Notes: Planet: Earth | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
The Sun, the Moon and all those objects shining in night sky are called celestial bodies. Some celestial bodies have their own heat and light, which they emit in large amounts, are called stars. There are countless stars in the sky. Some of the stars form a group and follow certain pattern which are called constellations. A huge system of billions of stars, clouds of dust and gases in spiral shape is called a galaxy. Universe is composed of millions of galaxies and Big Bear is an example of constellation. Akash Ganga is the galaxy of the Earth.
Formation of the Solar System
- Scientists think that our solar system was created from a mixture of gas, dust, and other particles known as the solar nebula. As this nebula collapsed due to gravity, it started to spin faster and flattened into a disc. The materials that were spread out got pulled in, leading to the formation of the Sun. The leftover particles collided with each other and formed planets, moons, and other objects.
- The solar wind from the Sun pushed lighter objects away, while heavier ones stayed closer, which helped in the formation of small, dense bodies.
Understanding Space
- Realising that space is limitless enhances our understanding of the universe. Within our solar system, planets orbit around the Sun, with Neptune being the farthest planet, located about 30 astronomical units away from the Sun.
An astronomical unit is defined as the distance between the Sun and Earth, which is approximately 149 million kilometers.
Planets
Our galaxy, known as the 'Milky Way,' is home to a wide variety of planets, each differing in type, shape, and size. Within our solar system, there are currently eight planets, including our own Earth, which is the only planet capable of supporting life, from tiny microbes to humans. In this chapter, we will explore these planets in detail.
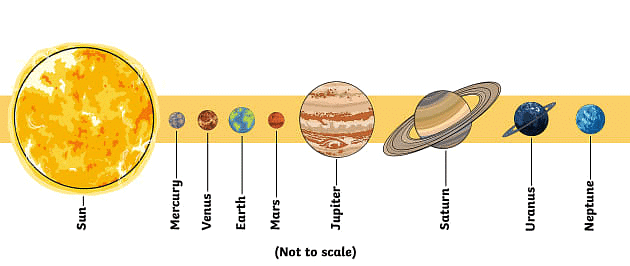
Mercury
- Mercury, being the planet closest to the Sun, is best viewed in the sky a couple of hours before sunrise.
- It is the smallest planet in our solar system and does not have any moons.
- Mercury has its own magnetic field, although its density is lower than that of water.
- The planet experiences extreme temperature variations, with scorching hot days and significantly cooler nights, with a temperature difference that can reach up to 560°C.
Venus
- Venus is the planet closest to Earth and is renowned for its brightness in the night sky.
- It is often called the evening star or morning star due to its visibility during these times.
- Interestingly, Venus has a unique rotation pattern, spinning clockwise on its axis, and it also lacks any moons.
Mars
- Mars is commonly referred to as the red planet because of its reddish hue, which is a result of iron oxide (rust) covering its surface.
- Like Earth, Mars has two polar regions: the North Pole and the South Pole.
- Mars is tilted at an angle of 25 degrees on its axis, which causes seasonal changes similar to those on Earth.
- A day on Mars, or one complete rotation on its axis, takes about 24 hours, while it takes 687 days for Mars to orbit the Sun. In comparison, Earth takes 365 days to complete one orbit around the Sun, which is what we call a year.
Jupiter
- Jupiter holds the title of the largest planet in our solar system.
- It has a very short day, rotating on its axis once every 10 hours. However, it takes about 12 years to complete one orbit around the Sun.
Saturn
- Saturn is the second-largest planet in our solar system.
- It is known for its distinctive yellowish color and is surrounded by a stunning system of seven rings.
- One of Saturn's most famous features is its largest moon, Titan, which is also the second-largest moon in the entire solar system.
Uranus
- Uranus ranks as the third-largest planet in our solar system.
- It has a frigid temperature, averaging around -215°C.
- Discovered by William Herschel in 1781, Uranus is unique in that it has nine rings, which are named alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon.
- Unlike most planets, Uranus rotates on its side, from east to west, which means that on Uranus, the Sun rises in the west and sets in the east.
