Nature and Scope of Strategic Management | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Strategic management represents a well-structured approach grounded in effective management principles and processes aimed at defining a business's corporate objectives or mission. It establishes appropriate targets to ensure goal achievement, identifies existing opportunities and constraints within the environment, and develops a logical, realistic approach to achieving company objectives. Strategic management embodies both a process and a set of beliefs for understanding and directing organizational dynamics within its dynamic environment. It entails defining methods and procedures to help management adapt to the evolving business landscape through the formulation of objectives and strategies. As a philosophy, it shifts managers' perspectives towards handling competitors, customers, markets, and internal organizational dynamics. Its goal is to heighten management awareness of the strategic implications of both environmental events and internal decisions.
Definition by Theorists:
- Glueck (1984): Strategic management is making decisions and taking actions to create effective strategies that help achieve corporate goals.
- Hofer and others (1984): It's the process of renewing and growing organizations by developing strategies, structures, and systems, and effectively managing the strategy formulation and implementation.
- Sharplin (1985): Involves formulating and implementing plans for matters crucial to the entire organization.
- Lawrence and William (1988): Similar to Glueck's definition, focusing on developing efficient strategies to achieve corporate objectives.
Strategic Management Process:
- Strategists set objectives and make strategic decisions.
- It focuses on achieving organizational goals considering internal and external factors.
- Porter (1985) emphasized the importance of aligning strategy with the company's environment.
- Strategic management helps manage change systematically and directs resources toward future goals.
- Chandler (1962) noted the importance of organizational structure in successful policies and economic performance.
- Harrison and St. John (1998) described it as a process of analyzing internal and external environments, establishing direction, creating strategies, and executing them to satisfy stakeholders.
Common Elements of Strategic Management:
- It involves decision-making, planning, and a series of activities related to formulating and executing strategies.
- Strategic management determines the long-term performance of firms.
- Key components include strategic intent, environmental scanning (both internal and external), strategy formulation (planning), implementation, and evaluation and control.
- Overall, it's the process by which organizations establish ways to achieve long-term goals.
overview of strategic management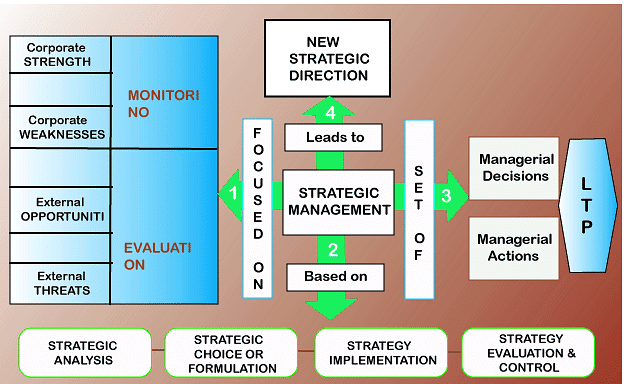
Strategic management is a methodical way of handling significant changes in strategy within an organization, involving:
- Determining the firm's position through strategy and capability planning.
- Responding promptly to strategic challenges through real-time issue management.
- Systematically managing resistance encountered during the implementation of strategic initiatives.
Establishing strategies and market positions is vital for guiding a firm, overcoming competitors, or navigating challenging environments. When a well-crafted strategy is successfully executed, it can secure a top position for even the least powerful firm compared to other industry leaders.
Nature and Scope of Strategic Management
Strategic management involves the art and science of making decisions that cut across different parts of a company, helping it achieve its goals.
Purpose:
- Its main goal is to create and use new opportunities for the future success of the organization.
Key Components:
- Provides a strategic direction agreed upon by the team and stakeholders.
- Offers a clear business strategy and a vision for the future.
- Establishes accountability methods and a governance structure at various levels.
- Sets up a logical framework for handling risks to ensure business continuity.
- Enables the ability to seize opportunities and respond to external changes through continuous strategic decisions.
Strategic Management Process:
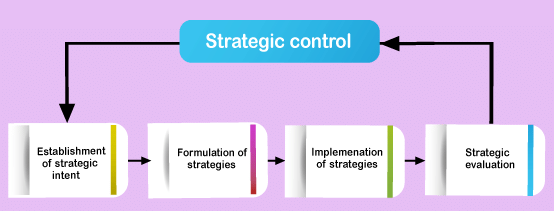
Phases:
- Establishing the hierarchy of strategic intent.
- Strategic formulation.
- Implementation.
- Evaluation and control.
Strategy Formulation:
- Develops a vision and mission.
- Identifies external opportunities and threats.
- Assesses internal strengths and weaknesses.
- Sets long-term objectives.
- Creates alternative strategies.
- Chooses specific strategies to pursue.
