Nazism & the Rise of Hitler Summary Class 9 Social Science Chapter 1
| Table of contents |

|
| Overview |

|
| Hitler’s Rise to Power |

|
| The Nazi Worldwide |

|
| Youth in Nazi Germany |

|
| Ordinary People and the Crimes Against Humanity |

|
Overview
Nazism and the Rise of Hitler delves into the significant events leading to Hitler's ascendancy in Germany. It explores the formation of the Weimar Republic, Hitler's rise to power, and the socio-political consequences of the years of depression. It sheds light on Hitler's destructive policies, the Nazi ideology's global impact, and the atrocities committed during the Holocaust. The narrative unfolds against the backdrop of economic crises, political radicalism, and the geopolitical concept of Lebensraum. The chapter also emphasizes the Nazi regime's indoctrination efforts, the cult of motherhood, and the profound impact of propaganda.
Birth of the Weimar Republic
- Germany's post-World War I democratic constitution established the Weimar Republic.
- Criticism arose due to the terms forced upon Germany after its defeat, leading to discontent.
Effects of the War and Political Radicalism
- The war had a profound psychological and financial impact on Europe.
- The economic crisis of 1923, hyperinflation, and political radicalization marked the early years of the Weimar Republic.
- Spartacist League and the Communist Party of Germany emerged.

The Years of Depression (1924-1928)
- Defects in the Weimar Republic included challenging proportional representation, emergency powers granted by Article 48, and public discontent over the Treaty of Versailles.
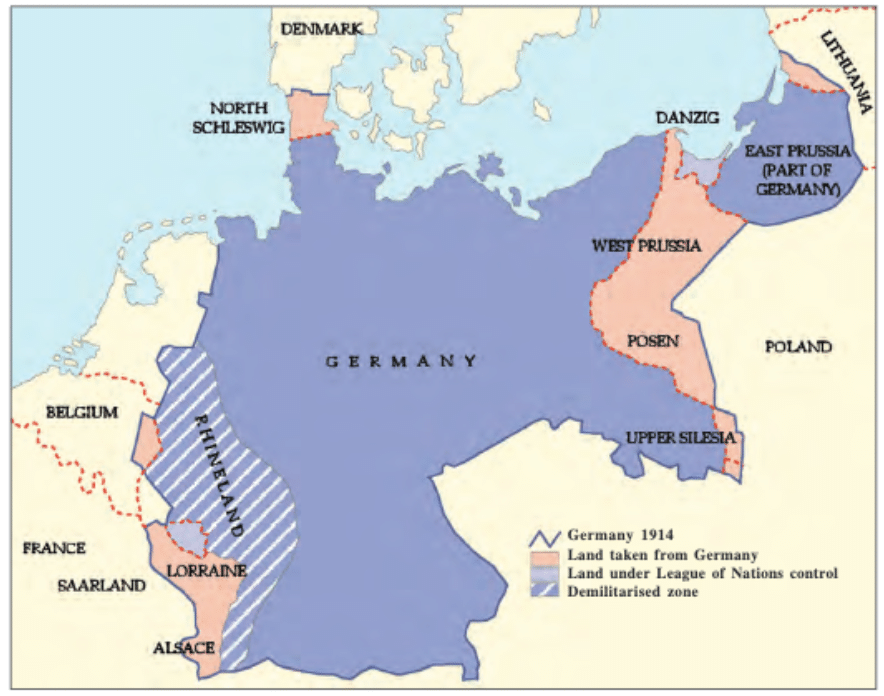
- The consequences of the Treaty of Versailles encompassed significant territorial and resource losses for Germany, contributing to post-war European financial instability and criticism of Weimar Republic supporters.
- World War I's impact shifted Europe from creditor to debtor, fostering nationalist sentiments, emphasizing military over civilian roles, and promoting aggressive war propaganda.
- Political radicalism arose with the formation of the Communist Party of Germany and the suppression of uprisings by the Weimar Republic, leading to economic crises marked by hyperinflation and global recession.
Hitler’s Rise to Power
- Hitler was born in Austria in 1889.
- He acted as a messenger and corporal in the First World War.
- He joined the German Workers Party and renamed it the National Socialist German Workers' Party.

