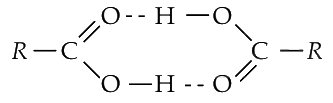
2017
Q1: Consider the reactions :- (NEET 2017)
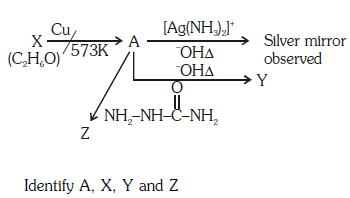
(a) A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanol, Y-Ethanoic acid, Z-Semicarbazide.
(b) A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal , Z-Semicarbazone
(c) A-Ethanol, X-Acetaldehyde, Y-Butanone, Z-Hydrazone
(d) A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanoic acid, Y-Acetate ion, Z-hydrazine
Ans: (b)
Since, A gives silver mirror test, it must be an aldehyde and aldehydes are formed by oxidation of 1o alcohols. Thus, ‘X’ is a 1o alcohol, i.e., CH3CH2OH. 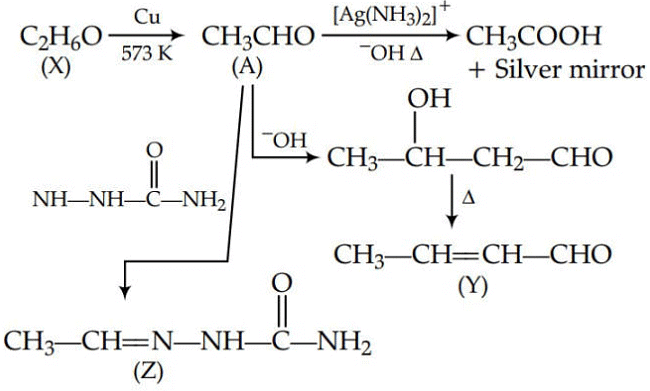
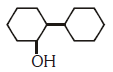
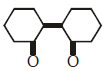
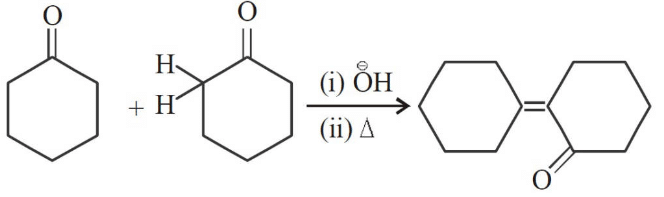
Q2: Of the following, which is the product formed when cyclohexanone undergoes aldol condensation followed by heating ?:- (NEET 2017)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
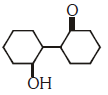
Ans: (a)
 2016
2016
Q1: The correct order of strengths of the carboxylic acids (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
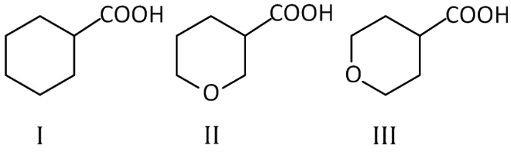
is
(a) I > II > III
(b) II > III > I
(c) III > II > I
(d) II > I > III
Ans: (b)
We know, Acidic strength ∝ – I effect
As oxygen is more electron withdrawing (II) and (III) show greater – I effect than (I). Thus, (I) is least acidic. Out of (II) and (III), (II) is more acidic than (III) as distance of O increases from —COOH group and acidic strength decreases.
Q2: Which of the following reagents would distinguish cis-cyclopenta-1,2- diol from the trans-isomer? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Aluminium isopropoxide
(b) Acetone
(c) Ozone
(d) MnO2
Ans: (b)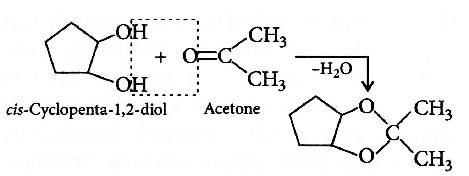
Trans isomer does not react with acetone as removal of H2O molecule is difficult.
