UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History for UPSC CSE > Nitin Singhania Summary: Unesco’s List Of Tangible World Heritage Sites In India
Nitin Singhania Summary: Unesco’s List Of Tangible World Heritage Sites In India | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Criteria for Selection
The nominated sites must be of "outstanding universal value" and should meet at least one of the ten mentioned criteria:
Criteria for Cultural Sites
- Represents a masterpiece of human creative genius.
- Exhibits an important interchange of human values over a span of time, or within a cultural area of the world, on developments in architecture or technology, monumental arts, town-planning or landscape design.
- Bears a unique or exceptional testimony to a cultural tradition or to a civilisation which is living or which has disappeared.
- Is an outstanding example of a type of building, architectural, or technological ensemble or landscape which illustrates a significant stage in human history.

- Is an outstanding example of a traditional human settlement, land-use or sea-use which is representative of a culture or human-interaction with the environment especially when it has become vulnerable under the impact of irreversible change.
- Is directly or tangibly associated with events or living traditions, with ideas, or with beliefs, with artistic and literary works of outstanding universal significance.
Criteria for Natural Sites
- Contains superlative natural phenomena or areas of exceptional natural beauty and aesthetic importance.
- Is an outstanding example representing major stages of the Earth's history, including the record of life, significant ongoing geological processes in the development of landforms, or significant geomorphic or physiographic features.
- Is an outstanding example representing significant ongoing ecological and biological processes in the evolution and development of terrestrial, freshwater, coastal, and marine ecosystems, and communities of plants and animals.
- Contains the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity, including those containing threatened species of outstanding universal value from the point of view of science or conservation.Question for Nitin Singhania Summary: Unesco’s List Of Tangible World Heritage Sites In IndiaTry yourself:Which of the following is a criterion for selecting a cultural site?View Solution
Legal Status of Designated Sites
- Designation as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO serves as initial proof of cultural sensitivity.
- Such sites are entitled to legal safeguarding under the Geneva Convention, its Articles, protocols, and customs.
- This protection extends to treaties like the Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict and International Law.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites In India
Cultural Sites




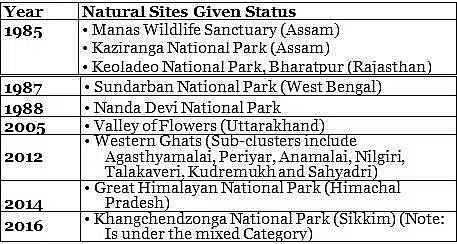
Natural Sites
 Benefits of the World Heritage Site Status
Benefits of the World Heritage Site Status
- Brings international attention to the need for site preservation and conservation.
- Attracts tourism, leading to economic benefits; UNESCO may offer funds for restoration, preservation, and training.
- Promotes close ties with the United Nations, offering prestige and support.
- Provides access to global project management resources.
- Facilitates partnerships among government, private sector, and NGOs to achieve conservation objectives.
- Site protection under the Geneva Convention during wartime.
The document Nitin Singhania Summary: Unesco’s List Of Tangible World Heritage Sites In India | History for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course History for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
121 videos|494 docs|176 tests
|
FAQs on Nitin Singhania Summary: Unesco’s List Of Tangible World Heritage Sites In India - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India? |  |
Ans. UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India are tangible cultural or natural sites that are considered to be of outstanding value to humanity and have been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
| 2. How many UNESCO World Heritage Sites are there in India? |  |
Ans. As of now, there are 38 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India, including cultural, natural, and mixed properties.
| 3. How are UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India selected? |  |
Ans. UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India are selected based on their cultural significance, historical importance, architectural uniqueness, or natural beauty. These sites must meet certain criteria set by UNESCO to be considered for inscription on the World Heritage List.
| 4. What is the importance of preserving UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India? |  |
Ans. Preserving UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India is important as it helps in conserving our cultural and natural heritage for future generations, promoting tourism and economic development, and fostering a sense of national pride and identity.
| 5. Can anyone visit UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India? |  |
Ans. Yes, most UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India are open to visitors, allowing them to explore and learn about the rich history and cultural heritage of the country.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

 Benefits of the World Heritage Site Status
Benefits of the World Heritage Site Status 

















