NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Evolution | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: The flippers of the Penguins and Dolphins are the example of the (NEET 2024)
(a) Adaptive radiation
(b) Natural selection
(c) Convergent evolution
(d) Divergent evolution
Ans: (c)
The flippers of penguins and dolphins are examples of convergent evolution. Convergent evolution occurs when different species independently evolve similar traits or structures because they adapt to similar environments or ecological niches, despite being of different lineages. This phenomenon leads to analogous structures, which perform similar functions but are not derived from a common ancestral trait.
Penguins are birds, and dolphins are mammals. Their ancestors did not possess flippers, but both these species have evolved this similar structure, which helps in swimming efficiently in aquatic environments. The development of flippers in both cases is an adaptation to enhance their abilities in similar environments (aquatic life), even though they come from different evolutionary paths.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Option C: Convergent evolution
Q2: Given below are some stages of human evolution. Arrange them in correct sequence. (Past to Recent)
A. Homo habilis
B. Homo sapiens
C. Homo neanderthalensis
D. Homo erectus
Choose the correct sequence of human evolution from the options given below: (NEET 2024)
(a) D-A-C-B
(b) B-A-D-C
(c) C-B-D-A
(d) A-D-C-B
Ans: (d)
To correctly arrange the stages of human evolution from past to most recent, we must place these species in chronological order based on when they first appeared according to scientific evidence.
Homo habilis - Often considered one of the earliest members of the genus Homo, appearing around 2.1 to 2.8 million years ago.
Homo erectus - Appeared around 1.9 million years ago and is known for its longer survival until about 140,000 years ago in some regions.
Homo neanderthalensis (Neanderthals) - Emerged around 400,000 years ago and disappeared around 40,000 years ago.
Homo sapiens - Our own species, which emerged around 300,000 years ago and is the only surviving species of the genus Homo.
Based on this information, the correct sequence from past to most recent would be:
A. Homo habilis
D. Homo erectus
C. Homo neanderthalensis
B. Homo sapiens
Thus, the correct sequence is represented by: Option D: A-D-C-B.
Q3: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024) Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: (d)
The question requires matching events in historical geological eras to the prevalent life forms of those periods. To do this accurately, knowledge of what characterized each era in terms of biodiversity is essential. Here's a breakdown:
Mesozoic Era (A): This era, often called the "Age of Reptiles," is renowned for its diverse reptilian species, including the dinosaurs, and also saw the emergence of birds from theropod dinosaurs. Hence, Mesozoic Era matches with "Birds & Reptiles (III)".
Proterozoic Era (B): The Proterozoic Era is part of the Precambrian period, characterized by the rise of simple, mostly unicellular life, including the first complex eukaryotic cells and multicellular forms like the Ediacara biota. Therefore, it should match with "Lower invertebrates (I)".
Cenozoic Era (C): Known as the "Age of Mammals," this period saw mammals diversifying after the extinction of the dinosaurs at the K-T boundary (the transition from Mesozoic to Cenozoic). Therefore, Cenozoic Era matches with "Mammals (IV)".
Paleozoic Era (D): During the Paleozoic Era, marine life flourished, and vertebrates began to emerge, including fishes and the first tetrapods (amphibians). Thus, Paleozoic Era corresponds to "Fish & Amphibia (II)".
Therefore, the correct matching based on the information given would be:
Option D: A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II. This option accurately aligns each era with the dominant life forms characterized within those eras.
Q4: Which one of the following factors will not affect the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? (NEET 2024)
(a) Genetic recombination
(b) Genetic drift
(c) Gene migration
(d) Constant gene pool
Ans: (d)
Sol: The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is a principle that predicts how gene frequencies in a population's gene pool will remain constant over time, assuming certain conditions are met. These conditions include no mutation, random mating, no gene flow, infinite population size, and no selection. If any of these conditions are violated, then the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium can be disrupted.
