Notes: Geography as a social study and as a science | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
The term "Geography" in English originates from the combination of two Greek words, 'Geo' meaning Earth and 'Graphy' meaning description. Thus, Geography denotes the description of Earth. Initially, geography was regarded as a social study. However, over time, scientific perspectives were integrated into geography, with scholars such as Malthus considering it a science. Contemporary geographers perceive geography as a fusion of social studies and science, indicating that while its subject matter is intertwined with society, its methodology is scientific.

Geography as a Social Study
Geography primarily focuses on the evolving nature and spatial organization of the Earth's surface. It has been defined by various geographers:
- Monkhouse: "Geography involves the study of regional differences in human habitation."
- Hartshorne: "Geography is the discipline that describes the changing forms on the Earth's surface from one place to another and interprets them as 'the Human world.'"
The study of geography initially took the form of a social study, providing details of geographical phenomena without delving into scientific explanations. Scholars like Eratosthenes and Ptolemy, who viewed geography as a social study, did incorporate logical thinking into the discipline.
Geography as a Science
With the evolution of scientific methods, the scientific study of geography emerged. Modern geography places emphasis on employing scientific methods and principles, exploring cause-effect relationships. Present-day geography can be regarded both as a social science and as a science.
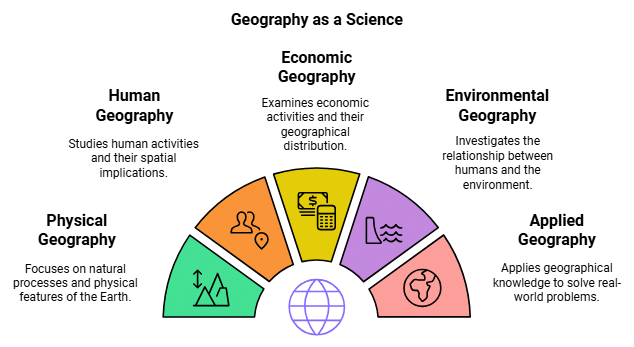
Branches of Geography
Physical Geography
Physical Geography studies natural forms and processes in the environment, aiming to explain the spatial characteristics of Earth's hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere, and lithosphere. It includes:
- In hydrology, the properties and movement of Earth's water in relation to land are studied.
- Geomorphology examines the physical features of Earth's surface in relation to its geological structure.
- Geodesy focuses on studying the size and shape of the Earth.
Human Geography
Human Geography deals with the built environment and explores how space is created, viewed, and managed by humans. It encompasses the study of patterns and processes shaping human society, including human, political, cultural, social, and economic aspects.
Economic Geography
Economic Geography studies the location, distribution, and spatial organization of economic activities worldwide, representing a traditional sub-field of geography.
Environmental Geography
Environmental Geography combines human and physical geography, examining their interaction with humans. It explores the relationships among socio-economic and spatial activities of humans, including the study of soil (Pedology) in their natural environment.
Applied Geography
Applied Geography applies geographical knowledge and skills to address real-world social, economic, and environmental problems. Examples include the use of the Global Positioning System (GPS) for navigation and its role in modernizing the global air traffic system.
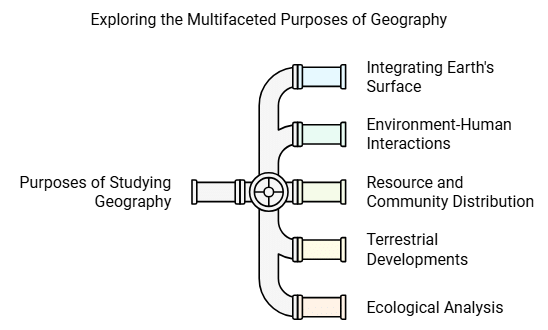
Purpose of Studying Geography
The purposes of studying geography include:
- Integrating and studying the Earth's surface based on different forms and dividing it into different areas.
- Studying the interactions between the environment and human beings.
- Examining differences in the distribution of resources, human communities, and habitats on Earth.
- Explaining terrestrial developments in different regions.
- Understanding the biological connection between environmental elements and human society through ecological analysis.
Geography and Other Subjects of Social Science
Geography is closely related to various other social sciences:
Geography and Economics
Geography determines the distribution of resources, which in turn influences economic activities. The successful development of the economy leads to diversification, innovation, growth, and prosperity.
