NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Nuclei | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
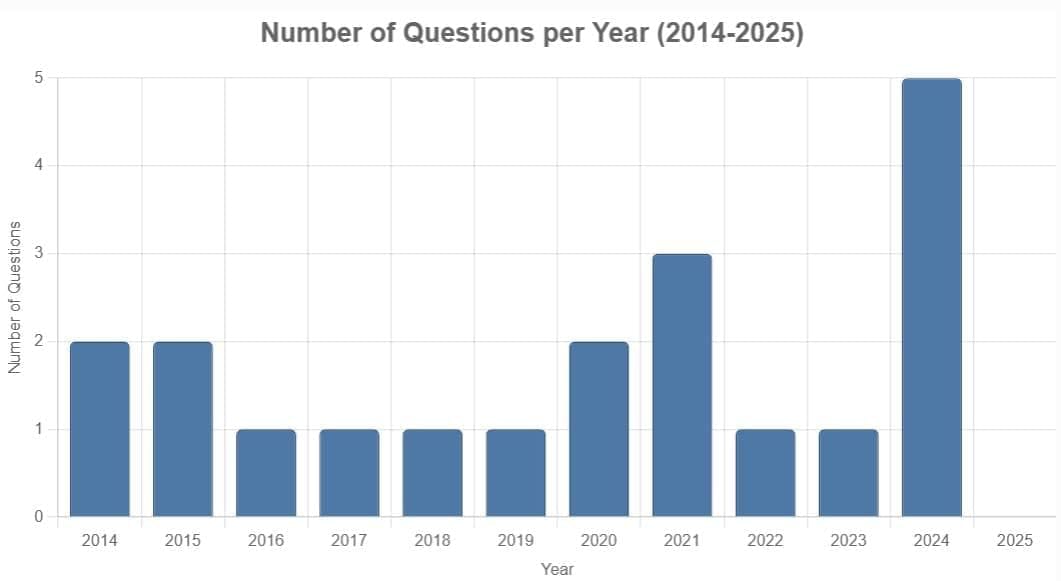
From 2014 to 2025, 20 questions were asked on the Nuclei chapter in the NEET exam. Typically, one to three questions appeared annually (scattered across 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024), with a peak of five questions in 2024 and none in 2025. The questions primarily focused on nuclear decay processes, half-life calculations, binding energy, nuclear reactions, and nuclear properties, with no specific difficulty distribution provided in the data. Key focus areas included alpha, beta, and gamma decay effects, half-life and activity calculations, binding energy in nuclear reactions, nuclear fission products, and properties like nuclear density and radius.
2024
Q1: 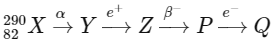
In the nuclear emission stated above, the mass number and atomic number of the product Q respectively, are (NEET 2024)
(a) 280, 81
(b) 286, 80
(c) 288, 82
(d) 286, 79
Ans: (d) 286, 79
To determine the mass number and atomic number of the final product Q in the provided nuclear reactions, we need to analyze the impact of each type of decay (alpha, positron emission, beta-minus decay, and electron capture) on the mass number and atomic number of the initial element 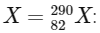
1. Alpha decay (α decay): In alpha decay, an alpha particle (which is a 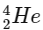 nucleus) is emitted. This reduces the mass number by 4 units and the atomic number by 2 units.
nucleus) is emitted. This reduces the mass number by 4 units and the atomic number by 2 units.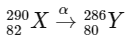
2. Beta plus decay (positron emission, e+): During positron emission, a proton in the nucleus is transformed into a neutron, and a positron is emitted. This decreases the atomic number by 1 but does not change the mass number.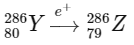
3. Beta-minus decay (β− decay): In a beta-minus decay, a neutron in the nucleus converts into a proton and an electron (beta particle) and an antineutrino are emitted. This results in an increase in the atomic number by 1, while the mass number remains unchanged.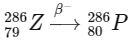
4. Electron capture (e− capture): During electron capture, an atomic electron is absorbed by the nucleus, causing a proton to convert into a neutron. This process decreases the atomic number by 1 without altering the mass number.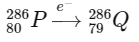
From the calculations above, the mass number of Q is 286, and its atomic number is 79.