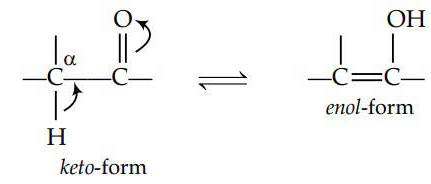
Q3: The correct statement regarding a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon, is : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this processes is known as keto-enol tautomerism .
(b) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon never equilibrates with its corresponding enol.
(c) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as aldehyde-ketone equilibration.
(d) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known a carbonylation.
Ans: (a)
Keto-enol tautomerism is as follows :
2015
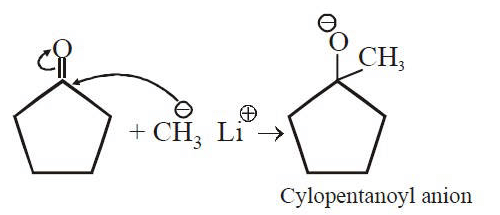
Q1: Treatment of cyclopentanone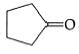 with methyl lithium gives which of the following species? (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
with methyl lithium gives which of the following species? (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Cyclopentanonyl biradical
(b) Cyclopentanonyl anion
(c) Cyclopentanonyl cation
(d) Cyclopentanonyl radical
Ans: (b)
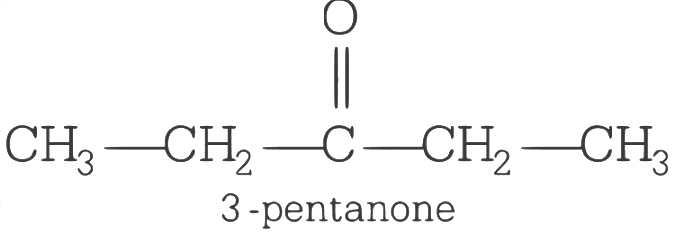
Q2: An organic compound X having molecular formula C5H10O yields phenyl hydrazone and gives negative response to the iodoform test and tollen test. It produces n-pentane on reduction X could be
(a) n-amyl alcohol
(b) pentanal
(c) 2-pentanone
(d) 3-pentanone (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
Ans: (d)
As the compound X yields phenyl hydrazone and gives negative response to the iodoform test and Tollen’s test so it must contain a C = O group but neither a methyl ketone nor in aldehyde. Thus, the structure of X will be
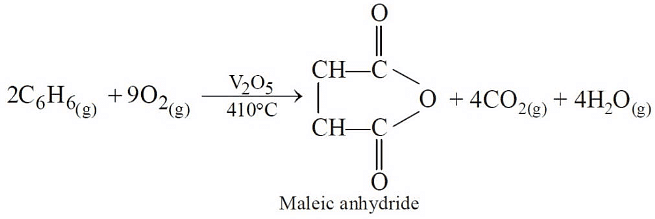
Q3:The oxidation of benzene by V2O5 in the presence of air produces (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
(a) maleic anhydride
(b) benzoic acid
(c) benzaldehyde
(d) benzoic anhydride.
Ans: (a)
2014
Q1: Which one is most reactive towards Nucleophilic addition reaction? (NEET / AIPMT 2014)
(a)
(b)
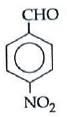
(c)

(d)
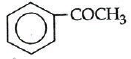
Ans: (b)
Electron withdrawing (–I, –M) groups are more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions. Thus, correct order is :
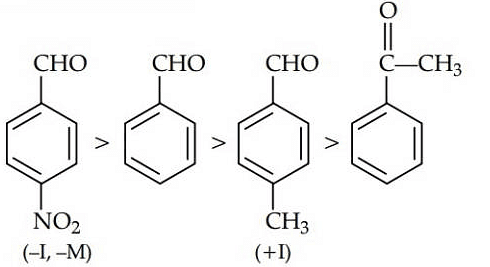
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are the common reactions of aldehydes and ketones? |  |
| 2. How can you distinguish between aldehydes and ketones? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of carboxylic acids? |  |
| 4. How do carboxylic acids react with bases? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids in organic chemistry? |  |

















