NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Amines | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: Given below are two statements:Statement I : Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction.
Statement II : Aniline cannot be prepared through Gabriel synthesis.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
- Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction due to salt formation with aluminium chloride, the Lewis acid, which is used as a catalyst.
- Aniline (aromatic primary amine) cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
2023
Q1: Which of the following reactions will NOT give primary amine as the product? (NEET 2023)(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

Ans: C

2022
Q1: Given below are two statements
Statement I: Primary aliphatic amines react with HNO2 to give unstable diazonium salts.
Statement II: Primary aromatic amines react with HNO2 to form diazonium salts which are stable even above 300 K. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below (NEET 2022)
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (a)
Statement II is incorrect. The aromatic diazonium salts are unstable above 300 K.
Q2: The product formed from the following reaction sequence is (NEET 2022)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (b)
2021
Q1: Identify the compound that will react with Hinsberg's reagent to give a solid which dissolves in alkali. (NEET 2021)
(a)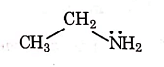
(b)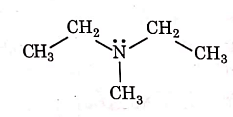
(c)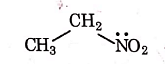
(d)
Ans: (a)
1° amines react with Hingsberg's reagent to give a solid, which dissolve in alkali.
Q2: The reagent 'R' in the given sequence of a chemical reaction is : (NEET 2021)
(a) HI
(b) CuCN/KCN
(c) H2O
(d) CH3CH2OH
Ans: (d)
R : CH3CH2OH
Certain mild reducing agents like hypophosphorus acid or ethanol reduce diazonium salts to arene and themselves get oxidised to phosphorous acid and ethanal respectively.
2020
Q1: Which of the following amine will give the carbylamine test? (NEET 2020)
(a)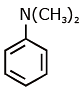
(b)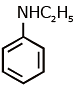
(c)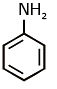
(d)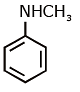
Ans: (c)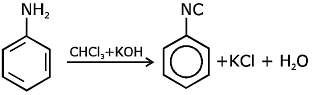 Carbylamine reaction is give by 1° amine & aniline.
Carbylamine reaction is give by 1° amine & aniline.
2019
Q1: The correct order of the basic strength of methyl substituted amines in aqueous solution is: (NEET 2019)
(a) (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N
(b) (CH3)3N > CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH
(c) (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2
(d) CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
Ans: (a)
In aqueous solution, electron donating inductive effect, solvation effect (H-bonding) and steric hindrance all together affect basic strength of substituted amines
Basic character:
2018
Q1: Nitration of aniline in strong acidic medium also gives m-nitroaniline because (NEET 2018)
(a) In spite of substituents nitro group always goes to only m-position.
(b) In electrophilic substitution reactions amino group is meta directive.
(c) In absence of substituents nitro group always goes to m-position
(d) In acidic (strong) medium aniline is present as anilinium ion.
Ans: (b)
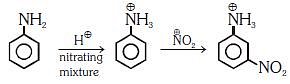 In acidic medium aniline is protonated to form anilinium ion which is metadirecting.
In acidic medium aniline is protonated to form anilinium ion which is metadirecting.
2017
Q1: Which of the following reactions is appropriate forconverting acetamide to methanamine? (NEET 2017)
(a) Hoffmann hypobromamide reaction
(b) Stephens reaction
(c) Gabriels phthalimide synthesis
(d) Carbylamine reaction
Ans: (a)
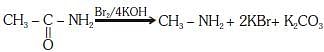
This reaction is known as hoffmann hypobromamide reaction.
2016
Q1:The correct statement regarding the basicity of arylamines is : (NEET 2016)
(a) Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines, because the nitrogen atom in arylamines is sp-hybridized.
(b) Arylamines are generally less basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone pair electrons are delocalized by interaction with the aromatic ring π electrons system.
(c) Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone pair electrons are not delocalized by interaction with the aromatic ring π electron system.
(d) Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because of aryl group
Ans: (b)
In arylamines, lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom is delocalised over the benzene ring, thus, not available for donation. So, arylamines are less basic than alkylamines.
2015
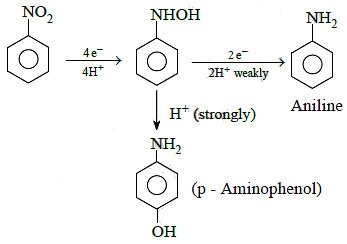
Q1: The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in strongly acidic medium produces: (NEET 2015)
(a) Aniline
(b) p-Aminophenol
(c) Azoxybenzene
(d) Azobenzene
Ans: (b)
Electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in weakly acidic medium gives aniline but in strongly acidic medium, it gives para-amino phenol obviously through the acid catalysed rearrangement of initially formed phenyl hydroxyl amine.
2014
Q1: In the following reaction, the product (A) (NEET 2014)
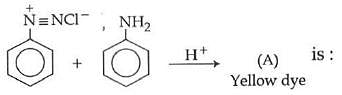
(a)
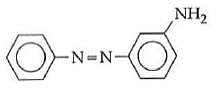
(b)
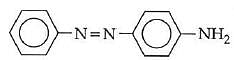
(c)
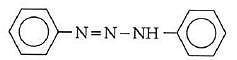
(d)

Ans: (b)
The above reaction is a coupling reaction of aniline with diazonium salt to give azo benzene compound. This coupling reaction takes place at the para-position to - NH2 group of benzene. This reaction act as electrophilic substitution reaction of aniline.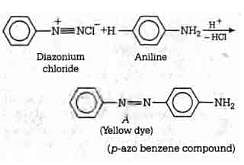
Q2: Which of the following will be most stable diazonium salt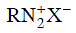 ? (NEET 2014)
? (NEET 2014)
(a)
(b)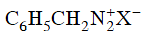
(c)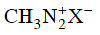
(d)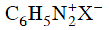
Ans: (d)
Diazonium salt containing aryl group directly linked to the nitrogen atom is most stable due to resonance stabilization between the benzene nucleus and N-atom.![[Resonance structure of benzene diazonium ion]](https://edurev.gumlet.io/ApplicationImages/Temp/3066490_fb68ba3b-0351-4d16-bcf7-35cb41c0ee9a_lg.png) [Resonance structure of benzene diazonium ion]
[Resonance structure of benzene diazonium ion]
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Amines - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are amines? |  |
| 2. How are amines classified? |  |
| 3. What are some common uses of amines? |  |
| 4. How do amines react with acids? |  |
| 5. How can amines be synthesized? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