D: Mass number = 286, Atomic number = 79
Q2: The ratio of nuclear densities and nuclear volumes of 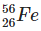 and
and 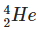 are, respectively: (NEET 2024)
are, respectively: (NEET 2024)
(a) 13 : 1 and 14 : 1
(b) 14 : 1 and 1 : 1
(c) 1 : 1 and 14 : 1
(d) 1 : 1 and 13 : 1
Ans: (c)
Nuclear density is nearly constant for all nuclei because it depends on mass and volume, and both increase proportionally with the mass number.
So, the ratio of nuclear densities of Fe-56 to He-4 is 1:1.
The volume of a nucleus is proportional to its mass number.
Fe has mass number 56 and He has 4.
Therefore, the volume ratio of Fe to He is 56:4, which simplifies to 14:1.
Q3: An excited heavy nucleus 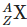 emits radiations in the following sequence: (NEET 2024)
emits radiations in the following sequence: (NEET 2024)
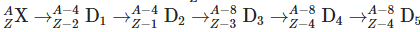
Where Z and A are the atomic and mass number of element X, respectively. The possible emitted particles or radiations in the sequence, respectively are:
(a) e⁺, α, e⁻, α, γ
(b) e⁻, α, e⁺, α, γ
(c) α, e⁻, α, e⁺, γ
(d) α, e⁺, α, e⁻, γ
Ans: (c)
- First step: Mass number decreases by 4, atomic number by 2 → alpha particle (α) emitted.
- Second step: Atomic number increases by 1 → beta-minus (e⁻) emitted.
- Third step: Mass number decreases by 4, atomic number by 2 → another alpha (α) emitted.
- Fourth step: Atomic number decreases by 1 → beta-plus (e⁺) emitted.
- Fifth step: No change in mass or atomic number → gamma (γ) radiation emitted.
Q4: Water is used as a coolant in a nuclear reactor because of its: (NEET 2024)
(a) High thermal expansion coefficient
(b) High specific heat capacity
(c) Low density
(d) Low boiling point
Ans: (b)
Water is an excellent coolant because it has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb and carry away a large amount of heat without undergoing a significant increase in temperature. This makes it very effective for removing the heat produced during nuclear fission in reactors. Options like low density or low boiling point would not be ideal for a coolant.
Q5: Select the correct statements among the following: (NEET 2024)
A. Slow neutrons can cause fission in  more effectively than fast neutrons.
more effectively than fast neutrons.
B. α-rays are helium nuclei.
C. β-rays are fast-moving electrons or positrons.
D. γ-rays are electromagnetic radiations of wavelengths larger than X-rays.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, and C only
(b) A, B, and D only
(c) A and B only
(d) C and D only
Ans: (a)
Statement A is correct: Slow (thermal) neutrons are more effective in inducing fission in Uranium-235 because they are more likely to be captured by the nucleus.
Statement B is correct: Alpha particles (α-rays) are indeed nuclei of helium atoms (2 protons and 2 neutrons).
Statement C is correct: Beta particles (β-rays) are either electrons (β⁻) or positrons (β⁺), moving at high speeds.
Statement D is incorrect: γ-rays have shorter wavelengths (higher energy) than X-rays, not longer.
2023
Q6: The half life of a radioactive substance is 20 minutes. In how much time, the activity of substance drops to (1/16)th of its initial value?
(a) 20 minutes
(b) 40 minutes
(c) 60 minutes
(d) 80 minutes
Ans: (d) 80 minutes
Solution: 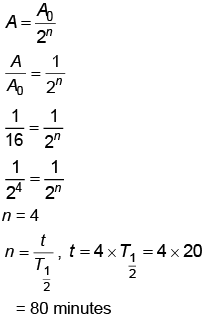
2022
Q7: In the given nuclear reaction, the element X is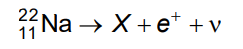
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 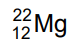
(d) 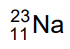
Ans: (b) 
Solution: 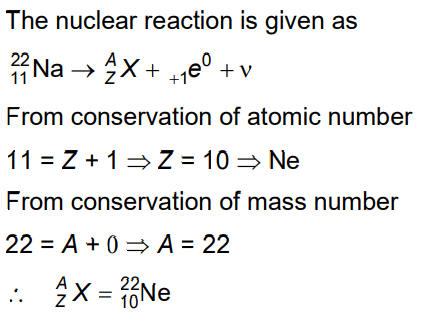
2021
Q8: A nucleus with mass number 240 breaks into fragments each of mass number 120, the binding energy per nucleon of unfragmented nuclei is 7.6 MeV while that of fragments is 8.5 MeV. The total gain in the Binding Energy in the process is:
(a) 804 MeV
(b) 216 MeV
(c) 0.9 MeV
(d) 9.4 MeV
Ans: (b) 216 MeV
Solution: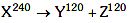
Given binding energy per nucleon of X, Y & Z are 7.6 MeV, 8.5 MeV & 8.5 MeV respectively.
