NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Electromagnetic Waves | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: A parallel plate capacitor is charged by connecting it to a battery through a resistor. If I is the current in the circuit, then in the gap between the plates: [2024]
(a) There is no current
(b) Displacement current of magnitude equal to I flows in the same direction as I
(c) Displacement current of magnitude equal to I flows in a direction opposite to that of I
(d) Displacement current of magnitude greater than I flows but can be in any direction
Ans: (b) According to modified Ampere's law
According to modified Ampere's law
Q2: The property which is not of an electromagnetic wave travelling in free space is that:
(a) They are transverse in nature
(b) The energy density in electric field is equal to energy density in magnetic field
(c) They travel with a speed equal to 1 / √μ0ε0
(d) They originate from charges moving with uniform speed [2024]
Ans: (d)
Electromagnetic waves have several defining characteristics when they propagate through free space. Let's evaluate each of the options provided:
Option A: They are transverse in nature.
This is true. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, meaning the directions of the electric field and magnetic field oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. The electric field (E) and magnetic field (B) vectors are also perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation.
Option B: The energy density in the electric field is equal to the energy density in the magnetic field.
This is also true. In electromagnetic waves, the energy density stored in the electric field is equal to the energy density stored in the magnetic field. This is because the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields are related by C = E / B where c is the speed of light in vacuum. The energy density for each is given by  for the electric field and
for the electric field and  for the magnetic field. Given the relationship between E and B in a wave, these two energy densities are equal.
for the magnetic field. Given the relationship between E and B in a wave, these two energy densities are equal.
Option C: They travel with a speed equal to 1 / √μ0ε0.
This statement is true. The speed of electromagnetic waves in vacuum is given by c = 1 / √μ0ε0, where μ0
Option D: They originate from charges moving with uniform speed.
This statement is false. Electromagnetic waves are not generally produced by charges moving with a uniform speed; rather, they are produced by charges that are accelerating. Uniform motion (where velocity is constant and acceleration is zero) does not result in radiation of electromagnetic waves. If a charge is accelerating – changing either the speed or direction of its motion – it emits electromagnetic radiation.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option D, as it is the property that is not true for electromagnetic waves traveling in free space.
2023
Q1: In a plane electromagnetic wave traveling in free space, the electric field component oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2.0 × 1010 Hz and amplitude of 48 V m–1. Then the amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field is (Speed of light in free space = 3 × 108 m s–1)
(a) 1.6 × 10–9 T
(b) 1.6 × 10–8 T
(c) 1.6 × 10–7 T
(d)1.6 × 10–6 T
Ans: (c)
From the properties of electromagnetic wave
we know that, 
E0 ⇒ Amplitude of oscillating electric field
B0 ⇒ Amplitude of oscillating magnetic field
2022
Q1: The magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by
 then the associated eectric field wil be:
then the associated eectric field wil be:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (a)


Q2: The ratio of the magnitude of the magnetic field and electric field intensity of a plane electromagnetic wave in free space of permeabilit μ0 and permittivity ε0 is (Given that c - velocity) of light in free space
(a) 
(b) C
(c) 1/c
(d) 
Ans: (c)
We know,

Q3: Match List-I with List-II 
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iv)
(b) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(c) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(d)(a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
Ans: (c)
| Waves | Wavelength |
| AM radio waves | 102 m |
| Microwaves | 10–2 m |
| Infrared radiations | 10–4 m |
| X-rays | 10–10 m |
(a) - (ii) (b) - (iii) (c) - (iv) (d) - (i)
Q4: When light propagates through a material medium of relative permittivity εr and relative permeability εr, the velocity of light μr, v is given by (c-velocity of light in vacuum)
(a)
(b) 
(c) 
(d)
Ans: (d)

2021
Q1: For a plane electromagnetic wave propagating in the x-direction, which one of the following combinations gives the correct possible directions for the electric field (E) and magnetic field (B) respectively?
(a)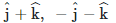
(b)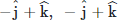
(c)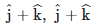
D: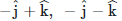
Ans: (d)
Solution:

Q2: A capacitor of capacitance 'C' is connected across an AC source of voltage V, given by  The displacement current between the plates of the capacitor would then be given by:
The displacement current between the plates of the capacitor would then be given by:
(a)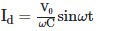
(b)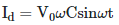
(c)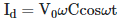
D: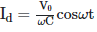
Ans: (c)
Solution:

Now, displacement current id is given by,

Hence, (C) is the correct answer.
2020
Q1: Light with an average flux of 20 W/cm2 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence having surface area 20 cm2 . The energy received by the surface during time span of 1 min is
(a) 12 × 103 J
(b) 24 × 103 J
(c) 48 × 103 J
(d) 10 × 103 J
Ans: (b)
Given, average flux = 20 W/cm2
Surface area = 20 cm2
Time = 1 min = 60 s
For non-reflecting surface, energy received = average flux × surface area × time
= 20 × 20 × 60
= 24 × 103 J
Q2: The electromagnetic wave with shortest wavelength among the following is
(a) UV-rays
(b) X-rays
(c) γ-rays
(d) microwaves
Ans: (c)
Gamma-rays has the shortest wavelength because it has higher frequency than UV-rays, microwaves and X-rays.
Q3: The ratio of contributions made by the electric field and magnetic field components to the intensity of an electromagnetic wave is : (c = speed of electromagnetic waves)
(a) 1 : c
(b) 1 : c2
(c) c : 1
(d)1 : 1
Ans: (d)
Solution:
The correct option is D = 1:1
Intensity of electromagnetic wave, I = Uavgc
In terms of the electric field, 
In terms of magnetic field, 
(∵Eo=cB0)
Now Uavg (due to electric field) 

The energy distribution in electric and magnetic fields is equal.
Therefore, the ratio of contributions by the electric field and magnetic field components to the intensity of the electromagnetic wave is 1:1
2019
Q1: A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance 20µ F is being charged by a voltage source whose potential is changing at the rate of 3 V/s. The conduction current through the connecting wires and the displacement current through the plates of the capacitor, would be, respectively.
(a) 60 µ A, 60µ A
(b) 60 µ A, zero
(c) zero, zero
(d) zero, 60 µ A
Ans: (a)
The displacement current is precisely equals to the conduction current, when the two are present in different parts of the circuit.
Given, C = 20 µ F = 20 × 10−6 F and

The displacement current in a circuit is given by


As displacement current is in between the plates of capacitor and conduction current is in the connecting wires which are equal to each other. So,

Q2: Which color of the light has the longest wavelength?
(a) Red
(b) Blue
(c) Green
(d)Violet
Ans: (a)
Solution:
Red has the longest wavelength among the given options.
2018
Q1: An em wave is propagating in a medium with a velocity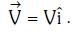 The instantaneous oscillating electric field of this em wave is along the +y axis. Then the direction of the oscillating magnetic field of the em wave will be along the:
The instantaneous oscillating electric field of this em wave is along the +y axis. Then the direction of the oscillating magnetic field of the em wave will be along the:
(a) –z-direction
(b) +z direction
(c) –y direction
(d)–x direction
Ans: (b)
Solution:

So +z direction is the correct answer option B
2017
Q1: In an electromagnetic wave in free space the root mean square value of the electric field is Erms = 6V/m. The peak value of the magnetic field is:
(a) 2.83 × 10–8 T
(b) 0.70 × 10–8 T
(c) 4.23 × 10–8 T
(d)1.41 × 10–8 T
Ans: (a)
Solution: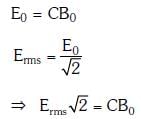
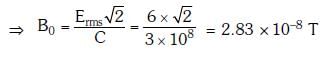
2016
Q1: Out of the following options which one can be used to produce a propagating electromagnetic wave?(a) An accelerating charge
(b) A charge moving at constant velocity
(c) A stationary charge
(d)A chargeless particle
Ans: (a)
Solution:
An electric charge at rest has an electric field in the region around it, but a magnetic field is absent. A moving charge produces both an electric and magnetic field. When a charge is moving with constant velocity, the electric and magnetic fields will not change with time. Therefore, no electromagnetic wave will be produced.
But, if the charge is moving with non-zero acceleration, the electric and magnetic fields will change with space and time. Electromagnetic waves will be produced.
Therefore, accelerated charge emits electromagnetic waves.
2015
Q1: A radiation of energy ‘E’ falls normally on a perfectly reflecting surface. The momentum transferred to the surface is (c = velocity of light)
(a) E/c
(b) 2E/c
(c) 2E/c2
(d) E/c2
Ans: (b)
The radiation energy is given by


Q2: The energy of the EM waves is of the order of 15 keV. To which part of the spectrum does it belong?
(a) X-rays
(b) Infrared rays
(c) Ultravioiet rays
(d) γ-rays
Ans: (a)
Given, energy of EM waves is of the order of 15 keV

Thus, this spectrum is a part of X-rays.
2014
Q1: Light with an energy flux of 25 × 104 Wm−2 falls on a perfectly reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface area is 15 cm2, the average force exerted on the surface is
(a) 1.25 × 10−6 N
(b) 2 .50 × 10−6 N
(c) 1.20 × 10−6 N
(d) 3.0 × 10−6 N
Ans: (b)

|
97 videos|336 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Electromagnetic Waves - Physics Class 12
| 1. What are electromagnetic waves? |  |
| 2. How do electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of electromagnetic waves? |  |
| 4. How are electromagnetic waves classified in the electromagnetic spectrum? |  |
| 5. How are electromagnetic waves used in everyday life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















