UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC > Nucleic acid Topology
Nucleic acid Topology | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Nucleus and Chromosomes
Nucleus
The nucleus is a crucial cellular organelle with several functions, including the transmission of hereditary information.
Chromosomes in the Nucleus
- Structure: Thread-like structures in the nucleus are chromosomes, which are long continuous molecules of DNA.
- Function: Chromosomes carry genes responsible for inheriting traits from parents to offspring.
- Visibility: Chromosomes are observable only during cell division.
Genes
A gene is the fundamental unit of inheritance controlling the transfer of hereditary characteristics.
Chromosomes: Structure and Organization
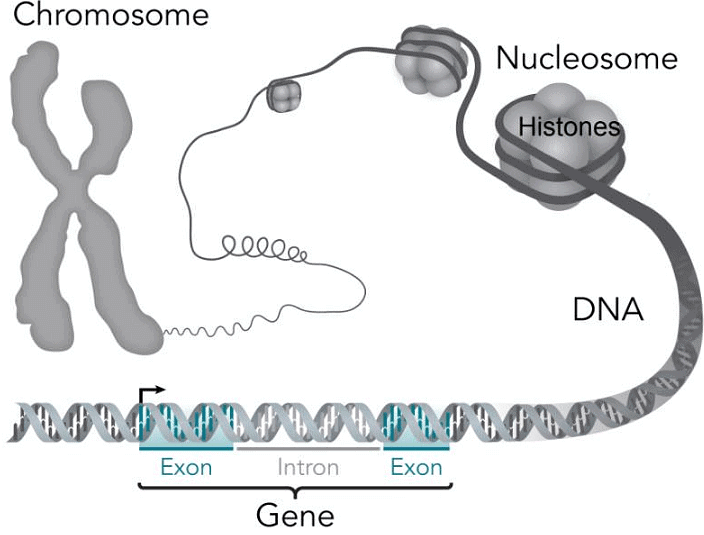
Chromatin Material
- Composition: DNA in non-dividing cells exists as chromatin material.
- Appearance: Chromatin appears as an entangled mass of thread-like structures.
Nucleosome
- Basic Unit: Nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin.
- Composition: Each nucleosome comprises almost two turns of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins.
- Organization: Chromatin material organizes into chromosomes during cell division.
Chromosomes Composition
- DNA and Protein: Chromosomes are composed of DNA and proteins.
- Information: DNA molecules within chromosomes contain information for inheritance.
Nucleotide, Nucleoside, and Heterocyclic Rings
Nucleotide and Nucleoside
- Carbon Compounds: Living organisms contain carbon compounds with heterocyclic rings.
- Nucleosides: Heterocyclic rings attached to sugar are nucleosides.
- Nucleotides: Nucleotides have a phosphate group esterified to the sugar.
Nucleic Acids

General Overview
- Macromolecule: Nucleic acids are macromolecules present in the acid-insoluble fraction of living tissues.
- Composition: Nucleic acids, along with polysaccharides and polypeptides, constitute the macromolecular fraction.
Structure of Nucleic Acids
- Building Blocks: Nucleotides are the building blocks, forming polymers known as polynucleotides.
- Covalent Bonds: Nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds, forming an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone.
- Components: A nucleotide consists of a heterocyclic compound, a monosaccharide, and phosphoric acid.
DNA and RNA
- Role of Nucleus: Nucleus, containing chromosomes and nucleic acids, is responsible for heredity.
- Types: Nucleic acids include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
- Bases: DNA and RNA share Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine, with Thymine in DNA and Uracil in RNA.
- Structure: DNA is double-stranded, forming a helix; RNA is a single-strand molecule.
- Function: DNA stores genetic information, while RNA carries out protein synthesis.

Biological Functions of Nucleic Acids
- Heredity: DNA is the basis of heredity, maintaining species identity over generations.
- Self-duplication: DNA can self-duplicate during cell division, transferring identical strands to daughter cells.
- Protein Synthesis: Nucleic acids play a crucial role in protein synthesis, with DNA providing the coded message.
DNA Fingerprinting
- Unique Characteristics: DNA sequences are unique for each individual, forming DNA fingerprints.
- Applications: Used in forensic identification, paternity determination, identifying bodies, and studying racial groups.
Recombinant DNA
Definition
Recombinant DNA molecules are formed by bringing genetic material from multiple sources through laboratory methods of genetic recombination.
Applications
- Widespread Use: Recombinant DNA technology is applied in biotechnology, medicine, and research.
- Gene Identification: Used to identify, map, and sequence genes and determine their functions.
- Product Applications: Applied in producing insulin, growth hormone, blood clotting factor VIII, hepatitis B vaccine, insect-resistant crops, etc.
The document Nucleic acid Topology | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
181 videos|346 docs
|
FAQs on Nucleic acid Topology - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the structure of chromosomes? |  |
Ans. Chromosomes are thread-like structures made up of DNA molecules tightly coiled around proteins called histones. They have a condensed and organized structure, consisting of two sister chromatids held together by a centromere.
| 2. What are nucleotides and nucleosides? |  |
Ans. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. They consist of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine in DNA; adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine in RNA). Nucleosides, on the other hand, are nucleotides without the phosphate group.
| 3. What are the biological functions of nucleic acids? |  |
Ans. Nucleic acids play crucial roles in living organisms. DNA carries the genetic information that determines an organism's traits and is involved in the process of inheritance. RNA is involved in protein synthesis, regulation of gene expression, and various other cellular processes.
| 4. What is DNA fingerprinting? |  |
Ans. DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify and analyze an individual's unique DNA sequence. It involves extracting DNA from a sample, amplifying specific regions of the DNA using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and analyzing the resulting DNA fragments. DNA fingerprinting is commonly used in forensic science, paternity testing, and identification of human remains.
| 5. What is recombinant DNA? |  |
Ans. Recombinant DNA refers to the artificial combination of DNA molecules from different sources. It involves cutting the DNA molecules using restriction enzymes, joining the fragments together using DNA ligase, and introducing the recombinant DNA into a host organism (such as bacteria) for replication and expression. Recombinant DNA technology has revolutionized various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