- The largest moon of Uranus is Titania, and some of its other moons have a rotation pattern that is the opposite of Earth's moon.
Neptune
- Neptune was first identified in 1846 by German astronomer Johann Galle.
- It is the most distant planet from the Sun in our solar system and is known for its greenish appearance.
- Neptune is characterized by cold methane clouds that swirl around the planet.
- The planet has several moons, with Triton being the most notable. Neptune is 17 times larger than Earth, making it a giant in our solar system.
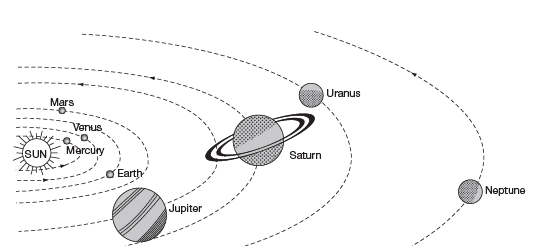
Earth in the Solar System
- Earth is a member of the solar system, which includes various objects such as natural satellites, asteroids, and comets. Like other planets, Earth does not emit its own light and is constantly rotating on its axis. All planets, including Earth, rotate from west to east, with the exceptions of Uranus and Venus.
- The nearest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri, part of the Alpha Centauri star group, located 4.22 light-years away. Proxima Centauri is similar in shape and appearance to Venus.
Shape and Size of Earth
- Contrary to popular belief, Earth is not a perfect sphere; it is shaped like an oblate spheroid. The equatorial diameter of Earth measures approximately 12,762 km, while the polar diameter is about 12,713.6 km.
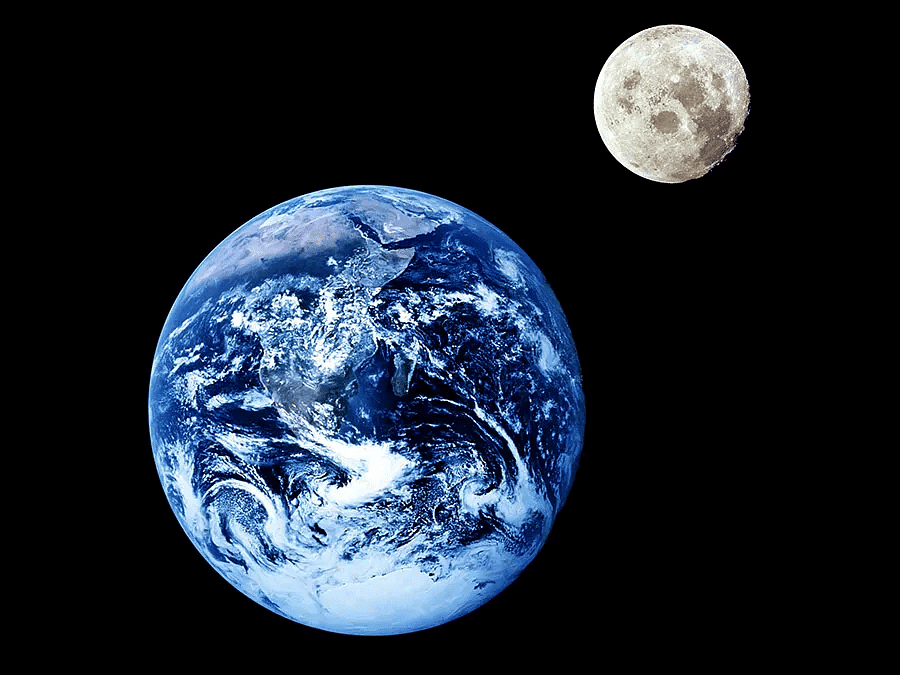

Moon (Natural Satellite)
- The Moon is the natural satellite of Earth, rotating on its axis while orbiting our planet. The Moon's axis is tilted at an angle of 58.48° relative to Earth's axis and is nearly parallel to it. With a radius of 3,480 km and a mass roughly 1/81 that of Earth, the Moon has a significant presence in our sky. When the Moon is closest to Earth, it is called perigee, at a distance of about 356,000 km. When it is farthest, known as apogee, the distance is approximately 407,000 km. The Moon takes about 29.53 days to complete one orbit around Earth, a period known as a synodic month. This duration is also referred to as a star month in stellar time. The tallest mountain on the Moon is Mons Huygens.
