UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Climatic Regions of the World
Climatic Regions of the World | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
A climatic region is a group of areas where the conditions of relief, temperature, rainfall, natural vegetation and consequently the cultural environment are more or less similar.
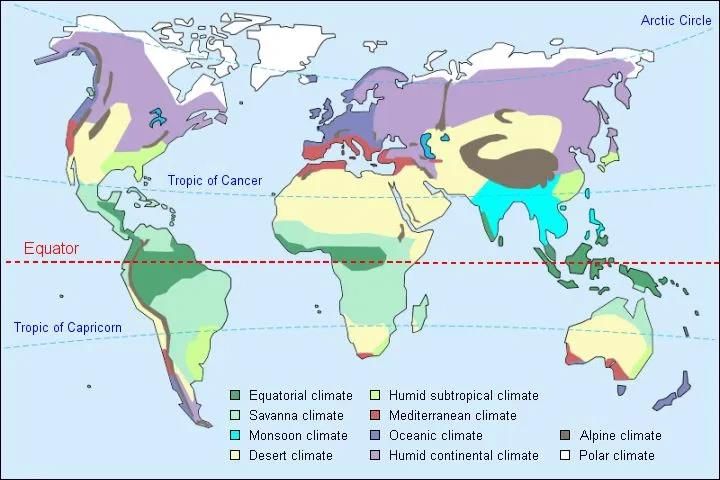
Climate World Map
- The boundaries of naturals regions are permanent because they are determined by ecological factors and can change over time.
- Unlike political borders, they are not fixed.
- But at the same time, the boundaries of natural regions are not well defined as political boundaries.
- As this is an introductory document, we will briefly go through the regions which will be covered extensively in the upcoming documents.
Natural Regions of the World
Equatorial Region
- The equatorial region spans from 0° latitude to approximately 10° to 15° north and south latitude.
- This region experiences a hot and humid climate throughout the year.
- The annual range of temperature is low, and seasonal contrasts are at a minimum.
- The combination of high temperature and high humidity makes it challenging for people to work, but it creates ideal conditions for plant growth.
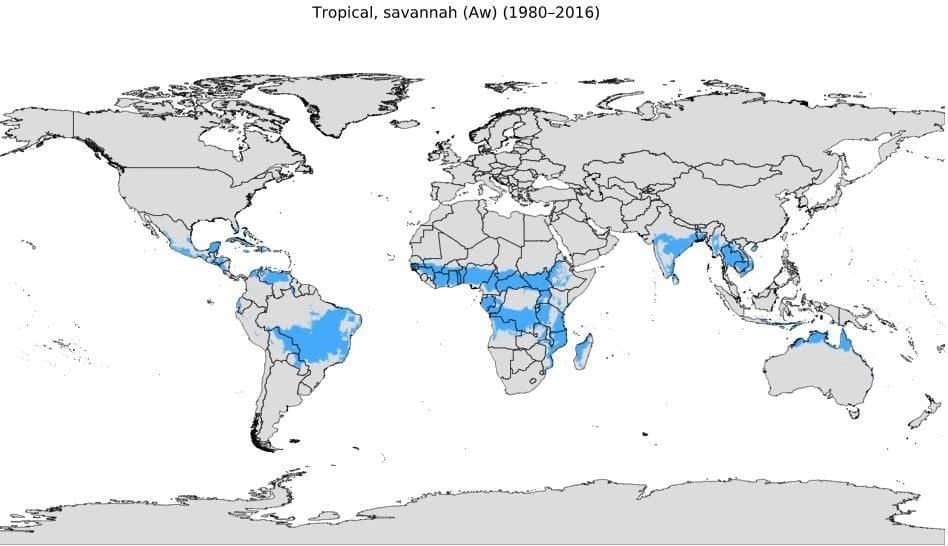
Tropical grassland (Savanna) Region
- This region lies in the interior of the continents extending up to the sea in the west in the tropical belt.
- It comes under the influence of equatorial belt of calms during summer and receives convectional rainfall and it is under the influence of trade winds during winter which are dry winds and the region experiences drought.
- It generally lies between 5°N and 20°S latitudes.
- This region has moderate rainfall and experiences a broader range of temperatures throughout the year.
- This region is primarily found in Africa, parts of the Brazilian Plateau, and the Orinoco basin in South America.