- This later came to be known as the Nazi Party.
- By 1932, it had become the largest party with 37 per cent of votes.
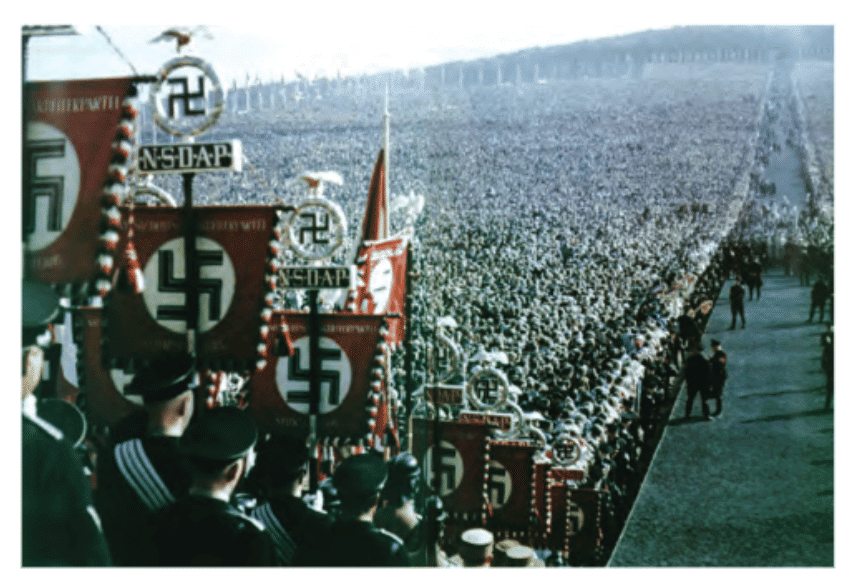
- Nazism became a mass movement only during the Great Depression.
- By 1932, it had become the largest party with 37 per cent of votes.
The Destruction of Democracy
- On 30 January 1933, Hitler achieved the highest position in the cabinet of ministries.
- Hitler now set out to dismantle the structures of democratic rule.
- The Fire Decree of 28 February 1933 suspended civic rights like freedom of speech, press and assembly.
- Communists were hurriedly packed off to newly established concentration camps.
- All political parties were banned.
- Special surveillance and security forces were created to control the people and rule with impunity.
Reconstruction
- Hjalmar Schacht took over the responsibility of economic recovery.
- The state-funded project produced the famous German superhighways and the people’s car, the Volkswagen.
- Hitler reoccupied the Rhineland in 1936.
- He integrated Austria and Germany in 1938.
- Acquired German-speaking Sudentenland.
- Hitler chose war to recover from the economic crisis.
World War II
- Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939.
- Tripartite Pact (1940) with Germany, Italy, and Japan.
- German attack on the Soviet Union in 1941.
- Defeat at Stalingrad, US entry into the war, and the end of World War II in 1945.
 World war II
World war II
The Nazi Worldwide
- Racial hierarchy and exclusivity of pure Germans.
- Implementation of racial ideologies, including the persecution of Jews, Gypsies, Blacks, Russians, Poles, and certain Germans.
- Hitler's belief in pseudoscientific theories and the total elimination of Jews.
Establishment of the Racial State
- Nazis wanted only pure Aryans.
- The disabled were killed.
- Jews, Gypsies, Blacks, Russians, and Poles were persecuted.
- Jews faced segregation and mass killings.
- Many were sent to gas chambers.
Racial Utopia
- Genocide and war intertwined.
- Forced migration in occupied Poland and segregation.
- The concentration of undesirable groups and mass killings in gas chambers.
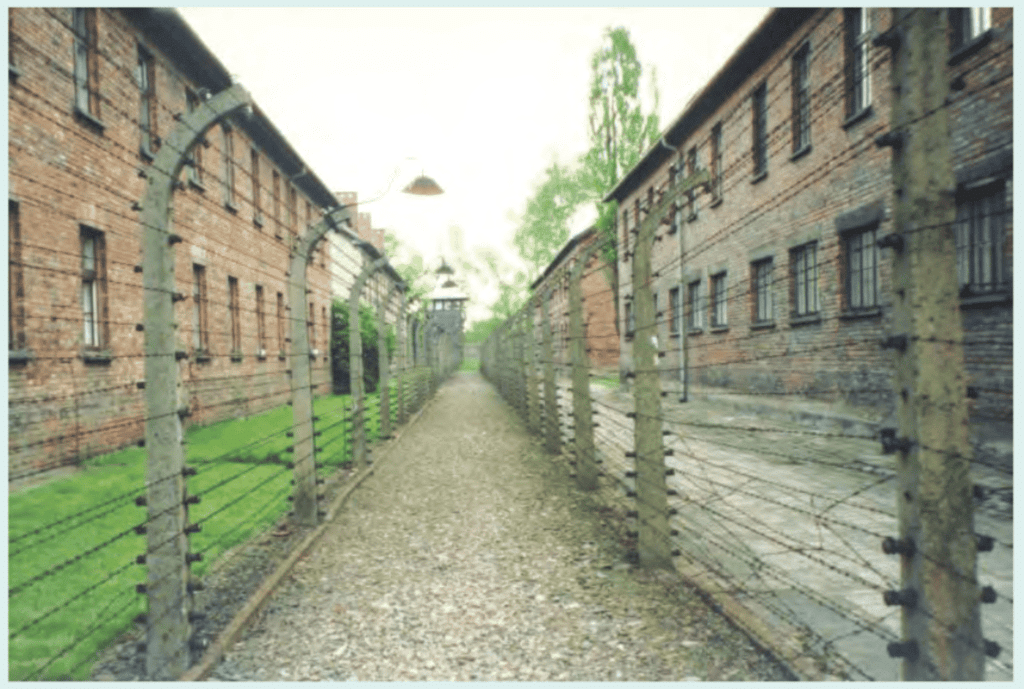 A Concentration Camp
A Concentration Camp