Geography and Sociology
Geography provides a physical understanding of the Earth, which is essential for sociology to comprehend human society and its relationship with the environment. Geography helps in understanding the social aspects of human life.
Geography and Political Science
Geographical and physical conditions are believed to significantly influence the character, national life, and political institutions of people. Aristotle emphasized the importance of geography in political and strategic wisdom. 'Bodin' was among the first modern writers to explore the relationship between political science and geography. Rousseau proposed a connection between climatic conditions and forms of government, suggesting warm climates favor despotism, cold climates favor barbarism, and moderate climates favor good governance.Geography and History
Geography and history are often intertwined, as certain locations hold significant historical importance. Understanding a region's geography can enhance the study of historical topics. Similarly, historical events can shed light on geographical features and their significance. For instance, Africa's diamond market and Australia's wildlife are historically renowned.Geography and Military Science
Military geography, a sub-field of geography, is utilized by the military, academics, and politicians to comprehend the geo-political landscape through a military lens. It involves considering topics ranging from geo-politics to physical locations' impacts on military operations, as well as the cultural and economic ramifications of military presence.
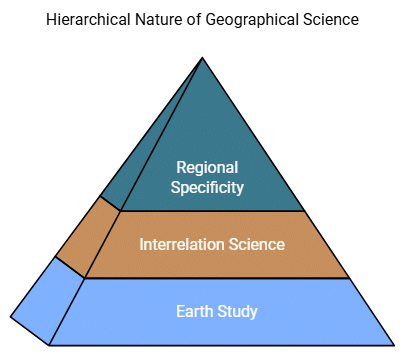
Geographical Science
Geographical science explores the practical applications and theoretical foundations of geography:
- Geography as a Science of Earth: Geography is the study of Earth and its inhabitants, defining the subject matter of geography.
- Geography as a Science of Interrelation of Elements: Geography studies the interconnectedness and interactions of elements on Earth, aiming to understand the complexities of different regions.
- Geography as a Representation of Regional Specificity: Geography delves into the demarcation and territorial details of regions, expressing the interrelations of principle groups and showcasing the specificity of each region.
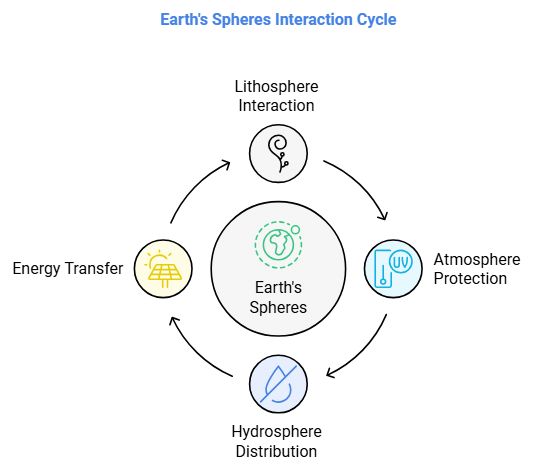
Study Area of Geography
The study area of geography encompasses various aspects of Earth's surface:
- Lithosphere: The Earth's lithosphere consists of the crust and uppermost mantle, forming the hard and rigid outer layer. It is divided into tectonic plates and interacts with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere through processes like soil formation. The uppermost part of the lithosphere, which reacts chemically with other spheres, is known as the pedosphere. Beneath the lithosphere lies the asthenosphere, a weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle
Atmosphere
The Earth's atmosphere is the layer of gases, commonly referred to as air, that envelops the planet and is held in place by Earth's gravity. It serves several vital functions:- Protecting life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation.
- Warming the surface through heat retention, known as the greenhouse effect.
- Regulating temperature extremes between day and night
- Hydrosphere: The hydrosphere encompasses all the water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. On Earth:
- There are approximately 1386 million cubic kilometers of water.
- This includes water in liquid and frozen form in groundwater, oceans, lakes, and streams.
- Saltwater accounts for 97.5% of this total.
4. Biosphere
The biosphere is the layer of Earth where life exists, spanning various environments:
- From heights up to 10 kilometers above sea level, utilized by some birds in flight.