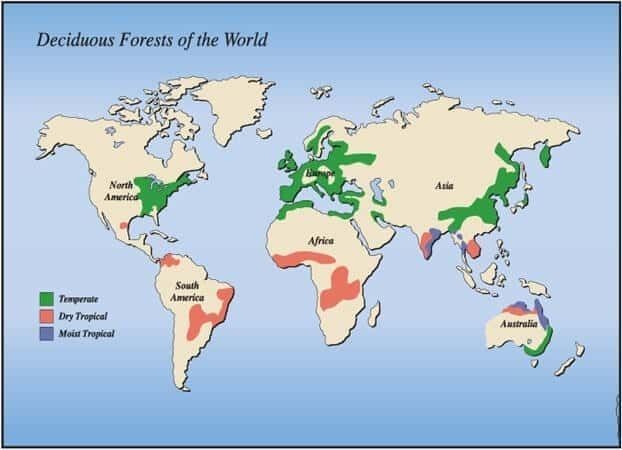
Tropical Deciduous forest region
- This region includes eastern margins of the continents between 10°N to 30°N and 10°S to 30°S.
- Rainfall is moderate except in coastal regions and mountainous tracts.
- Summers are characterized by hot and wet conditions, while winters are warm and dry.
Question for Climatic Regions of the WorldTry yourself:Which of the following region is situated between 10 degrees north and 10 degrees south?
View Solution
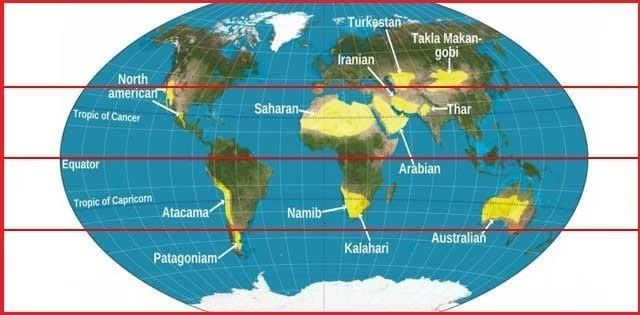
Tropical Deserts
- Tropical deserts are located on the western margins of continents in the Trade Wind belt roughly between 20° and 30° N and S latitudes and are known as hot or trade wind deserts.
- Annual precipitation is generally less than 25 cm.
- In most of the region, clear skies favour fired passage of insolation during day time and outgoing radiation from the earth during the night. Therefore, the diurnal range of temperature is high.
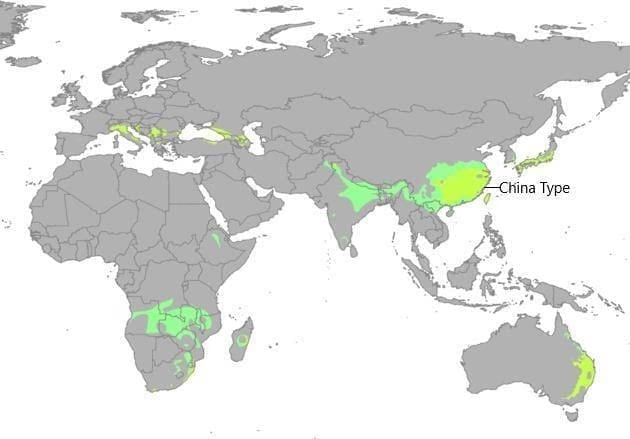
China type Region
- It lies on the eastern margins of the continents in the subtropical belt between 20° and 48° latitude in both hemispheres.
- The main characteristics of this region are summers are warm and moist and winters are cold, and during summer, trade winds blow from adjoining ocean and moderate rainfall occurs which decreases towards the equator and in winter, westerly winds blow from the interior towards the oceans.
- These land winds do not give rainfall and so winters are dry.
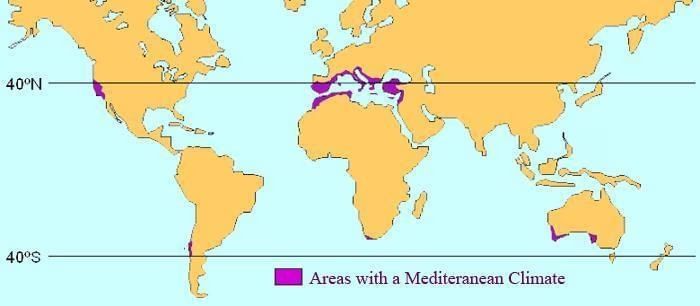
 Mediterranean type Region
Mediterranean type Region
- The Mediterranean type region is a unique climatic zone characterized by its location north of tropical deserts, specifically on the western sides of continents. This region lies roughly between 30° and 40° latitude in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- One of the defining features of the Mediterranean type region is its distinct seasonal variations. Summers in this region are hot and dry, while winters are mild and rainy. This contrast between the summer and winter seasons is a key aspect of the Mediterranean climate.
