NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Ecosystem | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: In an ecosystem if the Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of first trophic level is 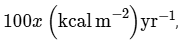 what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem?
what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem?
(a) 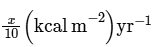
(b) 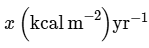
(c) 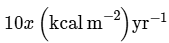
(d) 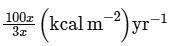
Ans: (c)
NPP at first trophic level would be the GPP for second trophic level. NPP at second trophic level would be GPP for third trophic level. Therefore, 100x(kcal/m2/yr) would be GPP at second trophic level and 100x * 10% (kcal/m2/yr) i.e 10x(kcal/m2/yr) energy would be GPP at third trophic level.
2023
Q1: Identify the correct statements: (NEET 2023)
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
C. Water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, D only
(b) C, D, E only
(c) D, E, A only
(d) A, B, C only
Ans: (a)
Let's evaluate each statement:
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
This statement is true. Detrivores, such as earthworms and beetles, break down detritus (dead organic material) into smaller pieces in a process called fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
This statement is true. Microbes, including bacteria and fungi, break down humus into inorganic nutrients in a process called mineralization.
C. Water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
This statement is true. Leaching refers to the process where nutrients are washed away from the soil into lower layers or into bodies of water.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
This statement is false. The detritus food chain begins with dead organic material or detritus, not living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
This statement is false. The process by which earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, not catabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, along with the release of energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is : Option D : A, B, C only.
Q2: In the equation GPP − R= NPP (NEET 2023)
GPP is Gross Primary Productivity
NPP is Net Primary Productivity
R here is ________.
(a) Photosynthetically active radiation
(b) Respiratory quotient
(c) Respiratory loss
(d) Reproductive allocation
Ans: (c)
In the equation GPP - R = NPP,
GPP stands for Gross Primary Productivity, NPP stands for Net Primary Productivity, and R represents the energy used by plants for their own metabolic processes, which is also known as Respiratory loss.
Q3: Which one of the following statements is NOT correct? (NEET 2023)
(a) The micro-organisms involved in biodegradation of organic matter in a sewage polluted water body consume a lot of oxygen causing the death of aquatic organisms
(b) Algal blooms caused by excess of organic matter in water improve water quality and promote fisheries
(c) Water hyacinth grows abundantly in eutrophic water bodies and leads to an imbalance in the ecosystem dynamics of the water body
(d) The amount of some toxic substances of industrial waste water increases in the organisms at successive trophic levels
Ans: (b)
Algal bloom imparts a distinct colour to the water bodies. It causes deterioration of the water quantity and fish mortality.
Q4: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2023)
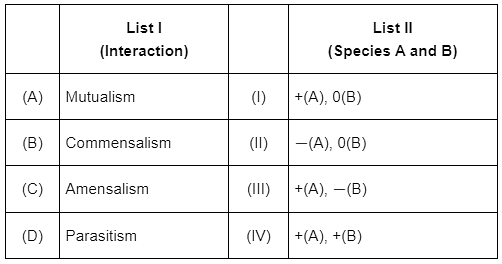
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(c) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(d) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
Ans: (a)
(+, +) Mutualism : In this interaction, both the interacting species are benefitted.
(+, 0) Commensalism : Only one species is benefitted and the other species remains unharmed.
(−, 0) Amensalism : Neither species is benefitted. One remains unharmed and the other is harmed.
(+, −) Parasitism : One species is benefitted and other is negatively effected.
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Statement I: Decomposition is a process in which the detritus is degraded into simpler substances by microbes.
Statement II: Decomposition is faster if the detritus is rich in lignin and chitin
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(b) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(c) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Ans: (b)
- Decomposition is the process by which decomposers breakdown complex organic matter into inorganic substances.
- The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. Decomposition is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars.
Q2: Which one of the following will accelerate phosphorus cycle? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Volconic activity
(b) Weathering of rocks
(c) Rain fall and storms
(d) Burning of fossil fuels
Ans: (b)
Phosphorus cycle is a sedimentary cycle. Reservoir pool of phosphorus in ecosystem is the earth's crust or lithosphere. Weathering of rocks accelerate phosphorus cycle.
Q3: Detritivores breakdown detritus into smaller particles. This process is called: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Fragmentation
(b) Humification
(c) Decomposition
(d) Catabolism
Ans: (a)
(Detritivores break down detritus into smaller particles) e.g. earthworm. This process is called fragmentation.