- To ocean depths like the Puerto Rico trench, exceeding 8 kilometers deep.
- While extremes exist, the biosphere is generally thin, with the upper atmosphere having little oxygen and low temperatures, and ocean depths below 1000 meters being dark and cold.
Geography and Its Connection with Social Science
Geography is the study of the Earth’s space and the differences between areas. It looks at the whole planet and each special region, including their features like landforms, climate, weather, and everything else, whether alive or not. When we think about Earth as a whole, we don’t just consider its physical parts but also its social and cultural aspects, especially how people and their activities fit into the picture. What people do is always affected by different geographic factors.Geography is the study of space and differences between areas on Earth. It includes everything about our planet, like its land, climate, weather, and living things. But it also looks at how people and their activities fit into all this because what people do is influenced by where they are.
Social Science Subjects
- Sociology studies people from different races, tribes, castes, and classes and how they live and interact.
- Economics looks at what people do for work and how they make a living.
- Political Science is about how governments are formed and how they provide for people’s needs through good governance.
Branches of Geography
- Physical Geography is about the natural parts of the Earth, like mountains, rivers, and forests.
- Human Geography focuses on how people live, work, and interact in different places.
- Regional Geography studies specific areas of the Earth that have similar characteristics, like climate, culture, or economy.
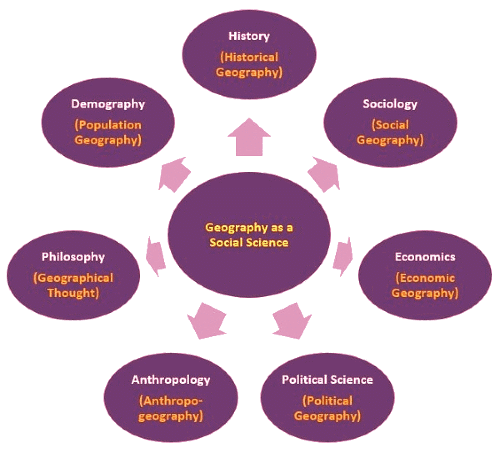
Subjects Related to Human Geography
Now, let’s look at the subjects within social science that are closely connected to human geography:
- History studies how people lived in the past and how their activities shaped different regions.
- Sociology looks at different groups of people and their social behaviors, which is important for understanding how they interact with their environment.
- Economics examines how people use the resources in their area to make a living, which is a key part of human geography.
- Political Science is about how local governments manage resources and provide services, which varies from one region to another.
- Anthropology studies the cultures and traditions of different groups, helping us understand their relationship with the land.
- Philosophy can offer insights into how people think about their place in the world, influencing their interaction with the environment.
- Demography looks at population trends and how they affect the use of resources in different areas.
Historical Geography: The Connection Between Human Geography and History
Human geography is deeply intertwined with history because understanding the present and the way people interact with their environment requires knowledge of past events and changes. History provides the timeline and context for human activities, while geography offers the spatial framework within which these activities occur.History and Geography: Inseparable Fields
- History looks at human activities over time, while geography examines them in space.
- Both fields rely on each other to provide a complete understanding of human life.
- For example, historians study how early civilizations settled near water bodies, while geographers explain the reasons for these settlements, such as the availability of resources and fertile land.
Tools Used by Historians
- Historians use various tools to investigate and interpret the past, including:
- Written documents
- Ancient buildings
- Paintings and pictures
- Sketches and carvings on stones
Historical Geography
- Historical geography is the branch of geography that studies the relationship between geography and history.
- It explores how geographical factors have influenced historical events and how, in turn, history has shaped the geographical landscape.
Relation between Human Geography and Sociology
- Sociology is a branch of social science that examines and explains the socio-cultural aspects of the world, both globally and at the level of individual societies or people. At the global level, sociology studies different human races, tribal groups, and religions along with their unique socio-cultural activities. At the personal level, it looks into individual behaviors and the social causes that influence them, such as family dynamics, racial diversity, religious practices, gender identity, and deviant behaviors. Sociology also investigates societal issues like crime, poverty, prejudice, discrimination, and social movements.
- Human geography, on the other hand, studies the physical aspects of human society, including the Earth’s surface, natural resources, and environmental conditions. These geographical factors directly or indirectly impact human lives and behaviors. There is a fundamental relationship between physical conditions and socio-cultural activities.