Option A: Genetic recombination
Genetic recombination refers to the process by which genetic material is rearranged or exchanged between different chromosomes or between different regions within the same chromosome. It can introduce new gene combinations into a population but does not itself change allele frequencies unless it is associated with differential survival or reproduction. Thus, genetic recombination alone does not disrupt Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Option B: Genetic drift
Genetic drift is a stochastic effect that occurs due to the random sampling of alleles when gametes are formed, and it can greatly influence the allele frequencies in small populations. It can cause random changes in allele frequencies over time, thereby affecting the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Option C: Gene migration
Gene migration or gene flow involves the transfer of alleles from one population to another. When individuals move between populations, they can introduce new alleles to the gene pool, or change the relative frequencies of existing alleles, both of which disturb the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Option D: Constant gene pool
A constant gene pool implies no change in allele frequencies over time, which is in line with the Hardy-Weinberg principle. Therefore, by definition, this factor does not affect or disrupt the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Based on these explanations, Option D: Constant gene pool is the factor that will not affect the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium as it represents the ideal condition where allele frequencies remain consistent, which is central to the Hardy-Weinberg principle.
2023
Q1: Select the correct group/set of Australian Marsupials exhibiting adaptive radiation.
(a) Tasmanian wolf, Bobcat, Marsupial mole
(b) Numbat, Spotted cuscus, Flying phalanger
(c) Mole, Flying squirrel, Tasmanian tiger cat
(d) Lemur, Anteater, Wolf [NEET 2023]
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer because numbat, spotted cuscus and flying phalanger are Australian marsupials exhibiting adaptive radiation.
Option (c) is incorrect because mole and flying squirrel are placental mammals.
Option (d) is incorrect because lemur and wolf are placental mammals.
Option (a) is incorrect because bobcat is a placental mammal.
Q2: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: RNA mutates at a faster rate.
Statement II: Viruses having RNA genome and shorter life span mutate and evolve faster.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(b) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(c) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are true. [NEET 2023]
Ans: (d)
- Statement I is true because RNA, particularly in RNA viruses, does mutate at a faster rate than DNA. This is largely due to the lack of proofreading mechanisms in RNA replication that are present in DNA replication.
- Statement II is also true. Viruses with an RNA genome, like the influenza virus or HIV, can mutate and evolve faster. The high mutation rate of RNA, combined with the short generation time of viruses, leads to rapid evolution, allowing these viruses to quickly adapt to new environments or hosts.
2022
Q1: Give the correct descending order of organisms with reference to their estimated number found in Amazon forest.
(a) Plants (b) Invertebrates (c) Fishes (d) Mammals (e) Birds
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (b) > (a) > (c) > (e) > (d)
(b) (a) > (b) > (e) > (d) > (c)
(c) (a) > (c) > (d) > (b) > (e)
(d) (b) > (a) > (e) > (d) > (c) [NEET 2022 Phase 2]
Ans: (a)
The numbers of species related to different taxa in Amazonian rain forest are as follows:

Q2: Select the correct statement regarding mutation theory of evolution.
(a) Large differences due to mutations arise gradually in a population
(b) This theory was proposed by Alfred Wallace
(c) Variations are small directional changes
(d) Single step large mutation is a cause of speciation [NEET 2022 Phase 2]
Ans: (d)
Correct answer is option no. (a) because
- Hugo de Vries, based on his work on evening primrose brought forth the idea of mutations. He believed that mutation caused speciation and hence called it saltation (Single step large mutation).
- Option (a) is incorrect because mutations are sudden (random) and directionless.
- Option (b) is incorrect because mutation theory was proposed by Hugo de Vries.
- Option (c) is incorrect because Darwinian variations are small and directional changes, but they are not related to mutation theory of evolution.
Q3: Natural selection where more individuals acquire specific character value other than the mean character value, leads to
(a) Stabilising change
(b) Directional change
(c) Disruptive change
(d) Random change [NEET 2022 Phase 1]
Ans: (b)
- Option (b) is correct because in directional natural selection more individuals acquire value other than the mean character value.
- Option (c) is incorrect because in disruptive change, more individuals acquire peripheral character value at both ends of the distribution curve.
- Option (d) is incorrect because there is no random change in natural selection.
- Option (a) is incorrect because natural selection leads to stabilisation when more individuals acquire mean character value.