Gain in binding energy is :-
Q = Binding Energy of products – Binding energy of reactants
= (120 × 8.5 × 2) – (240 × 7.6) MeV
= 216 MeV
Q9: A radioactive nucleus 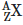 undergoes spontaneous decay in the sequence
undergoes spontaneous decay in the sequence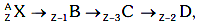
Where Z is the atomic number of element X. The possible decay particles in the sequence are :
(a) β+,α,β-
(b) β-,α,β+
(c) α,β-,β+
(d) α,β+,β-
Ans: (a) β+,α,β-
Solution: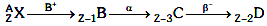 β+ decreases atomic number by 1
β+ decreases atomic number by 1
α decreases atomic number by 2
β- decreases atomic number by 1
Q10: The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 100 hours. The fraction of original activity that will remain after 150 hours would be:
(a) 2/3
(b) 2/3√2
(c) 1/2
(d) 1/2√2
Ans: (d) 1/2√2
Solution: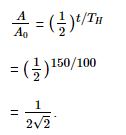
2020
Q11: The energy equivalent of 0.5 g of a substance is :
(a) 1.5×1013 J
(b) 0.5×1013J
(c) 4.5×1016J
(d) 4.5×1013J
Ans: (d) 4.5×1013J
Solution:
E = Δmc2 = 0.5 × 10-3 × (3 × 108)2
= 0.5 ×10-3 × 9 ×1016
E = 4.5 ×1013 J
Q12: When a uranium isotope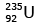 is bombarded with a neutron, it generates
is bombarded with a neutron, it generates 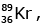 three neutrons and :
three neutrons and :
(a) 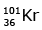
(b)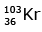
(c)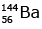
(d)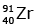
Ans: (c) 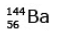
Solution: 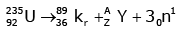
92 = 36 + Z; ← A + 89 + 3 = 235 ⇒ A = 144
Z = 56
2019
Q13: For a radioactive material, half-life is 10 minutes. If initially there are 600 number of nuclei, the time taken (in minutes) for the disintegration of 450 nuclei is:
(a) 20
(b) 10
(c) 30
(d) 15
Ans: (a) 20
Solution: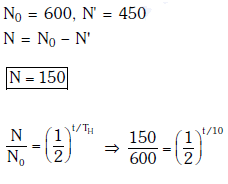
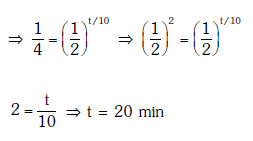
2018
Q14: For a radioactive material, half-life is 10 minutes. If initially there are 600 number of nuclei, the time taken (in minutes) for the disintegration of 450 nuclei is
(a) 20
(b) 10
(c) 30
(d) 15
Ans: (a) 20
Solution: Given N0 = 600, N1 = 450, T = 10 min
Number of nuclei remaining, N = 600 – 450 = 150 after time ‘t’
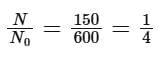
According to the law of radioactive decay,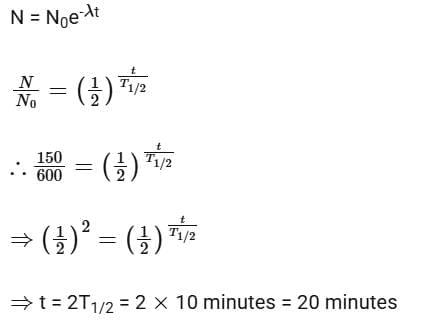
2017
Q15: Radioactive material 'A' has decay constant '8 λ' and material 'B' has decay constant 'λ'. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After what time, the ratio of number of nuclei of material 'B' to that 'A' will be 1/e?