Q4: Two butterfly species are competing for the same nectar of a flower in a garden. To survive and coexist together, they may avoid competition in the same garden by : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Predating on each other
(b) Feeding at the same time
(c) Choosing different foraging patterns
(d) Increasing time spent on attacking each other
Ans: (c)
Two individuals that are competing for same resource can avoid competition by choosing different times for feeding or different foraging patterns.
Q5: All successions irrespective of the habitat proceed to which type of climax community? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Edaphic
(b) Xeric
(c) Mesic
(d) Hydrophytic
Ans: (c)
Both hydrarch and xerarch succession lead to medium water condition called mesic condition. This condition is neither too dry nor too wet.
Q6: The pioneer species in a hydrarch succession are (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Filamentous algae
(b) Free-floating angiosperms
(c) Submerged rooted plants
(d) Phytoplanktons
Ans: (d)
In primary succession in water, the pioneers are the small phytoplanktons, which are replaced with time by rooted-submerged plants, rooted floating angiosperms followed by free-floating plants, then reed-swamp, marsh-meadow, scrub and finally trees.
Q7: The species that come to appear in bare area are called (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Species of seral community
(b) Pioneer species
(c) Invasive species
(d) Competitive species
Ans: (b)
- The species that invade a bare area are called pioneer species.
- The individual transitional communities in an ecological succession are termed as seral stages or seral communities.
Q8: The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis is called
(a) Net primary production
(b) Secondary production
(c) Primary production
(d) Gross primary production (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
- Productivity is the total amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area. Over a period of time by plants. This is also called Primary production.
- Productivity of consumer is called Secondary production.
2021
Q1: The amount of nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, etc. present in the soil at any given time, is referred to as the - (NEET 2021)
(a) Nutrient status of soil
(b) Standing state
(c) Standing crop
(d) Mineral state.
Ans: (b)
- Amount of all the inorganic substances or nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and calcium present in soil at any given time, is referred as standing state.
- Amount of living material present in different trophic levels at a given time, is referred s standing crop.
- Climax community is the last community in biotic succession which is relatively stable and is in near equilibrium with the environment of that area.
Q2: In the equation GPP - R = NPP (2021)
R represents:
(a) Environment factor
(b) Respiration losses
(c) Radiant energy
(d) Retardation factor
Ans: (b)
In the equation,
GPP - R = NPP
R refers to respiratory loss
GPP is gross primary productivity
NPP is net primary productivity
Q3: Which of the following statements is not correct? (2021)
(a) Pyramid of energy is always upright.
(b) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem is upright.
(c) Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally inverted.
(d) Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally upright.
Ans: (d)
- Pyramid of biomass in a sea is generally inverted because the primary producers (phytoplanktons) have a lower biomass than that of succeeding zooplanktons, which further have a lower biomass than that of succeeding small fishes and so on.
- Pyramid of energy is the only pyramid that can never be inverted and is always upright. This is because some amount of energy in the form of heat is always lost to the environment at every trophic level of the food chain.
- In a grassland ecosystem, the number of producers is always maximum, followed by reducing number of organisms at second trophic level, third trophic level and other higher level (if present). Thus, the pyramid of number in grassland is upright.
2020
Q1: In relation to Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity of an ecosystem. Which one of the following statements is correct? (NEET 2020)
(a) Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity are one and same.
(b) There is no relationship between Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity
(c) Gross primary productivity is always less than Net primary productivity.
(d) Gross primary productivity is always more than Net primary productivity.
Ans: (d)
Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Net primary productivity is GPP-respiration. Hence, gross primary productivity is always more than NPP.
Q2: Match the trophic levels with their correct species examples in grassland ecosystem. (NEET 2020)
(A) Fourth trophic level (i) Crow
(B) Second trophic level (ii) Vulture
(C) First trophic level (iii) Rabbit
(D) Third trophic level (iv) Grass
Select the correct option
(a) (A) → (iv), (B) → (iii), (C) → (ii), (D) → (i)
(b) (A) → (ii), (B) → (iii), (C) → (iv), (D) → (i)
(c) (A) → (i), (B) → (ii), (C) → (iii), (D) → (iv)
(d) (A) → (iii), (B) → (ii), (C) → (i), (D) → (iv)
Ans: (b)
Grassland ecosystem is a terrestrial ecosystem. It includes various trophic levels. First trophic level (T1) – Grass Second trophic level (T2) – Rabbit Third trophic level (T3) – Crow Fourth trophic level (T4) – Vulture.