Youth in Nazi Germany
- Indoctrination of Nazi ideology in schools.
- Division of children into desirable and undesirable groups.
- Promotion of violence and aggression through sports and youth organizations.
The Nazi Cult of Motherhood
- Boys were taught to be aggressive, masculine, and steel-hearted.
- Girls had to become good mothers and rear pure-blooded Aryan children.
- All mothers were not treated equally.
- Women who bore racially undesirable children were punished.
- Women who produced racially desirable children were awarded.
- Honor Crosses were awarded to encourage women to produce many children.
- Women who didn’t follow the prescribed code of conduct were publicly condemned, and severely punished.
The Art of Propaganda
- Mass killings were termed special treatment, final solution, euthanasia, selection and disinfection.
- Nazi ideas were spread through visual images, films, radio, posters, catchy slogans and leaflets.
- In posters, enemies of Germans such as Jews were shown as evil.
Ordinary People and the Crimes Against Humanity
- Many supported Nazism and hated Jews.
- Some resisted bravely despite the danger.
- Most stayed silent out of fear.
- Jews suffered mentally before they were killed.
Knowledge about the Holocaust
- Jews collected and preserved documents wrote diaries, kept notebooks, and created archives which are called the Holocaust.
- Jews wanted the world to remember the atrocities and sufferings they had endured during the Nazi killing operations.
Hitler's Legacy
- Hitler is remembered in history as a ruthless leader who manipulated and indoctrinated an entire generation.
- Recognition of the destructive impact of fascist ideals and their lasting consequences on individuals and societies.
|
55 videos|637 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Nazism & the Rise of Hitler Summary Class 9 Social Science Chapter 1
| 1. What were the key factors that contributed to Hitler's rise to power in Germany? |  |
| 2. How did the Nazi regime dismantle democracy in Germany? |  |
| 3. What was the significance of the Nazi ideology on global politics? |  |
| 4. How did the Nazi regime promote the cult of motherhood? |  |
| 5. What is Hitler's legacy in contemporary society? |  |
