- During the summer months, the prevailing trade winds blow from land to sea, resulting in very little rainfall. This dry period is a hallmark of the Mediterranean type region.
- In contrast, winter brings a change in weather patterns, with moist westerly winds blowing from the ocean. These winds bring cyclonic rain, contributing to the wetter conditions experienced during the winter season.
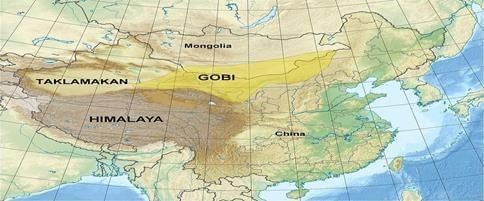
Mid-latitudes desert
- These deserts are located in the interior plateau and basins in Asia and North America. They are surrounded by high mountain regions.
- Tibet and Gobi are typical examples.
- The main characteristic of this region is that it receives scanty rainfall as the interior location is surrounded by high mountains which prevent the inflow of moist air.
- Interior location results in the greater extreme of temperature between summer and winter.
St. Lawrence type Region
- This region lies poleward of the Warm East Margin Region.
- The region has warm wet summer and cold dry winters.
- North Eastern United States and adjoining parts of Canada, North China, Manchuria, Korea, and Northern Japan are the main areas included in this Region.
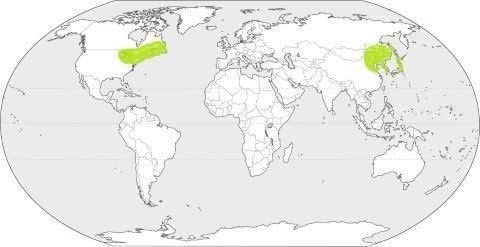 Mid Latitude grasslands
Mid Latitude grasslands
- This region lies in the interior of the continents and therefore receives low rainfall.
- The annual range of temperature is high between warm summer and cold winter.
- Rainfall occurs as a result of the convectional ascent of air during summer.
- Owing to low rainfall and cold winter, trees are generally absent.
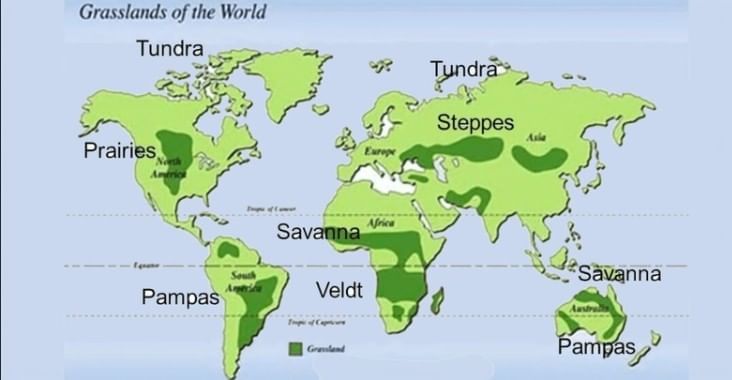
Cool (Mid Latitude) West European Type
- Regions of this type are found on the western margins of the continents in the permanent zone of westerlies.
- It includes Western Europe from Northern Norway to the British Isles, North-West United States, and Southern Chile in South America and Tasmania Island of New Zealand in Australia.
 Question for Climatic Regions of the WorldTry yourself:In which side margin is China type climate region found?View Solution
Question for Climatic Regions of the WorldTry yourself:In which side margin is China type climate region found?View Solution
The Taiga (coniferous) Region
- Location and Climate: The Taiga region is a vast area found in Europe, Asia, and North America. It lies between the mid-latitude grasslands to the south and the Polar Tundra to the north. The climate here is cold and moist, characterized by a long, harsh winter and a short, cool summer. During winter, rivers freeze, and snow covers the ground for several months. Annual precipitation is moderate, with a peak during the summer months.
