NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Thermodynamics | Physics Class 11 PDF Download
2024
Q1: A thermodynamic system is taken through the cycle abcda. The work done by the gas along the path bc is: [2024]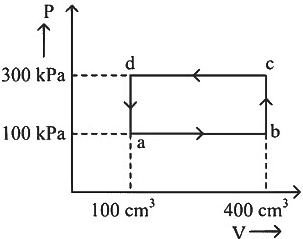 (a) Zero
(a) Zero
(b) 30 J
(c) −90 J
(d) −60 J
Ans: (a)
Path bc is an isochoric process.
∴ Work done by gas along path bc is zero.
2023
Q1: The equilibrium concentrations of the species in the reaction A+B ⇌ C+D are 2,3,10 and 6 mol L−1, respectively at 300K. ΔG0 for the reaction is (R = 2cal/mol K(a) -137.26 cal
(b) -1381.80 cal
(c) -13.73 cal
(d) 1372.60 cal [NEET 2023]
Ans: (b)
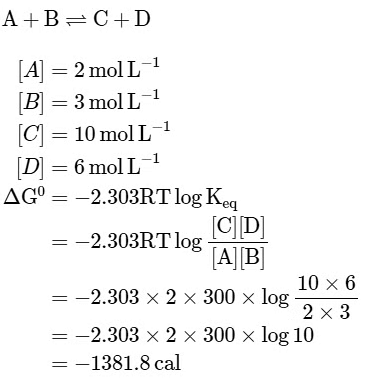
Q2: Which amongst the following options is the correct relation between change in enthalpy and change in internal energy? [NEET 2023]
(a) 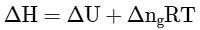
(b) 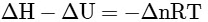
(c) 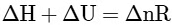
(d) 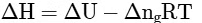
Ans: (a)

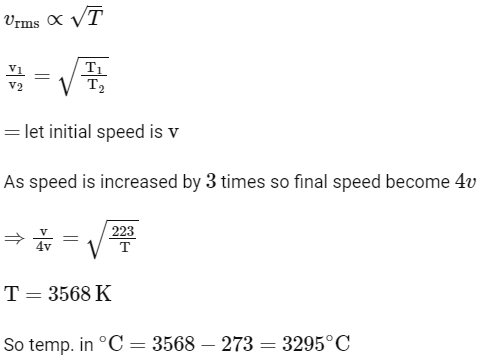
Q3: The temperature of a gas is −50∘C. To what temperature the gas should be heated so that the rms speed is increased by 3 times?
(a) 3295∘C
(b) 3097 K
(c) 223 K
(d) 669∘C [NEET 2023]
Ans: (a)
Q4: A Carnot engine has an efficiency of 50% when its source is at a temperature 327∘C. The temperature of the sink is :-
(a) 15∘C
(b) 100∘C
(c) 200∘C
(d) 27∘C [NEET 2023]
Ans: (d)
Efficiency of carnot engine
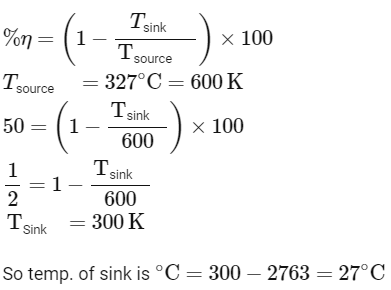
2022
Q1: Which of the following p-V curve represents maximum work done? [NEET 2022 Phase 1]
(a) 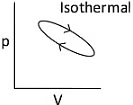
(b) 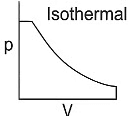
(c) 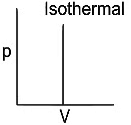
(d) 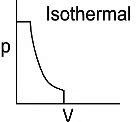
Ans: (b)
Work done under any thermodynamic process can be determined by area under the 'p-V' graph. As it can be observed maximum area is covered in option '2'.
Q2: One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K is expanded isothermally from 1 L to 10 L volume. ΔU for this process is :
(Use R = 8.314 J k−1 mol−1) [NEET 2022 Phase 2]
(a) 0 J
(b) 1260 J
(c) 2520 J
(d) 5040 J
Ans: (a)
For isothermal condition; ΔT = 0
ΔU = 0
Q3: A vessel contains 3.2 g of dioxygen gas at STP (273.15 K and 1 atm pressure). The gas is now transferred to another vessel at constant temperature, where pressure becomes one third of the original pressure. The volume of new vessel in L is : (Given : molar volume at STP is 22.4 L) [NEET 2022 Phase 2]
(a) 67.2
(b) 6.72
(c) 2.24
(d) 22.4
Ans: (b)
At constant temperature and amount