2019
Q1: Which of the following is the most important cause for animals and plants being driven to extinction? (NEET 2019)
(a) Economic exploitation
(b) Alien species invasion
(c) Habitat loss and fragmentation
(d) Drought and floods
Ans: (c)
Habitat loss and fragmentation is the major cause of biodiversity loss and extinction of plants and animals. Habitat of various organisms are altered or destroyed by uncontrolled and unsustainable human activities such as deforestation, slash, and burn agricultural, mining and urbanisation. This results in the breaking up of the habitat into small pieces, which effects the movement of migratory animals and also, decreases the genetic exchange between populations leading to a declination of species.
Q2: Which of the following ecological pyramids is generally inverted? (NEET 2019)
(a) Pyramid of biomass in a sea
(b) Pyramid of numbers in grassland
(c) Pyramid of energy
(d) Pyramid of biomass in a forest
Ans: (a)
Pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem (e.g., pond, sea) is usually inverted because the biomass of fishes exceeds the biomass of phytoplanktons.
2018
Q2: What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained with the following data? (NEET 2018)
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g
Primary producer : 10 g
(a) Inverted pyramid of biomass
(b) Pyramid of energy
(c) Upright pyramid of numbers
(d) Upright pyramid of biomass
Ans: (a)
The given data depicts the inverted pyramid of biomass, usually present in aquatic ecosystem. Upright pyramid of biomass and numbers are not possible, as the data depicts primary producer is less than primary consumer and this is less than secondary consumers. Pyramid of energy is always upright.
2017
Q1: Which ecosystem has the maximum biomass? (2017)
(a) Grassland ecosystem
(b) Pond ecosystem
(c) Lake ecosystem
(d) Forest ecosystem
Ans: (d)
Forest ecosystem has the maximum biomass.
Some very high productive ecosystem are
– Tropical rain forest
– Coral reef
– Estuaries
– Sugarcane fields
2016
Q1: The primary producers of the deep-sea hydrothermal vent ecosystem are (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Green algae
(b) Chemosynthetic bacteria
(c) Blue-green algae
(d) Coral reefs
Ans: (b)
Solution.
Hydrothermal vents are cracks in the ocean floor that emit jets of hot water loaded with minerals and chemosynthetic bacteria. These bacteria are autotrophs that oxidise hydrogen sulphide in vent water to obtain energy which is used to produce organic material. These chemosynthetic bacteria are the primary producers and form the base of vent food webs. All vent animals ultimately depend on bacteria for food.
Q2: Which of the following would appear as the pioneer organisms on bare rocks? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Mosses
(b) Green algae
(c) Lichens
(d) Liverworts
Ans: (c)
Lichens produce small amounts of carbonic acids from their “roots” and these slowly dissolve the rock, releasing nutrients. Other nutrients are obtained from water-borne or air-borne particles of both organic and inorganic materials. The body of a lichen contains an alga; this is able to photosynthesise sugars, some of which are passed on to the fungal component of the lichen. In return the alga gets a tiny but significant amount of shelter within the tissues of the lichen.
Q3: Which one of the following is a characteristic feature of cropland ecosystem? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Absence of weeds
(b) Ecological succession
(c) Absence of soil organisms
(d) Least genetic diversity
Ans: (d)
Cropland ecosystem is an artificial or manmade terrestrial ecosystem which is created and maintained by human beings for their maximum benefits. Therefore, they will have least genetic diversity.
Q4: The term ecosystem was coined by (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) E. Haeckel
(b) E.Warming
(c) E.P. Odum
(d) A.G. Tansley
Ans: (d)
Sir Arthur George Tansley was an English botanist and a pioneer in the science of ecology who coined the term ecosystem.
|
87 videos|294 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Ecosystem - Biology Class 12
| 1. What is an ecosystem? |  |
| 2. How do biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of biodiversity in an ecosystem? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact ecosystems? |  |
| 5. What are some ways to protect and conserve ecosystems? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|

