Q4: Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) Analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution
(b) Sweet potato and potato is an example of analogy
(c) Homology indicates common ancestry
(d) Flippers of penguins and dolphins are a pair of homologous organs [NEET 2022 Phase 1]
Ans: (d)
- Option (d) is the correct answer because flippers of penguins and dolphins are analogous organs as they help in swimming but do not have the same structure.
- Option (c), (a) and (b) are true statements and hence cannot be the correct answer.
- Homologous organs have the same structure but have different functions according to the needs of the organisms. Hence, homology indicates common ancestry.
- Analogous structures have developed for the same function but do not show a similarity in structure. Hence, they are a result of convergent evolution.
- Sweet potato is a root modification for food storage whereas potato is an underground stem modification for storage. Hence they are analogous.
2021
Q1: The factor that leads to Founder effect in a population is: [NEET 2021]
(a) Mutation
(b) Genetic drift
(c) Natural selection
(d) Genetic recombination
Ans: (b)
- Change in gene frequency in a small population by chance is known as genetic drift. Genetic drift has two ramifications, one i bottle neck effect and another is founder's effect.
- When accidentally a few individuals are dispersed and act as founders of a new isolated population, founder's effect is said to be observed.
- Crossing over which occurs during gamete formation results in genetic recombination.
- Mutations are random and directionless.
Q2: Match List-I with List-II [NEET 2021]
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Ans: (c)
The correct option is (c)
- Adaptive radiation is the process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography, for example : Darwin's finches.
- Analogous organs which are not anatomically similar structures though they perform similar functions, are a result of convergent evolution, for example: Wings of butterfly and of birds.
- Homologous organs which are anatomically similar structures but perform different functions according to their needs, are a result of divergent evolution, for example: Bones of forelimbs in man and whale.
- Evolution by anthropogenic action means evolution due to human interference, for example: Antibiotic resistant microbes, herbicides resistant varieties and pesticide resistant varieties.
2020
Q1: From his experiments, S.L. Miller produced amino acids by mixing the following in a closed flask: [NEET 2020]
(a) CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapor at 600°C
(b) CH3, H2, NH3 and water vapor at 600°C
(c) CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapor at 800°C
(d) CH3, H2, NH4 and water vapor at 800°C
Ans: (c)
In 1953, S.L. Miller, an American scientist created electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH4 , H2 , NH3 and water vapor at 800°C.
Q2: Which of the following refer to correct example(s) of organisms which have evolved due to changes of the environment brought about by anthropogenic action? [NEET 2020]
(i) Darwin’s Finches of Galapagos islands.
(ii) Herbicide-resistant weeds
(iii) Drug-resistant eukaryotes.
(iv) Man-created breeds of domesticated animals like dogs.
(a) (ii), (iii) & (iv)
(b) only (iv)
(c) only (i)
(d) (i) & (iii)
Ans: (a)
Herbicide resistant weeds, drug resistant eukaryotes and man-created breeds of domesticated animals like dogs are examples of evolution by anthropogenic action. Darwin’s Finches of Galapagos islands are example of natural selection, adaptive radiation and founder’s effect.
Q3: Flippers of Penguins and Dolphins are examples of [NEET 2020]
(a) Adaptive radiation
(b) Natural selection
(c) Industrial melanism
(d) Convergent evolution
Ans: (d)
The flippers of penguins and dolphins are examples of convergent evolution.
- Convergent evolution is a process in which organisms that are not closely related independently evolve similar adaptations to similar environments or ecological niches. In the case of penguins and dolphins, both are adapted to aquatic environments and have evolved similar adaptations in their body shape and appendages to optimize swimming and diving.
- Penguins and dolphins are not closely related; penguins are birds, while dolphins are mammals. However, they have evolved similar adaptations for swimming, such as streamlined bodies and flippers that are modified for swimming rather than flight or walking.
- Adaptive radiation is a process in which a single ancestral species gives rise to a diverse array of descendant species, each adapted to a different ecological niche. Natural selection is a mechanism of evolution in which individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those traits to their offspring. Industrial melanism is a phenomenon in which dark-colored individuals of a species become more common in industrialized areas due to environmental pollution.
So, option D, "Convergent evolution," is the correct answer.