(a) 1/7λ
(b) 1/8λ
(c) 1/9λ
(d) 1/10λ
Ans: (a) 1/7λ
Solution: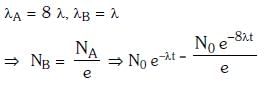
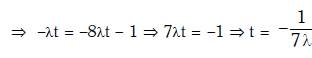

2016
Q16: When an alpha
(a) 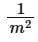
(b) m
(c) 1/m
(d) 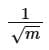
Ans: (c) 1/m
Solution:
At closest distance of approach, the kinetic energy of the particle will convert completely into electrostatic potential energy.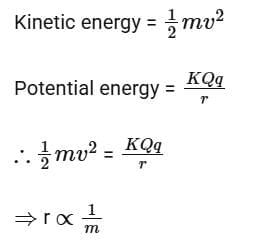
2015
Q17: A nucleus of uranium decays at rest into nuclei of thorium and helium. Then
(a) The helium nucleus has more momentum than the thorium nucleus.
(b) The helium nucleus has less kinetic energy than the thorium nucleus.
(c) The helium nucleus has more kinetic energy than the thorium nucleus.
(d) The helium nucleus has less momentum than the thorium nucleus.
Ans: (c) The helium nucleus has more kinetic energy than the thorium nucleus.
Solution:
In an explosion a body breaks up into two pieces of unequal masses both part will have numerically equal momentum and lighter part will have more velocity.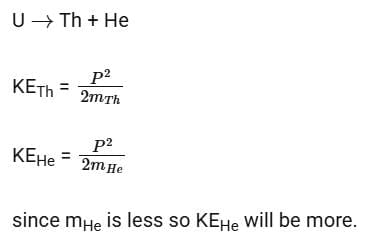
Q18: If radius of the 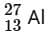 nucleus is taken to be RAl, then
nucleus is taken to be RAl, then
the radius of 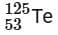 nucleus is nearly
nucleus is nearly
(a) 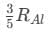
(b) 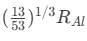 (c)
(c)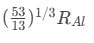 (d)
(d) 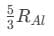
Ans: (d) 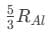
Solution:
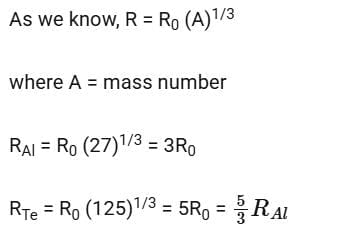
2014
Q19: The Binding energy per nucleon of 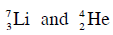 nuclei are 5.60 MeV and 7.06 MeV, respectively. In the nuclear reaction
nuclei are 5.60 MeV and 7.06 MeV, respectively. In the nuclear reaction 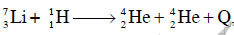 the value of energy Q released is :
the value of energy Q released is :
(a) 8.4 MeV
(b) 17.3 MeV
(c) 19.6 MeV
(d) −2.4 MeV
Ans: (b) 17.3 MeV
Solution: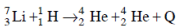
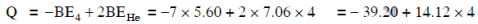
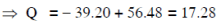
Q20: A radio isotope ‘X’ with a half life 1.4 × 109 years decays to ‘Y’ which is stable. A sample of the rock from a cave was found to contain ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the ratio 1 : 7. The age of the rock is
(a) 4.20 × 109 years
(b) 8.40 × 109 years
(c) 1.96 × 109 years
(d) 3.92 × 109 years
Ans: (a) 4.20 × 109 years
Solution:
Ratio of X:Y is given = 1:7
That is,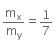
⇒ 7mx = my
Let, the initial total mass is m.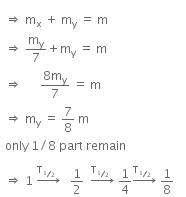
Therefore, time taken to become 1/8 unstable part
= 3 x T1/2
= 3 x 1.4 x 109
= 4.2 x 109 y
|
90 videos|420 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Nuclei - Physics Class 12
| 1. What is the significance of nuclear reactions in NEET exam preparation? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively study for the Nuclei chapter for NEET? |  |
| 3. What types of questions related to Nuclei can I expect in the NEET exam? |  |
| 4. How important is the concept of binding energy in NEET exams? |  |
| 5. Are there any common mistakes to avoid when studying the Nuclei chapter for NEET? |  |






