- Vegetation: The Taiga is home to coniferous forests dominated by softwood trees such as spruce, fir, and pine. These trees are well adapted to the cold climate and are a defining feature of the region.

Polar Lowlands (Tundra)
- The Polar Lowlands, commonly known as Tundras, are vast, low-lying cold deserts situated along the shores of the Arctic Ocean. These regions are characterized by permafrost, where the ground remains frozen for most of the year. Tundras act as a transitional zone between the regions of eternal snow and ice to the north and the coniferous forests to the south.
- Location: Tundras are found in the northern parts of Asia, Canada, and Europe. In these areas, Tundras are often referred to as Barren lands due to their harsh living conditions and sparse vegetation.
- Climate: The Tundra experiences a long and severe cold winter, followed by a short and cool summer. The extreme cold and short growing season limit the types of vegetation that can thrive in this environment.
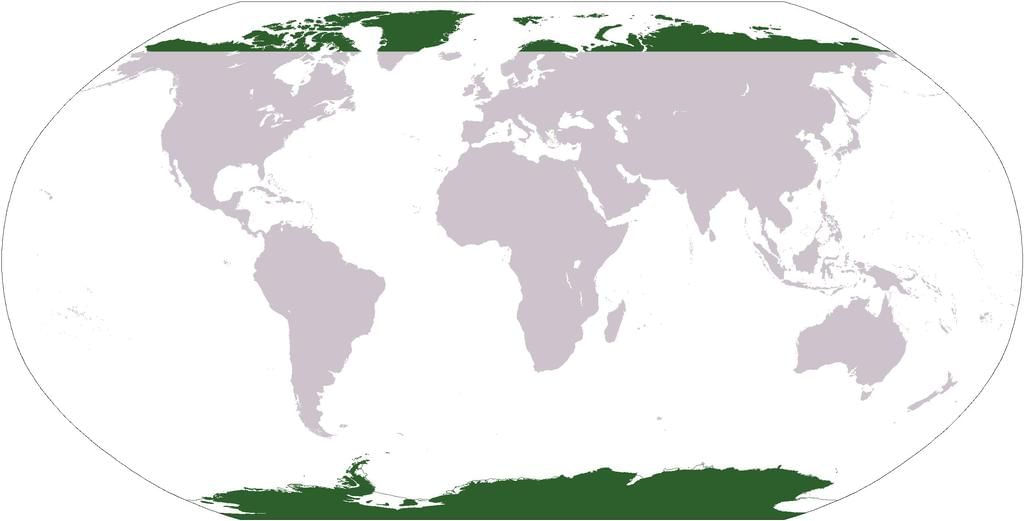
Polar Highlands (Icecap type)
- Antarctica: Antarctica is a vast landmass located in the polar region, covered by a permanent ice cap. The temperatures in Antarctica during the summer months do not exceed 10°C, making it one of the coldest places on Earth. Precipitation in Antarctica is low, primarily occurring as snowfall during the winter months.
- Greenland: Similar to Antarctica, Greenland is a large landmass in the polar region with a permanent ice cap. The climate in Greenland is also characterized by low temperatures and minimal precipitation, mainly in the form of snowfall during winter.
The document Climatic Regions of the World | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Climatic Regions of the World - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are climatic regions? |  |
Ans. Climatic regions are areas of the world that are defined and distinguished by their climate and weather patterns. These regions are characterized by their temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions.
| 2. What are the major climatic regions of the world? |  |
Ans. The major climatic regions of the world are the tropical rainforest, tropical savanna, desert, Mediterranean, humid subtropical, marine west coast, humid continental, subarctic, and tundra regions.
| 3. How are climatic regions determined? |  |
Ans. Climatic regions are determined by analyzing various climatic factors such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, winds, and atmospheric pressure. These factors are used to classify areas of the world into different climatic regions.
| 4. What are some characteristics of the tropical rainforest region? |  |
Ans. The tropical rainforest region is characterized by high temperatures and high precipitation levels throughout the year. The region is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species, and is known for its dense vegetation and lush greenery.
| 5. What are some characteristics of the desert region? |  |
Ans. The desert region is characterized by arid and dry conditions, with very little precipitation and high temperatures during the day. The region is typically barren and devoid of vegetation, and is home to a unique range of animal species adapted to living in harsh desert conditions.
Related Searches






