- For instance, people living in different climatic regions, such as equatorial, temperate, tropical, or arctic regions, exhibit distinct lifestyles, food habits, occupations, and ways of thinking. Sociology might study the specific cultural practices of a group, such as the Bushmen tribe in South Africa, while geography explains how the physical environment influences these practices. Similarly, the unique lifestyle of the Eskimo tribe in the Arctic can be understood through the lens of geography and sociology.
The branch of geography that explores the relationship between geography and sociology is called "Social Geography."
Human Geography's Connection with Economics
- Economics is a branch of social science that studies how goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed, both globally and at individual levels. It looks into how different agents like households, buyers, sellers, and firms interact in markets and what the outcomes of these interactions are. Economics also explores the relationships between production, consumption, saving, and investment, considering factors like labor availability, suitable land, natural resources, government policies, and currency inflation.
- Now, let's understand how geography is related to economics. Geography examines the physical aspects of a region, such as soil types, climate, relief features, rivers, mountains, plateaus, natural resource availability, and human settlements. On the other hand, economics focuses on the production, distribution, and consumption of agricultural and industrial products. The types of agricultural produce are influenced by geographical factors like soil type, climate, relief features, and the presence of rivers. Similarly, geographical factors such as natural resource availability, labor, transportation systems, and markets determine the locations and types of industries.
In this way, geography plays a crucial role in determining the types of agricultural products and industries in a region and predicting future economic growth prospects. The field of geography that studies the relationship between geography and economics is called "Economic Geography."
Human Geography and Its Connection with Other Social Sciences
Human geography is closely linked with various disciplines within social science, each contributing to a deeper understanding of how human activities interact with geographical factors.
Human Geography and Political Science
- Political science is the study of how governments are formed, the different types of governments, and how they govern people at various levels – local, state, national, and international.
- It also looks into political activities like how people vote, how political parties and pressure groups are formed, and the rules and administration related to politics.
Now, let’s explore how geography is connected to political science.
- Geographic factors such as land types, climate, natural resources, rivers, and mountains play a crucial role in shaping politics.
- These factors influence not only domestic politics but also international relations.
- For instance, the study of geopolitics focuses on how geographical features impact political relationships and international affairs.
- An example of this is the relationship between India, China, and Nepal, where Nepal’s geographical position as a buffer zone is significant.
- Similarly, recent events like Russia’s invasion of Ukraine highlight the importance of geographical factors in political actions.
The branch of geography that explores its relationship with political science is called Political Geography.
Human Geography and Anthropology
- Anthropology is the study of how humans have evolved and how people in different geographic regions are different from each other, both in the past and present.
- It also involves examining human remains to understand physical characteristics and cultural behaviors.
Geography is related to anthropology because factors like climate, natural resources, and arable land have played important roles in human evolution.

Understanding geography helps anthropologists trace the evolutionary patterns of humans in different regions.
The branch of geography that focuses on its relationship with anthropology is known as Anthropogeography.
Human Geography and Philosophy
- Philosophy deals with fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, values, and language.
- Geographers, on the other hand, study the evolution of geographic phenomena and the physical aspects of the Earth using various approaches developed over time.
- Like philosophy, geography also poses questions about human existence and behavior in different regions, trying to explain them using geographic knowledge.
The branch of geography that explores its connection with philosophy is called Geographical Thought.
Human Geography and Demography
- Demography studies the distribution, age structure, and gender composition of human populations, as well as their growth and changing patterns in different geographic areas.
- Population geography, a branch of geography, focuses on similar aspects of human populations, and the terms demography and population geography are sometimes used interchangeably because of their similar content.
Conclusion
- Geography has a deep and essential relationship with human activities.
- Natural events and geographical factors significantly influence social activities and vice versa.
- The physical elements of the Earth and their phenomena are tightly connected to social behaviors.
- This is why geography is related to all subjects within social science.
|
75 videos|320 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Geography as a social study and as a science - Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the main branches of geography? |  |
| 2. How does geography relate to other social sciences? |  |
| 3. What is historical geography and its significance? |  |
| 4. In what ways does human geography connect with sociology? |  |
| 5. How does human geography relate to economics? |  |






