2019
Q1: Variations caused by mutation, as proposed by Hugo de Vries, are [NEET 2019]
(a) Small and directionless
(b) Random and directional
(c) Random and directionless
(d) Small and directional
Ans: (c)
According to De Vries, Variations are large, random and directionless.
Q2: Among the following sets of examples for divergent evolution, select the incorrect option. [NEET 2019]
(a) Forelimbs of man, bat and cheetah
(b) Heart of bat, man and cheetah
(c) Brain of bat, man and cheetah
(d) Eye of octopus, bat and man
Ans: (d)
Divergent evolution occurs in the same structure which have developed along different directions due to adaptation to different needs, examples, forelimbs, heart, brain of vertebrates. Eyes of octopus, bat and man are examples showing convergent evolution.
Q3: In a species, the weight of a newborn ranges from 2 to 5 kg. 97% of the newborn with an average weight between 3 to 3.3 kg survive whereas 99% of the infants born with weights from 2 to 2.5 o r 4.5 to 5 kg die. Which type of selection process is taking place? [NEET 2019]
(a) Cyclical selection
(b) Directional selection
(c) Stabilising selection
(d) Disruptive Selection
Ans: (c)
It shows stabilizing selection as most of the newborn having average weight between 3 to 3.3 kg survive and babies with less and more weight have low survival rate. Stabilizing is a type of natural selection in which the population mean stabilizes on a particular nonextreme trait value.
Q4: Match the hominids with their correct brain size. [NEET 2019] 
Select the correct option.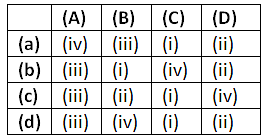
Ans: (d)
Correct match of hominids with their brain sizes are as follows :
- Homo habilis - 650-800 cc
- Homo neanderthalensis -1400 cc
- Homo erectus - 900 cc
- Homo sapiens - 1350 cc
2018
Q1: The similarity of bone structure in the forelimbs of many vertebrates is an example of [NEET 2018]
(a) Homology
(b) Analogy
(c) Convergent evolution
(d) Adaptive radiation.
Ans: (a)
Bird and bat wings are analogous, as forelimb is homologous. In different vertebrates, bones of forelimbs are similar but their forelimbs are adapted in different way as per their adaptation, show homology.
Q2: Among the following sets of examples for divergent evolution, select the incorrect option. [NEET 2018]
(a) Forelimbs of man, bat and cheetah
(b) Heart of bat, man and cheetah
(c) Brain of bat, man and cheetah
(d) Eye of octopus, bat and man
Ans: (d)
Divergent evolution occurs in the same structure which have developed along different directions due to adaptation to different needs, examples, forelimbs, heart, brain of vertebrates. Eyes of octopus, bat and man are examples showing convergent evolution.
Q15: According to Hugo de Vries, the mechanism of evolution is [NEET 2018]
(a) Multiple-step mutations
(b) Saltation
(c) Phenotypic variations
(d) Minor mutations
Ans: (b)
As per mutation theory given by Hugo de Vries, the evolution is a discontinuous phenomenon or saltatory phenomenon (single step large mutation).
2016
Q1: Genetic drill operates in [NEET 2016]
(a) Small isolated population
(b) Large isolated population
(c) non-reproductive population
(d) Slow reproductive population
Ans: (a)
Genetic drift (Sewall Wright effect) is the random change in the frequency of alleles in a population over successive generations in the gametes. Each new generation differs from its parental generation with regard to allele frequencies simply because of random variation in the distribution of gametes. This process is more rapid in smaller populations, or when the alleles concerned confer no apparent benefit compared to their counterparts.