2021
Q1: Which one among the following is the correct option for right relationship between Cp and CV for one mole of ideal gas ? [NEET 2021]
(a) CP = RCV
(b) CP = RCV
(c) CP + CV = R
(d) CP - CV = R
Ans: (d)
At constant volume, qV = CVΔT = ΔU
At constant pressure, qP = CP ΔT = ΔH
For a mole of an ideal gas,
ΔH = ΔU + Δ( PV )
=ΔU+Δ(RT)
=ΔU+RΔT
On putting the values of ΔH and ΔU, we have CPΔT = CVΔT+RΔT
CP = CV + R
CP–CV = R
Q2: For irreversible expansion of an ideal gas under isothermal condition, the correct option is : [NEET 2021]
(a) ΔU = 0, Δ Stotal ≠ 0
(b) ∆U ≠ 0, ∆ Stotal = 0
(c) ∆U = 0, ∆ Stotal = 0
(d) ∆U ≠ 0, ∆ Stotal ≠ 0
Ans: (a)
Hint: ∆U = nCV∆T
In the case of isothermal process, ΔT is zero. The value of ΔU is also zero from the relation, ∆U=nCV∆T.
Thus, for reversible and irreversible expansion for an ideal gas, under isothermal conditions, ∆U = 0. But the value ∆S for irreversible expansion of an ideal gas under isothermal conditions is not equal to zero.
The total entropy change ( ∆S total) for the system and surroundings of a spontaneous process is given by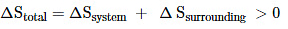
2020
Q1: For the reaction, 2Cl(g) → Cl2(g), the correct option is: [NEET 2020]
(a) ΔrH < 0 and ΔrS > 0
(b) ΔrH < 0 and ΔrS < 0
(c) ΔrH > 0 and ΔrS > 0
(d) ΔrH > 0 and ΔrS < 0
Ans: (b)
2Cl(g) → Cl2(g) + Heat
Due to bond formation stability increases which results in release of heat.
∴ ΔHr = -ve or exothermic process
ΔHr < O
& ΔS < O, because number of Cl atoms decreases in the formation of Cl2(g)
Q2: The correct option for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition is : [NEET 2020]
(a) q = 0, Δ T < 0 and w > 0
(b) q < 0, Δ T = 0 and w = 0
(c) q > 0, Δ T > 0 and w > 0
(d) q = 0, Δ T = 0 and w = 0
Ans: (d)
Free expansion, so pex = 0
So, w = − pexΔ V = 0
Since, adiabatic process, so q = 0
Since both q and w are equal to zero. Then according to first law of thermodynamics Δ E = q + w
Δ U = 0
Hence, Δ T = 0
2019
Q1: In which case change in entropy is negative? [NEET 2019]
(a) Sublimation of solid to gas
(b) 2H(g)
(c) Evaporation of water
(d) Expansion of a gas at temperature
Ans: (b)
2H(g) → H2(g)
Due to bond formation, entropy decreases.
Q2: Under isothermal condition, a gas at 300 K expands from 0.1 L to 0.25 L against a constant external pressure of 2 bar. The work done by the gas is [Given that 1 L bar = 100 J] [NEET 2019]
(a) 25 J
(b) 30 J
(c) -30 J
(d) 5 KJ
Ans: (c)
W = –Pext (V2–V1)
Pext = 2 bar
V1 = 0.1 L
V2 = 0.25 L
W = –2 bar[0.25 – 0.1] L
W = –2 × 0.15 bar L
W = –0.30 bar L
W = (–0.30) × 100 = –30 J
2018
Q1: The bond dissociation energies of X2 , Y2 and XY are in the ratio of 1 : 0.5 : 1.
(a) 800 kJ mol–1
(b) 200 kJ mol–1
(c) 400 kJ mol–1
(d) 100 kJ mol–1
Ans: (a)
Let bond dissociation energies of X2 , Y2 and XY are x kJ mol–1 , 0.5x kJ mol–1 and x kJ mol–1 respectively.
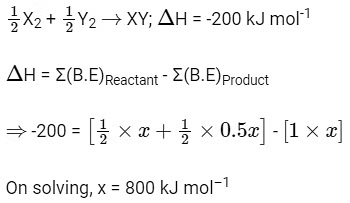
2017
Q1: A gas is allowed to expand in a well insulated container against a constant external pressure of 2.5 atm from an initial volume of 2.50 L to a final volume of 4.50 L. The change in internal energy ΔU of the gas in joules will be [NEET 2017]
(a) -500 J
(b) -505 J
(c) +505 J
(d) 1136.25 J
Ans: (b)
w = - PextΔV = -2.5(4.50 - 2.50)
ΔU = q + w
As, the container is insulted, thus q = 0
Hence, ΔU = w = -506.625 J = - 505.5 J ( nearly equals)
Q2: For a given reaction, ΔH = 35.5 kJ mol
(a) T > 425 K
(b) Ball temperatures
(c) T > 298 K
(d) T < 425 K
Ans: (a)
For a spontaneous reaction,

2016
Q1: For a sample of perfect gas when its pressure is changed isothermally from pi to pf, the entropy change is given by [NEET 2016]
(a) 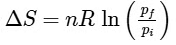
(b) 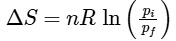
(c) 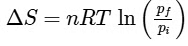
(d) 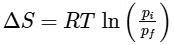
Ans: (b)
For an ideal gas undergoing reversible expansion, when temperature changes from Ti to Tf and pressure changes from Pi to Pf.

2015
(b) −630 kJ
Ans: (a)
Given,
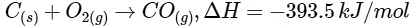
Then amount of heat released on formation of 44 g CO2 = 393.5 kJ
∴ Amount of heat released on formation of
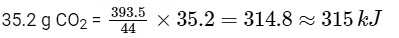
2014
Ans: (b)
Using Gibb's-Helmholtz equation,
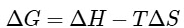
During adsorption of a gas, entropy decreases i.e, ΔS < 0
For spontaneous adsorption, ΔG should be negative, which is possible when ΔH is highly negative.
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Thermodynamics - Physics Class 11
| 1. What is the first law of thermodynamics and how does it apply to closed systems? |  |
| 2. What are the key differences between isothermal and adiabatic processes in thermodynamics? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate the efficiency of a heat engine using thermodynamic principles? |  |
| 4. What is entropy and why is it important in thermodynamics? |  |
| 5. How does the concept of heat transfer relate to thermodynamics in practical applications? |  |




