Strategy Implementation:
- Defines annual objectives.
- Develops policies.
- Motivates employees.
- Allocates resources to put formulated strategies into action.
- Involves creating a supportive culture, organizing the company effectively, adjusting marketing efforts, budgeting, implementing information systems, and linking employee rewards to performance.
Strategy Evaluation:
- The final stage in strategic management.
- Helps managers identify when certain strategies are not working well.
- Essential for obtaining information about the effectiveness of the strategies in place.
Phases of Strategic management process
Strategic Intent
Strategic Intent is a crucial concept in management, representing a high-level statement of how an organization achieves its vision.
Challenges in Business:
- Many management teams try hard to emulate the competitive advantage of international rivals, but often end up only copying their activities.
- Imitation doesn't create real Strategic Intent as competitors have already implemented those techniques, making imitation ineffective for competitive revival.
Origins and Importance:
- Strategic Intent originated post-World War II, notably seen in Japanese organizations.
- Despite limited resources, Japan set ambitious goals and became a leader in the global economy for 10-15 years, teaching international business leaders how to thrive under challenging conditions.
Strategic intent
Explanation by Theorists:
- Theorists Hamel and Prahalad describe Strategic Intent as an ambitious and compelling dream that energizes and guides the organization's journey to the future.
- It provides direction, focus, and motivation for the entire organization, playing a vital role in its architectural and organizational progress.
Core Competencies:
- While immediate success stems from market recognition of current offerings, future success depends on foreseeing market possibilities, understanding customer needs, and developing the necessary skills and capabilities for future products.
Functional Model:
- Strategic Intent serves as a functional model for setting and maintaining organizational goals amidst internal and external pressures.
- It goes beyond traditional strategic planning by representing objectives that cannot be planned for.
- Strategic Intent provides a common target for organizational evolution and directs the accumulation of necessary competencies, giving intra-organizational processes a unified purpose.
Features of Strategic Intent: Attributes of Strategic Intent
There are three major attributes of Strategic Intent:
Strategic Intent involves three key attributes: Sense of Direction, Sense of Discovery, and Sense of Destiny.
Attributes Explained:
- Sense of Direction: Long-term market or competitive position.
- Sense of Discovery: A unique viewpoint about the future, emphasizing the importance of employees being aligned and convinced about the concept of Strategic Intent.
- Sense of Destiny: Involves emotions, creating a harmonious progress for everyone in the organization.
Importance Emphasized by Hamel & Prahalad:
- Strategic Intent is more than just ambition; it's an active management process.
- Focuses attention on winning, motivates by communicating the value of the target, allows room for individual and team contributions, sustains enthusiasm, and guides resource allocation consistently.
Vision
A vision is an aspiration expressed through strategic intent, leading to an organization's end goal.
Different Perspectives on Vision:
- Kotter: Describes it as a description of an organization, culture, business, technology, or activity in the future.
- EL Namaki: Views it as a mental perception of the environment an organization aspires to create over a broad time horizon.
- Miller and Dess: Envision it as broad, all-inclusive, forward-thinking intentions.
Benefits of a Good Vision:
- Inspiring and exhilarating.
- Creates a common identity and a shared sense of purpose.
- Fosters risk-taking and experimentation.
- Promotes long-term thinking.
- Represents integrity in the marketplace.
Objectives
Objectives are specific results an organization aims to accomplish for its basic mission, stating direction, aiding evaluation, and revealing priorities.
Importance in Strategic Management:
- Define the organization's relationships with its environment.
- Commit the organization to achieving goals for employees, customers, and society.
- Provide a basis for strategic decision-making.
- Set standards for performance appraisal.
Features of Objectives:
- Must be understandable and comprehensive.
- Should be concrete, specific, and related to a time frame.
- Measurable, controllable, and challenging.
- Different objectives should correlate with each other.
- Set within constraints.
Challenges in Objective Setting:
- Specificity: Objectives can be stated at different levels of specificity.
- Multiplicity: Organizations need to set a variety of objectives to cover all performance areas.
- Periodicity: Objectives are devised for different time periods and must be integrated.
- Verifiability: Objectives must be testable and quantifiable.
- Reality: Official versus operative objectives, what is professed versus what is achieved.
- Quality: Objectives should provide a specific direction and a tangible basis for performance evaluation.
Assessment of Strategic Objectives:
- Used to operationalize the mission statement.
- Provide guidance for the organization to achieve high goals in the goal hierarchy of the mission and vision.
- More specific and cover a well-defined time frame.
- Directed towards generating profits, returns, and societal contributions.
- Set in areas of strategic importance to the organization, such as market standing, innovation, productivity, and more.
Major factors in Formulating Strategic Objectives
Mission of the Organization:
- The organization's mission is the starting point for setting strategic objectives.