Q2: In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, the frequency of heterozygous individual is represented by [NEET 2016]
(a) p2
(b) 2pq
(c) pq
(d) q2
Ans: (b)
In a stable population, for a gene with two alleles, ‘A’ (dominant) and ‘a’ (recessive), if the frequency of‘A’ is p and the frequency of‘a’ is q, then the frequencies of the three possible genotypes (AA, Aa and aa) can be expressed by the Hardy-Weinberg
equation: A
p2 + 2pq + q2= 1
where
p2 = Frequency of AA (homozygous dominant) individuals
q2 = Frequency of aa (homozygous recessive) individuals
2pq = Frequency of Aa (heterozygous) individuals
Q3: The chronological order of human evolution from early to the recent is [NEET 2016 Phase 2]
(a) Australopithecus → Ramapithecus → Homo habit is → Homo erectus
(b) Ramapithecus → Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus
(c) Ramapithecus → Homo habilis → Australopithecus → Homo erectus
(d) Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Ramapithecus → Homo erectus
Ans: (b)
- Australopithecus are the Southern apes found in Africa about 4.2 to 1.9 million years ago. It was first discovered in 1924 in Taung, Africa as a type specimen. There were similarities of about 35% between the brains of Australopithecus and humans. They had 32 teeth like humans including canine, molar etc but had less interlocking pattern.
- Unlike other apes, they possess thick enamel in their teeth. They ate only vegetables, fruits or other tubers.
- Homo habilis were also called handyman. They were found in the era Pleistocene about 2.3 to 1.64 million years ago. Homo habilis are supposed to evolve from Homo erectus. They had a comparatively larger brain than Australopithecus and possessed teeth with smaller premolar and molar.
- Ramapithecus also called Sivapithecus is one of the ancient extinct apes. They were found about 12.2 million years ago in the 19th-century Miocene era. They were like a jaw and had evolved into humans gradually. Their length was about 1.5 meter and had similarities with Orangutan. They ate only tough foods like savanna grasses, solid fruits etc.
- Homo erectus is also an extinct ape found in the era of Pleistocene of about 1.5 to 2 million years ago. As the fossils were discovered from Central Jawa, it was also called the Jawa man. It was supposed to be the first one who began to use fire as their need.
Q4: Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in the origin of life?
I. Formation of protobionts
II. Synthesis of organic monomers
III. Synthesis of organic polymers
IV. Formation of DNA-based genetic systems [NEET 2016]
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) I, III, II, IV
(c) II, III, I, IV
(d) II, III, IV, I
Ans: (c)
The sequence of the origin of life events is as follows-
- The organic monomers were synthesised first and then the formation of the organic polymers took place.
- All these organic compounds were then aggregated together and surrounded by a feeble membrane.
- This structure was known as the protobionts.Much more complex DNA based genetic system evolved after thatSO, the correct option is 'II, III, I, IV'
Q5: Which of the following structures is homologous to the wing of a bird? [NEET 2016]
(a) Hindlimb of rabbit
(b) Flipper,of whale
(c) Dorsal fin of a shark
(d) Wing of a moth
Ans: (b)
Wings of a bird and flippers of a whale are modified forelimbs.
Q6: Analogous structures are a result of [NEET 2016]
(a) Shared ancestry
(b) Stabilising selection
(c) Divergent evolution
(d) Convergent evolution
Ans: (d)
Analogous structures are those that have the same function, but they are not derived from a common ancestor and have undergone different patterns of development i.e., Convergent evolution which is natural selection that favors the same type of structure in different ancestors.
Q7: Following are the two statements regarding the origin of life. [NEET 2016]
(A) The earliest organisms that appeared on the earth were non-green and presumably anaerobes,
(B) The first autotrophic organisms were the chemo-autotrophs that never released oxygen.
Of the above statements which one of the following options is correct?
(a) Both (A) and (B) are correct.
(b) Both (A) and (B) are false.
(c) (A) is correct but (B) is false.
(d) (B) is correct but (A) is false.
Ans: (a)
Both statements are correct because primitive atmosphere was reducing and chlorophyll appeared later on. Chemoautotrophs were the first autotrophic organisms unable to perform photolysis of water and never released oxygen.
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Evolution - Biology Class 12
| 1. What is the significance of studying Evolution for the NEET exam? |  |
| 2. How can knowledge of Evolution help in answering NEET questions on genetics and inheritance? |  |
| 3. What are the key concepts students should focus on while preparing for Evolution in the NEET exam? |  |
| 4. How can the study of Evolution help in understanding the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria? |  |
| 5. How does the theory of Evolution contribute to the field of medicine and healthcare? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