- A blue moon occurs when there are two full moons within a single calendar month. This phenomenon is relatively rare, happening approximately every 31 days, usually once every two to three years. The most recent blue moons occurred in 2012 and 2018. If a blue moon happens more than once in a year, that year is designated as a blue moon year, as was the case in 2018.
Dwarf Planets
- Pluto is one of the examples of dwarf planet. It was discovered in the year 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh.
- In 2006 International Astronomical Union (IAU) Prague conference, it was categorised as dwarf planet (Bone Graha), because it was not following the criteria of a planet.
- Its size is smaller than the moon, it is crossing the orbit of Neptune, and its orbit was not circular. Its new name is 134340 Pluto. Another such planet is Ceres. It was discovered by Giuseppe Piazzi, and its new name is 1 Ceres.
Asteroids
Asteroids
- Asteroids are small celestial bodies that orbit the Sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. They are believed to be remnants from the early solar system, leftover material from when a star or planet completed its lifecycle and exploded. Asteroids can vary significantly in size, with some being as large as 940 kilometers across, while others can be as small as 20 feet in diameter. They usually have irregular shapes and are often surrounded by dust.
- When asteroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere and collide with its surface, they can create large craters or pits. An example of such a crater is Lonar Lake in Maharashtra, India, which was formed by a meteor impact.
- There are three main types of asteroids, classified based on their composition:
- Type-C (carbonaceous) asteroids are greyish in color and are made up of clay and stones. These asteroids are typically found in the outer part of the asteroid belt.
- Type-S (silicaceous) asteroids have greenish or reddish hues and are composed of nickel iron and silicate materials. They are commonly located in the inner part of the asteroid belt.
- Type-M (metallic) asteroids are reddish in color and are primarily made of nickel iron. These asteroids are usually found in the middle region of the asteroid belt.
Comets
There are millions of heavy bodies on the exteriors of solar system, which are called comets. Basically, these are combinations of gases and dusts. These can be seen in the sky with a bright long tail. These can be seen when they move towards the Sun, which make them observe like shooting stars. The rotational time of the comet is called Halley, which is 76 years. Last time, it was seen in the year 1886 and in the year 1962.
Meteoroids
Meteoroids are seen in the sky as a shining line that shine for a moment and extinct. These are the tiny parts of comets and asteroids.
Constellation
Constellations are units that divide the sky to identify the position of stars. These were named on many mythological characters. There are 88 identified constellations in total. Constellations may be rectangular slices consisting stars within it. In simple words, constellation is defined as organised group of stars that provide a shape or pattern in the sky.
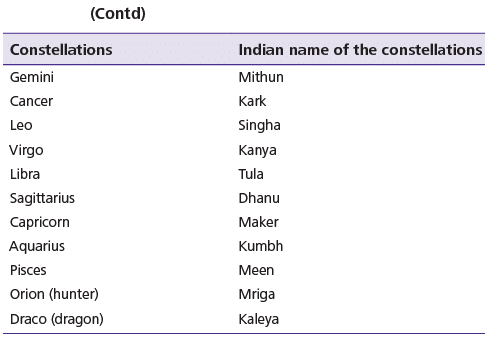
Different types of constellations and their Indian names

|
75 videos|320 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Planet: Earth - Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are some important topics related to the planet Earth that are covered in the CTET & State TET exams? |  |
| 2. How can knowledge about the planet Earth be beneficial for teachers appearing for the CTET & State TET exams? |  |
| 3. What are some common misconceptions about the planet Earth that teachers should be aware of for the CTET & State TET exams? |  |
| 4. How can teachers incorporate lessons about the planet Earth into their curriculum for the CTET & State TET exams? |  |
| 5. What are some resources or study materials that teachers can use to prepare for questions related to the planet Earth in the CTET & State TET exams? |  |
