External Factors:
- External factors like market conditions, legislation, and political/economic trends influence the strategic objectives to achieve the desired outcomes.
Management Values:
- The values held by the management play a crucial role in formulating objectives, ranging from ethical standards to their stance on social welfare.
Management Experience:
- The management's experience, especially in a specific market, is a key factor in shaping strategic objectives.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
- Strategic objectives should capitalize on the strengths of the business rather than exposing weaknesses. The cost of each option should be weighed against the benefits.
Benefits of Strategic Objectives:
- Channel employees towards common goals.
- Focus and conserve valuable resources.
- Encourage commitment and effort through challenging objectives.
- Resolve conflicts effectively.
- Provide a standard for rewards and incentives.
Policies:
- Policies are the means through which annual objectives are achieved.
- They include guidelines, rules, and procedures in areas like management, marketing, finance/accounting, production/operations, research and development, and computer information systems.
- Policies help ensure consistent operations across the organization and facilitate coordination and communication between different units.
- Competitors' policies also influence organizational policies.
- Business policies set overall guidelines, providing limits and directions for managerial actions.
Effectiveness of Strategic Management
Alli (1992) stated following attributes of an effective strategic management:
Clear Direction and Purpose:
- Ensuring everyone knows where the organization is heading and why.
Objectives, Goals, and Strategic Consistency:
- Setting clear goals and objectives that align with the overall strategy.
Continuous Monitoring of Internal and External Environment:
- Keeping track of what's happening inside and outside the organization.
Integration of Budgets with Strategic Plans:
- Making sure financial plans support the strategic goals.
Continuous Monitoring and Revision of Plans:
- Adjusting plans and programs as needed based on progress and changing circumstances.
Creating a Strategic Atmosphere:
- Fostering teamwork and collaboration among employees.
Commitment of Necessary Resources:
- Providing the resources and information needed for effective management.
Viewpoints on Strategic Management Efficacy:
Goal-Centered Approach: Evaluating organizational effectiveness based on achieving planning objectives.
Balancing Creativity and Control: Viewing creativity and control as essential aspects of successful planning.
Impact of Corporate Planning on Organizational Efficacy: Analyzing how corporate planning affects overall organizational performance.
Benefits of Strategic Management
Policy Development:
- Helps organizations develop viable policies using a systematic approach.
Communication and Empowerment:
- Facilitates understanding and commitment throughout the organization, leading to empowerment.
Financial Benefits:
- Research shows that organizations using strategic management are more profitable and successful, with better long-term financial performance.
Non-Financial Benefits:
- Enhances awareness of external threats, understanding of competitors, productivity, and reduces resistance to change.
- Brings order and discipline to struggling firms.
Benefits According to Greenley:
- Identifies, prioritizes, and exploits opportunities.
- Provides an objective view of management problems.
- Improves synchronization and control of activities.
- Reduces the effects of adverse conditions and changes.
- Supports major decisions.
- Distributes time and resources effectively.
- Clarifies individual responsibilities.
- Promotes forward thinking and positive attitudes toward change.
- Adds discipline and formality to business management.
Limitation
Principle Reliance:
- Strategic Management relies on certain principles, and if these principles are not suitable, the formulated strategies may not be effective.
SWOT Analysis Challenges:
- SWOT analysis, a crucial exercise in Strategic Management, requires extensive information and action. Lack of these can lead to questionable results and the formulation of incorrect strategies.
Implementation Challenges:
- Effective implementation demands various factors, including resource allocation, leadership, the right structure, and thorough evaluation. Failure in implementation is a common cause of strategy failure.
Internal Involvement:
- Lack of involvement from internal stakeholders in strategy formulation and a lack of confidence can lead to serious issues within the company.
Complexity and Cost:
- Strategic planning is a complex task that requires vision, expertise, commitment, and a suitable system. Additionally, Strategic Management is an expensive process.
Over-Determination Risk:
- Strategic Management may sometimes make an organization overly determined, leading to disruptions if goals are not achieved.
Impractical Strategies:
- The formulation of impractical strategies can result in serious problems for the organization.
Summary of Strategic Management
- Enables organizations to make long-term decisions based on predictions.
- Helps organizations take early action in response to new trends, considering lead-time for effective management.
- Emphasizes monitoring external opportunities and threats, aligning with the company's strengths and weaknesses to create and implement innovative strategic directions.
FAQs on Nature and Scope of Strategic Management - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the nature and scope of strategic management? |  |
| 2. What is strategic intent and what are its features? |  |
| 3. What are the major factors in formulating strategic objectives? |  |
| 4. How can the effectiveness of strategic management be measured? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of strategic management? |  |















